refractory period
... action potential - a threshold has been crossed. • A threshold stimulus - defined in terms of current intensity and duration - is one that is able to initiate an action potential 50% of the time. ...
... action potential - a threshold has been crossed. • A threshold stimulus - defined in terms of current intensity and duration - is one that is able to initiate an action potential 50% of the time. ...
Nervous System Review ANSWERS File
... 25. What hormones are released from the anterior pituitary? ACTH, TSH, FSH, LH, GH, prolactin & melatonin. How are they regulated? Through negative feedback 26. Why do nerve impulses not move backwards? Depolarization of the membrane moves in one direction and directly behind it, the membrane will b ...
... 25. What hormones are released from the anterior pituitary? ACTH, TSH, FSH, LH, GH, prolactin & melatonin. How are they regulated? Through negative feedback 26. Why do nerve impulses not move backwards? Depolarization of the membrane moves in one direction and directly behind it, the membrane will b ...
Notes of Neuronal Firing
... permeant ions. The weighting (amount of influence) given to each ion is proportional to that ion's permeability. The more permeable the ion, the closer the resting potential will match that of the ion. Another important concept to understand is that at the steady state of the resting membrane potent ...
... permeant ions. The weighting (amount of influence) given to each ion is proportional to that ion's permeability. The more permeable the ion, the closer the resting potential will match that of the ion. Another important concept to understand is that at the steady state of the resting membrane potent ...
Module I. Introduction to biophysical models of individual cells and... plane analysis important to capture phenomenology and sometimes – biophysical mechanisms
... differently than what happens in class) Sections 1, 2 of the Lecture notes; chapters 1,2,4 of I, chapters 1,3 of ET Exercises: 1. Read about neurons, or about phase-plane methods. We are learning terminology, getting everybody on the same page 2. Simulate a Hodgkin-huxley model in matlab, make it sp ...
... differently than what happens in class) Sections 1, 2 of the Lecture notes; chapters 1,2,4 of I, chapters 1,3 of ET Exercises: 1. Read about neurons, or about phase-plane methods. We are learning terminology, getting everybody on the same page 2. Simulate a Hodgkin-huxley model in matlab, make it sp ...
Gated Channels
... channels regenerate the action potential at each point along the axon, so voltage does not decay. Conduction is slow because movements of ions and of the gates of channel proteins take time and must occur before voltage regeneration occurs. ...
... channels regenerate the action potential at each point along the axon, so voltage does not decay. Conduction is slow because movements of ions and of the gates of channel proteins take time and must occur before voltage regeneration occurs. ...
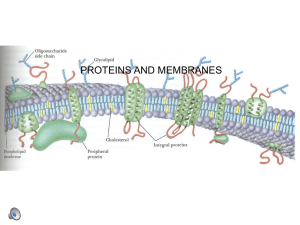
Membrane Domains and Membrane Potential
... opposes the tendency for diffusion down the concentration difference. At electrochemical equilibrium, the chemical and electrical driving forces acting on an ion are ugual and opposite. "Balance" means that the electrical force that acts to move the ions tends to increase until it is equal in magnit ...
... opposes the tendency for diffusion down the concentration difference. At electrochemical equilibrium, the chemical and electrical driving forces acting on an ion are ugual and opposite. "Balance" means that the electrical force that acts to move the ions tends to increase until it is equal in magnit ...
here
... 19. During depolarization, which ions rush in? How does this change the inside of the membrane? ...
... 19. During depolarization, which ions rush in? How does this change the inside of the membrane? ...
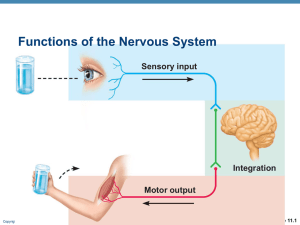
The master controlling and communicating system of the body Functions
... Nerve impulses reach the axonal terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis in response to synaptotagmin Neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron Postsynaptic membra ...
... Nerve impulses reach the axonal terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis in response to synaptotagmin Neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron Postsynaptic membra ...
BIOLOGICAL BASES OF BEHAVIOR
... neuron does not fire. • The strength of the action potential is constant. It either fires or doesn't –known as the “all or none principle.” ...
