CENTENNIAL HONORS COLLEGE Western Illinois University Undergraduate Research Day 2015
... Characterizing an Abnormal Action Potential Pattern in Ion-Channel-Mutant Drosophila Mariah Maiman Faculty Mentor: Jeffrey Engel Biology Repetitive activities such as flight are organized by neural networks called central pattern generators and the patterns of action potentials they produce is thoug ...
... Characterizing an Abnormal Action Potential Pattern in Ion-Channel-Mutant Drosophila Mariah Maiman Faculty Mentor: Jeffrey Engel Biology Repetitive activities such as flight are organized by neural networks called central pattern generators and the patterns of action potentials they produce is thoug ...
11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... When ion channels are open, ions diffuse across the membrane, creating electrical currents. C. The Resting Membrane Potential (pp. 396–398; Figs. 11.7–11.8) ...
... When ion channels are open, ions diffuse across the membrane, creating electrical currents. C. The Resting Membrane Potential (pp. 396–398; Figs. 11.7–11.8) ...
axon - the long extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses
... slender processes - a little like antennae. The processes that pick up messages are called dendrites. Those that conduct messages to the next cell are called axons. Let's see how a message travels down an axon. The neuron has the special ability to build up a charge - much like a battery - across it ...
... slender processes - a little like antennae. The processes that pick up messages are called dendrites. Those that conduct messages to the next cell are called axons. Let's see how a message travels down an axon. The neuron has the special ability to build up a charge - much like a battery - across it ...
ppt
... The Electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to diagnose heart problems. The Electroencephalograph (EEG) is used to measure brain-wave activity Action Potential – the voltage difference across a nerve cell membrane when the nerve is excited Resting Potential – voltage difference across a nerve cell membrane ...
... The Electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to diagnose heart problems. The Electroencephalograph (EEG) is used to measure brain-wave activity Action Potential – the voltage difference across a nerve cell membrane when the nerve is excited Resting Potential – voltage difference across a nerve cell membrane ...
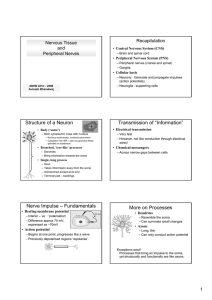
Structure of a Neuron Transmission of “Information” Nerve Impulse
... Takes information away from the soma Unbranched except at its end Terminal part – swellings ...
... Takes information away from the soma Unbranched except at its end Terminal part – swellings ...
NAME: AP Biology/ Ms. Gaynor (Unit #10: Animal Physiology
... 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. ...
... 1. Draw and label the parts of a neuron including: cell body, dendrites, nucleus, axon, myelin sheath, Schwann cells, and Nodes of Ranvier. Then add arrows to your drawing to show the direction of impulse. ...
Nervous system - Lancaster High School
... Neurons are not stimulated, not transmitting signals 1. Fixed anions Proteins, carbohydrates & nucleic acids More abundant inside 2. Sodium/potassium pump ...
... Neurons are not stimulated, not transmitting signals 1. Fixed anions Proteins, carbohydrates & nucleic acids More abundant inside 2. Sodium/potassium pump ...
General Physiology
... pressure required to stop the flow of water • If the pressure in the compartment into which water is flowing is raised to the equivalent of the osmotic pressure, movement of water will stop • osmotic pressure is dependant on the number of particles in solution • If the total osmotic pressure of two ...
... pressure required to stop the flow of water • If the pressure in the compartment into which water is flowing is raised to the equivalent of the osmotic pressure, movement of water will stop • osmotic pressure is dependant on the number of particles in solution • If the total osmotic pressure of two ...
Communication within the Nervous System
... • This difference in electrical charge is referred to as a voltage. • A potential is any change in a membrane’s voltage. ...
... • This difference in electrical charge is referred to as a voltage. • A potential is any change in a membrane’s voltage. ...
File - Mr. Haan`s Science
... 4. Resting Potential a. Nerve cells at rest b. Higher concentration of Na+ outside and higher conc. of K+ inside membrane c. Na+K+ pump works d. K+ diffuses out quickly causing the outside to be + and inside to be – in comparison e. Resting potential = difference in charges ...
... 4. Resting Potential a. Nerve cells at rest b. Higher concentration of Na+ outside and higher conc. of K+ inside membrane c. Na+K+ pump works d. K+ diffuses out quickly causing the outside to be + and inside to be – in comparison e. Resting potential = difference in charges ...
Nervous System Neurons And Synapses
... 20. impulses; presence of ion channels and resting membrane potential (RMP) 21. little; ion; leakage; voltage-gated 22. polarized; negative; -70 mV; Fig 9.2 shown below 23. K+ 24. large; Their size prohibits them from leaving the cell. 25. Na+/K+ pump; active; Na+; ATP 26. negativity inside the cell ...
... 20. impulses; presence of ion channels and resting membrane potential (RMP) 21. little; ion; leakage; voltage-gated 22. polarized; negative; -70 mV; Fig 9.2 shown below 23. K+ 24. large; Their size prohibits them from leaving the cell. 25. Na+/K+ pump; active; Na+; ATP 26. negativity inside the cell ...
Biology 3B Exam 3 Stuff – Here`s a quick list of items for the next
... Where and how nutrients are absorbed and enter general circulation Chapter 48 – neurons, synapses and signaling Understand information processing (sensors, integrators and effectors) Understand the membrane potential and how it’s generated Know the Nerst equation and be able to use to calcul ...
... Where and how nutrients are absorbed and enter general circulation Chapter 48 – neurons, synapses and signaling Understand information processing (sensors, integrators and effectors) Understand the membrane potential and how it’s generated Know the Nerst equation and be able to use to calcul ...
nervous system
... • Motor neurons – convey impulses from CNS to effector cells (muscles and glands) ...
