Arrhythmias 3
... Ventricular rate = 150 bpm or 100 bpm, due to AVN block ratio of 2:1 or 3:1 Ectopic atrial beat causes a re-entrant circuit within the atria. Causes ...
... Ventricular rate = 150 bpm or 100 bpm, due to AVN block ratio of 2:1 or 3:1 Ectopic atrial beat causes a re-entrant circuit within the atria. Causes ...
Origin and Conduction of the Heart Beat
... , which divides into left and right branches. Each branch gives rise to a network of nervous conducting fibres called which are made up of cells high in glycogen. Nerve impulses from the Purkinje fibres pass down the septum separating the left and right ventricles, then up the sides to the apex. The ...
... , which divides into left and right branches. Each branch gives rise to a network of nervous conducting fibres called which are made up of cells high in glycogen. Nerve impulses from the Purkinje fibres pass down the septum separating the left and right ventricles, then up the sides to the apex. The ...
The basic`s of a 12 lead ECG part 3
... These are just extra heart beats that originate from somewhere else in the heart (the ventricles or somewhere other than the SAN in the atria) ...
... These are just extra heart beats that originate from somewhere else in the heart (the ventricles or somewhere other than the SAN in the atria) ...
Cardiovascular Disorders/homeostatic Imbalances
... • http://www.medindia.net/animation/heart_a ttack.asp ...
... • http://www.medindia.net/animation/heart_a ttack.asp ...
ECG Event Represented Duration (Sec)
... •Excessive sympathetic stimulation •Ischemia •Increased temperature ...
... •Excessive sympathetic stimulation •Ischemia •Increased temperature ...
Atrial Fibrillation - Northwestern Medicine
... When the heart does not pump well, blood clots may form inside the heart. Often, these occur in the left atrial appendage, a small pocket of tissue. If the blood clot breaks free, it can travel to the brain and cause a stroke. Atrial fibrillation is common and may cause: ■ An increased risk of stro ...
... When the heart does not pump well, blood clots may form inside the heart. Often, these occur in the left atrial appendage, a small pocket of tissue. If the blood clot breaks free, it can travel to the brain and cause a stroke. Atrial fibrillation is common and may cause: ■ An increased risk of stro ...
Rate or rhythm control for the patient twith atrial fibrillation?
... and stroke, systemic embolism, bleeding, and life-threatening arrhythmic events) comparing strict versus lenient rate control ...
... and stroke, systemic embolism, bleeding, and life-threatening arrhythmic events) comparing strict versus lenient rate control ...
Slide 1 - Annals of Internal Medicine
... after cardiac surgery, a strategy of rhythm management or rate management should be chosen. For patients who are hemodynamically unstable or highly symptomatic or who have a contraindication to anticoagulation, rhythm management is preferred. Unstable patients should undergo urgent electrical cardio ...
... after cardiac surgery, a strategy of rhythm management or rate management should be chosen. For patients who are hemodynamically unstable or highly symptomatic or who have a contraindication to anticoagulation, rhythm management is preferred. Unstable patients should undergo urgent electrical cardio ...
Warfarin Use in Thrombocytopenic Young Adult Male with Atrial
... A 16 year-old male came to the ER with dyspnea on exertion since 3 days prior to admission. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea and edema of extremities were also complained. There was no previous history of similar complain. There was a history of untreated pharyngitis followed by shortness of breath on c ...
... A 16 year-old male came to the ER with dyspnea on exertion since 3 days prior to admission. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea and edema of extremities were also complained. There was no previous history of similar complain. There was a history of untreated pharyngitis followed by shortness of breath on c ...
4_control_of_heart_contraction
... • SAN sets the rhythm for all other cardiac cells to contract (1/second) • SAN sends out electrical impulses to the rest of the atria • This spreads across the both atrial walls as a wave of depolarisation or excitation • Cardiac muscle in the walls of both atria contract in time with the SAN ...