... neuron does not fire. • The strength of the action potential is constant. It either fires or doesn't –known as the “all or none principle.” ...
Lecture #19 - Suraj @ LUMS
... • The plasma membrane of neurons, has an unequal distribution of ions and electrical charges between the two sides of the membrane. • The outside of the membrane has a (+), inside has is (-). • This charge difference is a resting potential and is measured in millivolts. • Passage of ions across the ...
... • The plasma membrane of neurons, has an unequal distribution of ions and electrical charges between the two sides of the membrane. • The outside of the membrane has a (+), inside has is (-). • This charge difference is a resting potential and is measured in millivolts. • Passage of ions across the ...
Central Nervous System
... There is a slightly negative charge on the inside, and a positive charge on the outside….. Why? ...
... There is a slightly negative charge on the inside, and a positive charge on the outside….. Why? ...
Document
... • Muscle and nerve cells are exciteable • When a muscle or nerve cell is stimulated Na+ channels open and Na+ rushes into the cell • This causes a local potential • This local potential may not result in action potential – Doesn’t cross the threshold ...
... • Muscle and nerve cells are exciteable • When a muscle or nerve cell is stimulated Na+ channels open and Na+ rushes into the cell • This causes a local potential • This local potential may not result in action potential – Doesn’t cross the threshold ...
The Cellular Level of Organization
... • Speed of impulse conduction (propagation) determined by: Diameter of fiber - the greater the diameter the greater density of voltage gated Na+ channels; the greater the diameter, the faster the transmission ...
... • Speed of impulse conduction (propagation) determined by: Diameter of fiber - the greater the diameter the greater density of voltage gated Na+ channels; the greater the diameter, the faster the transmission ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Neurons are electrically excitable due to the voltage difference across their membrane • Communicate with 2 types of electric signals – action potentials that can travel long distances – graded potentials that are local membrane changes only ...
... • Neurons are electrically excitable due to the voltage difference across their membrane • Communicate with 2 types of electric signals – action potentials that can travel long distances – graded potentials that are local membrane changes only ...
Summary
... applied heat stimuli to 186 healthy women, they found that those with the rare version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
... applied heat stimuli to 186 healthy women, they found that those with the rare version were more likely to have lower pain thresholds. It was as if the normal subjects had taken an ibuprofen, but the subjects with the rare SNP hadn't. ...
2013 Action Potential Modeling in PYTHON
... +50mV, the sodium gate becomes inactivated and Na+ channels close. This marks the end of the depolarization phase. Each gating variable modifies ion conductance to produce the action potential shown in Figure 4. This action potential will be compared to the measured membrane action potential trace ...
... +50mV, the sodium gate becomes inactivated and Na+ channels close. This marks the end of the depolarization phase. Each gating variable modifies ion conductance to produce the action potential shown in Figure 4. This action potential will be compared to the measured membrane action potential trace ...
Supporting Cells - Net Start Class
... transmission occurs when the membrane potential is changed within a neuron. ► A stimulus causes the membrane to become permeable to sodium thus changing the membrane potential. ► A charge separation between the outside of the cell and the cytoplasm creates voltage across the membrane. This voltage ...
... transmission occurs when the membrane potential is changed within a neuron. ► A stimulus causes the membrane to become permeable to sodium thus changing the membrane potential. ► A charge separation between the outside of the cell and the cytoplasm creates voltage across the membrane. This voltage ...
Lesson 4 Section 9.2 Electrochemical Impulse
... Once the overall charge becomes negative (more + than – on the inside of the membrane) the Na+ gates close The cell works to restore the original polarity by using a sodium/potassium pump o 3 Na+ are pumped out, while 2 K+ are pumped in o ATP fuels this o The membrane is now repolarized, or back to ...
... Once the overall charge becomes negative (more + than – on the inside of the membrane) the Na+ gates close The cell works to restore the original polarity by using a sodium/potassium pump o 3 Na+ are pumped out, while 2 K+ are pumped in o ATP fuels this o The membrane is now repolarized, or back to ...