... • Motor neurons – convey impulses from CNS to effector cells (muscles and glands) ...
No Slide Title
... more positive (depolarisation). • If a sufficiently strong charge is applied then the threshold of excitation is reached, and the neuron produces an action potential. • Here the membrane potential is rapidly reversed and becomes strongly positive (up to +40mV) with respect to the exterior. • The mem ...
... more positive (depolarisation). • If a sufficiently strong charge is applied then the threshold of excitation is reached, and the neuron produces an action potential. • Here the membrane potential is rapidly reversed and becomes strongly positive (up to +40mV) with respect to the exterior. • The mem ...
Nervous System webquest……
... Work efficiently because there are many part to this webquest. Research and findings will go on a separate sheet of paper. Part 1: Who was Phineas Gage? http://www.smithsonianmag.com/history-archaeology/Phineas-Gage-NeurosciencesMost-Famous-Patient.html Who was Phineas Gage and what happened to him? ...
... Work efficiently because there are many part to this webquest. Research and findings will go on a separate sheet of paper. Part 1: Who was Phineas Gage? http://www.smithsonianmag.com/history-archaeology/Phineas-Gage-NeurosciencesMost-Famous-Patient.html Who was Phineas Gage and what happened to him? ...
Document
... crucial to the transport of substances into and out of the cell • The plasma membrane that surrounds the cell is impermeable to MOST dissolved substances ie these cannot get in or out easily • BUT the cell membrane is permeable to some substances ...
... crucial to the transport of substances into and out of the cell • The plasma membrane that surrounds the cell is impermeable to MOST dissolved substances ie these cannot get in or out easily • BUT the cell membrane is permeable to some substances ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... or other cell that separates the cell’s intracellular fluid from extracellular fluid ...
... or other cell that separates the cell’s intracellular fluid from extracellular fluid ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse) or over a long distance (from the secretory organ, through the blood, to its site of action). ...
... its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse) or over a long distance (from the secretory organ, through the blood, to its site of action). ...
External anatomy of the ear
... Sectional View of the Cochlear as it will appear on a microscope slide ...
... Sectional View of the Cochlear as it will appear on a microscope slide ...
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... ______4. Period during which potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron. ______5. Transmission of the depolarization wave along the neuron’s membrane. ______6. The chief positive intracellular ion in a resting neuron. ______7. Process by which ATP is used to move sodium ions out of the cell and potass ...
... ______4. Period during which potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron. ______5. Transmission of the depolarization wave along the neuron’s membrane. ______6. The chief positive intracellular ion in a resting neuron. ______7. Process by which ATP is used to move sodium ions out of the cell and potass ...
Ch. 48 - Ltcconline.net
... A. Neurons maintain resting potential across membranes via ion pumps and channels 1. Resting neurons possess potential energy 2. potential energy is used to send signals across body, from one neuron to another 3. potential energy resides in electrical charge difference across neuron’s plasma membran ...
... A. Neurons maintain resting potential across membranes via ion pumps and channels 1. Resting neurons possess potential energy 2. potential energy is used to send signals across body, from one neuron to another 3. potential energy resides in electrical charge difference across neuron’s plasma membran ...
CARDIAC ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
... The inactivation of the slow channels preventing further influx of Ca++ and Na+ and the efflux K+ out of the cell causing the intracellular environment to become more negative, thereby reestablishing the RMP. Phase 4: Resting membrane potential On returning to the RMP, the excess Na+ that entered th ...
... The inactivation of the slow channels preventing further influx of Ca++ and Na+ and the efflux K+ out of the cell causing the intracellular environment to become more negative, thereby reestablishing the RMP. Phase 4: Resting membrane potential On returning to the RMP, the excess Na+ that entered th ...
Resting potential

The relatively static membrane potential of quiescent cells is called the resting membrane potential (or resting voltage), as opposed to the specific dynamic electrochemical phenomena called action potential and graded membrane potential.Apart from the latter two, which occur in excitable cells (neurons, muscles, and some secretory cells in glands), membrane voltage in the majority of non-excitable cells can also undergo changes in response to environmental or intracellular stimuli. In principle, there is no difference between resting membrane potential and dynamic voltage changes like action potential from a biophysical point of view: all these phenomena are caused by specific changes in membrane permeabilities for potassium, sodium, calcium, and chloride ions, which in turn result from concerted changes in functional activity of various ion channels, ion transporters, and exchangers. Conventionally, resting membrane potential can be defined as a relatively stable, ground value of transmembrane voltage in animal and plant cells.Any voltage is a difference in electric potential between two points—for example, the separation of positive and negative electric charges on opposite sides of a resistive barrier. The typical resting membrane potential of a cell arises from the separation of potassium ions from intracellular, relatively immobile anions across the membrane of the cell. Because the membrane permeability for potassium is much higher than that for other ions (disregarding voltage-gated channels at this stage), and because of the strong chemical gradient for potassium, potassium ions flow from the cytosol into the extracellular space carrying out positive charge, until their movement is balanced by build-up of negative charge on the inner surface of the membrane. Again, because of the high relative permeability for potassium, the resulting membrane potential is almost always close to the potassium reversal potential. But in order for this process to occur, a concentration gradient of potassium ions must first be set up. This work is done by the ion pumps/transporters and/or exchangers and generally is powered by ATP.In the case of the resting membrane potential across an animal cell's plasma membrane, potassium (and sodium) gradients are established by the Na+/K+-ATPase (sodium-potassium pump) which transports 2 potassium ions inside and 3 sodium ions outside at the cost of 1 ATP molecule. In other cases, for example, a membrane potential may be established by acidification of the inside of a membranous compartment (such as the proton pump that generates membrane potential across synaptic vesicle membranes).