... • SAN sets the rhythm for all other cardiac cells to contract (1/second) • SAN sends out electrical impulses to the rest of the atria • This spreads across the both atrial walls as a wave of depolarisation or excitation • Cardiac muscle in the walls of both atria contract in time with the SAN ...
Managing Atrial Fibrillation: Taking the Lead with Evidence
... Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and often rapid heart rhythm, caused by extremely rapid and chaotic electrical impulses within the heart's atria (the two upper cardiac chambers). The two main adverse effects of this heart rhythm are: 1. Stroke (due to clots that form in the heart and travel to t ...
... Atrial fibrillation is an irregular and often rapid heart rhythm, caused by extremely rapid and chaotic electrical impulses within the heart's atria (the two upper cardiac chambers). The two main adverse effects of this heart rhythm are: 1. Stroke (due to clots that form in the heart and travel to t ...
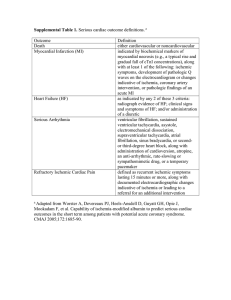
Supplemental Table 1
... indicated by biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis (e.g., a typical rise and gradual fall of cTnI concentrations), along with at least 1 of the following: ischemic symptoms, development of pathologic Q waves on the electrocardiogram or changes indicative of ischemia, coronary artery interventio ...
... indicated by biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis (e.g., a typical rise and gradual fall of cTnI concentrations), along with at least 1 of the following: ischemic symptoms, development of pathologic Q waves on the electrocardiogram or changes indicative of ischemia, coronary artery interventio ...
Editorials Original Articles Advances in Arrhythmia and
... Copyright © 2017 American Heart Association, Inc. All rights reserved. Print ISSN: 1941-3149. Online ISSN: 1941-3084 ...
... Copyright © 2017 American Heart Association, Inc. All rights reserved. Print ISSN: 1941-3149. Online ISSN: 1941-3084 ...
5-Cardiomyopathy and Myocarditis
... Diagnostic Studies: ECG: chamber enlargement (atria > ventricles); low voltage, atrial fibrillation. Chest X ray: normal to enlarged heart with pulmonary vascular congestion. Echocardiogram: Thickened walls, markedly dilated atria, normal systolic function, mitral/tricuspid regurgitation Catheteriza ...
... Diagnostic Studies: ECG: chamber enlargement (atria > ventricles); low voltage, atrial fibrillation. Chest X ray: normal to enlarged heart with pulmonary vascular congestion. Echocardiogram: Thickened walls, markedly dilated atria, normal systolic function, mitral/tricuspid regurgitation Catheteriza ...
Let`s Talk About: Atrial Fibrillation
... High blood pressure, heart failure, heart attack, cardiomyopathy, valvular heart disease, sick sinus syndrome, open heart surgery, genetic / familial Lung conditions Sleep apnea, pneumonia, COPD, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hypertension Others Excessive alcohol, hyperthyroid, habitual aerobi ...
... High blood pressure, heart failure, heart attack, cardiomyopathy, valvular heart disease, sick sinus syndrome, open heart surgery, genetic / familial Lung conditions Sleep apnea, pneumonia, COPD, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hypertension Others Excessive alcohol, hyperthyroid, habitual aerobi ...
Atrial Fibrilation And Whole Body Vibration1
... from the atrium of the heart. These signals are sent to the ventricles of the heart at irregular intervals resulting in an irregular, fast heart rate. It is the most common type of arrhythmia. It generally is assymptomatic and arrhythmias can last anywhere from minutes to years. It is generally a no ...
... from the atrium of the heart. These signals are sent to the ventricles of the heart at irregular intervals resulting in an irregular, fast heart rate. It is the most common type of arrhythmia. It generally is assymptomatic and arrhythmias can last anywhere from minutes to years. It is generally a no ...