Chapter 2
... 31. Which of the following would contribute to the negative resting membrane potential of a neuron? (p 17) 32. Which of the following states is true regarding the resting membrane potential of a neuron? (45) 33. When the membrane potential becomes positive, this is called __________. (p 46) 34. Wha ...
... 31. Which of the following would contribute to the negative resting membrane potential of a neuron? (p 17) 32. Which of the following states is true regarding the resting membrane potential of a neuron? (45) 33. When the membrane potential becomes positive, this is called __________. (p 46) 34. Wha ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... Excitatory Transmission Neurotransmitter causes depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron by opening postsynaptic ion channels Na+ rushes in causing depolarization and an action potential Inhibitory Transmission Neurotransmitter causes hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic neuron (-75 mV to -9 ...
... Excitatory Transmission Neurotransmitter causes depolarization of the postsynaptic neuron by opening postsynaptic ion channels Na+ rushes in causing depolarization and an action potential Inhibitory Transmission Neurotransmitter causes hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic neuron (-75 mV to -9 ...
Ch10 Reading Guide
... AA. Chromatophilic substance is ____________________________________________ BB. Mature neurons generally do not _____________________ but neural stem cells do. CC. Dendrites are usually highly _____________________________________________ to provide _________________________________________________ ...
... AA. Chromatophilic substance is ____________________________________________ BB. Mature neurons generally do not _____________________ but neural stem cells do. CC. Dendrites are usually highly _____________________________________________ to provide _________________________________________________ ...
Nervous System
... axon is a nerve impulse. It is a short (~10ms) electrical wave that passes down the dendrite and axon. To understand the impulse, you first need to learn how neurons maintain a resting potential. The cell membrane of the neuron has proteins in it that act as ion-specific channels that are described ...
... axon is a nerve impulse. It is a short (~10ms) electrical wave that passes down the dendrite and axon. To understand the impulse, you first need to learn how neurons maintain a resting potential. The cell membrane of the neuron has proteins in it that act as ion-specific channels that are described ...
Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... little movement of K+ or other ions across plasma membrane (Movement of K out through leakage channels = movement of ions is due to attraction to trapped proteins: N.B. leakage channels work in both directions. Movement of ions depends upon concentration gradient.) • Na+, Cl-, and Ca2+ do not have a ...
... little movement of K+ or other ions across plasma membrane (Movement of K out through leakage channels = movement of ions is due to attraction to trapped proteins: N.B. leakage channels work in both directions. Movement of ions depends upon concentration gradient.) • Na+, Cl-, and Ca2+ do not have a ...
Resting potential

The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential.Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in the majority of non-excitable cells can also undergo changes in response to environmental or intracellular stimuli. In principle, there is no difference between resting membrane potential and dynamic voltage changes like action potential from a biophysical point of view: all these phenomena are caused by specific changes in membrane permeabilities for potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which in turn result from concerted changes in functional activity of various ion channels, ion transporters, and exchangers. Conventionally, resting membrane potential can be defined as a relatively stable, ground value of transmembrane voltage in animal and plant cells.Any voltage is a difference in electric potential between two points—for example, the separation of positive and negative electric charges on opposite sides of a resistive barrier. The typical resting membrane potential of a cell arises from the separation of potassium ions from intracellular, relatively immobile anions across the membrane of the cell. Because the membrane permeability for potassium is much higher than that for other ions (disregarding voltage-gated channels at this stage), and because of the strong chemical gradient for potassium, potassium ions flow from the cytosol into the extracellular space carrying out positive charge, until their movement is balanced by build-up of negative charge on the inner surface of the membrane. Again, because of the high relative permeability for potassium, the resulting membrane potential is almost always close to the potassium reversal potential. But in order for this process to occur, a concentration gradient of potassium ions must first be set up. This work is done by the ion pumps/transporters and/or exchangers and generally is powered by ATP.In the case of the resting membrane potential across an animal cell's plasma membrane, potassium (and sodium) gradients are established by the Na+/K+-ATPase (sodium-potassium pump) which transports 2 potassium ions inside and 3 sodium ions outside at the cost of 1 ATP molecule. In other cases, for example, a membrane potential may be established by acidification of the inside of a membranous compartment (such as the proton pump that generates membrane potential across synaptic vesicle membranes).