
Encoding of Action History in the Rat Ventral Striatum
... reward prediction errors. In addition, the process of reinforcement learning would be greatly facilitated if memory signals related to the animal’s recent actions are also available in the same anatomical structure involved in updating the value functions because a reward or penalty resulting from a ...
... reward prediction errors. In addition, the process of reinforcement learning would be greatly facilitated if memory signals related to the animal’s recent actions are also available in the same anatomical structure involved in updating the value functions because a reward or penalty resulting from a ...
Neural Control of Interappendage Phase During Locomotion
... It is desirable to determine the minimum piece of nervous tissue which is capable of producing the normal rhythmic output to a limb. The technique which has been utilized in the crayfish swimmeret system is the isolation of the presumptive control center from the remainder of the CNS. The abdominal ...
... It is desirable to determine the minimum piece of nervous tissue which is capable of producing the normal rhythmic output to a limb. The technique which has been utilized in the crayfish swimmeret system is the isolation of the presumptive control center from the remainder of the CNS. The abdominal ...
Skeletal System
... decreasing in strength as it travels If this depolarizing signal is strong enough when it reaches the initial segment of the axon, it acts as the trigger that initiates an action potential in the axon Signals from the receptive zone determine if the axon will fire an impulse ...
... decreasing in strength as it travels If this depolarizing signal is strong enough when it reaches the initial segment of the axon, it acts as the trigger that initiates an action potential in the axon Signals from the receptive zone determine if the axon will fire an impulse ...
PDF
... of U by modifying the length constant p and the cut off R for several choices of the gain g and threshold K. Figure 2 shows a typical example, a plot of the propagation velocity against the inverse of the synaptic length constant p for different length cutoffs R. For convenience, we have divided the ...
... of U by modifying the length constant p and the cut off R for several choices of the gain g and threshold K. Figure 2 shows a typical example, a plot of the propagation velocity against the inverse of the synaptic length constant p for different length cutoffs R. For convenience, we have divided the ...
A Neural Circuit Basis for Spatial Working Memory
... discharges of neurons in a distributed brain network. The representation of the spatial location of a remembered visual stimulus has been studied most extensively and provides the best-understood model of how mnemonic information is encoded in the brain. Neural correlates of spatial working memory a ...
... discharges of neurons in a distributed brain network. The representation of the spatial location of a remembered visual stimulus has been studied most extensively and provides the best-understood model of how mnemonic information is encoded in the brain. Neural correlates of spatial working memory a ...
Functional Synaptic Contacts by Intranuclear
... Increased magnification of main axon with two identified axon collaterals (outlined areas). Biii,Biv, Details of the two collaterals apparent lack of a low threshold calcium (arrowheads) outlined in Bii. spike (Fig. 3A). These interneurons had an average resting membrane potential of ⫺65 ⫾ 5 (SD) mV ...
... Increased magnification of main axon with two identified axon collaterals (outlined areas). Biii,Biv, Details of the two collaterals apparent lack of a low threshold calcium (arrowheads) outlined in Bii. spike (Fig. 3A). These interneurons had an average resting membrane potential of ⫺65 ⫾ 5 (SD) mV ...
The response of cat visual cortex to flicker stimuli of variable frequency
... 1994; Contreras & Steriade, 1997). Frequencies below 5 Hz (delta) are observed during pathological states, e.g. coma, but also during anaesthesia and slow wave sleep. Activity in the theta-band prevails in limbic structures during exploratory behaviour. Oscillatory activity in the 10 Hz range, also ...
... 1994; Contreras & Steriade, 1997). Frequencies below 5 Hz (delta) are observed during pathological states, e.g. coma, but also during anaesthesia and slow wave sleep. Activity in the theta-band prevails in limbic structures during exploratory behaviour. Oscillatory activity in the 10 Hz range, also ...
PDF
... (NAA) and N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) for supply of energy, and on the nature of “neuronal words and languages” for intercellular communication, insights into the brain’s modular structural and functional units have been gained. In this article, it is proposed that the basic structural unit in ...
... (NAA) and N-acetylaspartylglutamate (NAAG) for supply of energy, and on the nature of “neuronal words and languages” for intercellular communication, insights into the brain’s modular structural and functional units have been gained. In this article, it is proposed that the basic structural unit in ...
Modulation of Neuronal Activity in the Monkey Putamen Associated
... overlearned sequence of arm reaching movements to examine whether task-related activities are sensitive to manipulations of the serial order of stimulus-target locations. The monkeys’ capacity to learn sequential regularities was assessed by comparing arm movement latencies and saccadic ocular react ...