Atrial Fibrillation Information Sheet
... If atrial fibrillation causes chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness or congestive heart failure (water in the lungs), the arrhythmia may be dangerous and need to be corrected promptly. Usually however symptoms are not that severe and the arrhythmia may be dealt with less acutely. The major long ...
... If atrial fibrillation causes chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness or congestive heart failure (water in the lungs), the arrhythmia may be dangerous and need to be corrected promptly. Usually however symptoms are not that severe and the arrhythmia may be dealt with less acutely. The major long ...
What is AFib?
... the AV node and, that will govern how fast the lower chambers (the ventricles), will contract, or how fast your heart beat will be. ...
... the AV node and, that will govern how fast the lower chambers (the ventricles), will contract, or how fast your heart beat will be. ...
PBL- Case 1: Cardiac Arrhythmias Pre
... High prevalence of CAD, CHF and valvular disease and calcification (common in older patients) puts them at higher risk of atrial fibrillation. Cardiac valvular stenosis or regurgitation caused by either rheumatic or age related degenerative changes increases left atrial pressure and results in the e ...
... High prevalence of CAD, CHF and valvular disease and calcification (common in older patients) puts them at higher risk of atrial fibrillation. Cardiac valvular stenosis or regurgitation caused by either rheumatic or age related degenerative changes increases left atrial pressure and results in the e ...
Ventricular tachycardia (broad complex)
... complexes must be generated in the ventricles independently from the atria. If this occurs either due to left or right bundle branch block or the presence of ventricular arrhythmias, QRS complxes will be broad (as the bundle/Purkinje system is that which ensures narrow complexes) VENTRICULAR TACHYCA ...
... complexes must be generated in the ventricles independently from the atria. If this occurs either due to left or right bundle branch block or the presence of ventricular arrhythmias, QRS complxes will be broad (as the bundle/Purkinje system is that which ensures narrow complexes) VENTRICULAR TACHYCA ...
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation (AF or A-fib) is an abnormal heart rhythm characterized by rapid and irregular beating. Often it starts as brief periods of abnormal beating which become longer and possibly constant over time. Most episodes have no symptoms. Occasionally there may be heart palpitations, fainting, shortness of breath, or chest pain. The disease increases the risk of heart failure, dementia, and stroke.Hypertension and valvular heart disease are the most common alterable risk factors for AF. Other heart-related risk factors include heart failure, coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy, and congenital heart disease. In the developing world valvular heart disease often occurs as a result of rheumatic fever. Lung-related risk factors include COPD, obesity, and sleep apnea. Other factors include excess alcohol intake, diabetes mellitus, and thyrotoxicosis. However, half of cases are not associated with one of these risks. A diagnosis is made by feeling the pulse and may be confirmed using an electrocardiogram (ECG). The typical ECG shows no P waves and an irregular ventricular rate.AF is often treated with medications to slow the heart rate to a near normal range (known as rate control) or to convert the rhythm to normal sinus rhythm (known as rhythm control). Electrical cardioversion can also be used to convert AF to a normal sinus rhythm and is often used emergently if the person is unstable. Ablation may prevent recurrence in some people. Depending on the risk of stroke either aspirin or anti-clotting medications such as warfarin or a novel oral anticoagulant may be recommended. While these medications reduce this risk, they increase rates of major bleeding.Atrial fibrillation is the most common serious abnormal heart rhythm. In Europe and North America, as of 2014, it affects about 2% to 3% of the population. This is an increase from 0.4 to 1% of the population around 2005. In the developing world about 0.6% of males and 0.4% of females are affected. The percentage of people with AF increases with age with 0.14% under 50 years old, 4% between 60 and 70 years old, and 14% over 80 years old being affected. A-fib and atrial flutter resulted in 112,000 deaths in 2013, up from 29,000 in 1990. The first known report of an irregular pulse was by John Baptist Senac in 1749. This was first documented by ECG in 1909 by Thomas Lewis.