... overlearned sequence of arm reaching movements to examine whether task-related activities are sensitive to manipulations of the serial order of stimulus-target locations. The monkeys’ capacity to learn sequential regularities was assessed by comparing arm movement latencies and saccadic ocular react ...
Optogenetic drive of neocortical pyramidal neurons generates fMRI
... The BOLD signal showed a gradual increase in amplitude with increasing rate of stimulation for both periodic and Poisson stimulation, with a greater increase in overall amplitude for Poisson stimuli at all frequencies (Fig. 4A), confirmed as statistically significant by a reliable main effect of sti ...
... The BOLD signal showed a gradual increase in amplitude with increasing rate of stimulation for both periodic and Poisson stimulation, with a greater increase in overall amplitude for Poisson stimuli at all frequencies (Fig. 4A), confirmed as statistically significant by a reliable main effect of sti ...
Tsodyks-Banbury-2006
... Open questions: How do precise spike patterns emerge in the cortex? How can they be robust in the presence of random firing of surrounding neurons? (Synfire chains? – I don’t like it!) What is the relation between the spike patterns and the stimuli that they are coding for? How can the information ...
... Open questions: How do precise spike patterns emerge in the cortex? How can they be robust in the presence of random firing of surrounding neurons? (Synfire chains? – I don’t like it!) What is the relation between the spike patterns and the stimuli that they are coding for? How can the information ...
Do cortical areas emerge from a protocottex?
... neocortical area is remodeled chiefly through the selective elimination of particular axon collaterals or long distal segments of the primary axons without a concomitant death of the projection neurons. For example, in adult rats, pyramidal tract neurons (which extend a long axon through the pyramid ...
... neocortical area is remodeled chiefly through the selective elimination of particular axon collaterals or long distal segments of the primary axons without a concomitant death of the projection neurons. For example, in adult rats, pyramidal tract neurons (which extend a long axon through the pyramid ...
An overview of reservoir computing: theory, applications and
... In [36] it was shown that when no prior knowledge of the problem at had is given, it is best to create the reservoir with a uniform pole placement, so that all possible frequencies are maximally covered, an idea which originated from the identification of linear systems using Kautz filters. The rand ...
... In [36] it was shown that when no prior knowledge of the problem at had is given, it is best to create the reservoir with a uniform pole placement, so that all possible frequencies are maximally covered, an idea which originated from the identification of linear systems using Kautz filters. The rand ...
The evolution of nervous system centralization
... what their initial structure and function was. It is also unclear whether the CNS of vertebrates and invertebrates trace back to a common CNS precursor (Arendt & Nübler-Jung 1999) or whether they are of independent evolutionary origin (Holland 2003; Lowe et al. 2003). This review addresses the ques ...
... what their initial structure and function was. It is also unclear whether the CNS of vertebrates and invertebrates trace back to a common CNS precursor (Arendt & Nübler-Jung 1999) or whether they are of independent evolutionary origin (Holland 2003; Lowe et al. 2003). This review addresses the ques ...
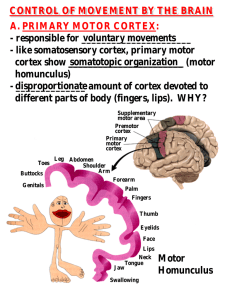
CONTROL OF MOVEMENT BY THE BRAIN A. PRIMARY MOTOR
... -caudate and putamen neurons then send their axons to ____________________; internal globus pallidus - in turn, GP axons contact the ________________, thalamus (VA/VL) which feedback onto cortex to modulate movement force. ...
... -caudate and putamen neurons then send their axons to ____________________; internal globus pallidus - in turn, GP axons contact the ________________, thalamus (VA/VL) which feedback onto cortex to modulate movement force. ...
Brain Stem Catecholamine Mechanisms in Tonic and
... been elaborated on only over the past 20 years. The evidence for its role in control of AP stems from a variety of physiological and anatomical studies.5"8 In brief: (1) The NTS has been demonstrated by retrograde transport techniques to be the site of termination of afferents that arise from cardio ...
... been elaborated on only over the past 20 years. The evidence for its role in control of AP stems from a variety of physiological and anatomical studies.5"8 In brief: (1) The NTS has been demonstrated by retrograde transport techniques to be the site of termination of afferents that arise from cardio ...
TESIS DOCTORAL Dynamics and Synchronization in Neuronal Models
... believed concept that the nervous system was a reticulum or a continuum meshwork. Using a histological staining technique, Cajal could resolve in detail the structure and concluded that the nervous system was composed of individual neurons rather than a continuum. For this discovery, Cajal was award ...
... believed concept that the nervous system was a reticulum or a continuum meshwork. Using a histological staining technique, Cajal could resolve in detail the structure and concluded that the nervous system was composed of individual neurons rather than a continuum. For this discovery, Cajal was award ...
A computational account for the ontogeny of mirror neurons via
... At the time Hebbian learning was introduced by Donald Hebb (1949), the field of neuroscience, let alone the field of neuroinformatics, was still in its infancy. Hebb’s postulate was introduced in a general, qualitative manner. It implies that learning occurs due to changes in synaptic strength, and ...
... At the time Hebbian learning was introduced by Donald Hebb (1949), the field of neuroscience, let alone the field of neuroinformatics, was still in its infancy. Hebb’s postulate was introduced in a general, qualitative manner. It implies that learning occurs due to changes in synaptic strength, and ...
No Direct Projection is Observed from the Substantia Nigra to the
... injection of the retrograde tracer fluoro-gold (FG) into the DVC, FG-labeled neurons were observed in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN), lateral hypothalamus (LH), inferior olive (IO), and locus coeruleus (LC). No FG-positive cells were observed in the SN or striatum. Furthermore, after ...
... injection of the retrograde tracer fluoro-gold (FG) into the DVC, FG-labeled neurons were observed in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN), lateral hypothalamus (LH), inferior olive (IO), and locus coeruleus (LC). No FG-positive cells were observed in the SN or striatum. Furthermore, after ...
Chapter 4 monkey
... Thompson 2008). It therefore appears that this area is an integral part of the circuitries which mediate both attentional and decision-making processes if the task requires an eye movement response. The roles of area FEF and the principal sulcus (PS) in decision making have been investigated in a ta ...
... Thompson 2008). It therefore appears that this area is an integral part of the circuitries which mediate both attentional and decision-making processes if the task requires an eye movement response. The roles of area FEF and the principal sulcus (PS) in decision making have been investigated in a ta ...
Cortical remodelling induced by activity of ventral tegmental
... These positive and negative frequency-speci®c representational changes resulted in emergent sharp transitions in best frequency maps (Fig. 1b, indicated by the arrows; also see Figs 1e, f and 2a). Pairing procedures did not change response properties such as latency or the number of spikes evoked by ...
... These positive and negative frequency-speci®c representational changes resulted in emergent sharp transitions in best frequency maps (Fig. 1b, indicated by the arrows; also see Figs 1e, f and 2a). Pairing procedures did not change response properties such as latency or the number of spikes evoked by ...
36_LectureSlidesAdde..
... • Leptin stimulates POMC otherwise known as aMSH/CART neurons. This increases excitation of the catabolic pathway, and it increases inhibition of the anabolic pathway. The result again is a net increase in activity of the catabolic pathway relative to the anabolic pathway. • The net increase in cata ...
... • Leptin stimulates POMC otherwise known as aMSH/CART neurons. This increases excitation of the catabolic pathway, and it increases inhibition of the anabolic pathway. The result again is a net increase in activity of the catabolic pathway relative to the anabolic pathway. • The net increase in cata ...
Synaptic pathways and inhibitory gates in the spinal cord dorsal horn
... inhibition, whereas about a half of lamina II neurons received pure GABAergic and the rest received mixed GABAergic and glycinergic inhibition.20 In addition, other studies have focused on cell typespecific inhibition in the dorsal horn. For example, central cells, which are commonly situated in the ...
... inhibition, whereas about a half of lamina II neurons received pure GABAergic and the rest received mixed GABAergic and glycinergic inhibition.20 In addition, other studies have focused on cell typespecific inhibition in the dorsal horn. For example, central cells, which are commonly situated in the ...
[j26]Chapter 9#
... norepinephrine, epinephrine, and related neurotransmitter substances; and those that are cholinergic, receiving acetylcholine (ACh). Interestingly, because the receptor types can vary from neuron to neuron, the same neurotransmitter may cause the response of one neuron to differ from that of another ...
... norepinephrine, epinephrine, and related neurotransmitter substances; and those that are cholinergic, receiving acetylcholine (ACh). Interestingly, because the receptor types can vary from neuron to neuron, the same neurotransmitter may cause the response of one neuron to differ from that of another ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.






















![[j26]Chapter 9#](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009372212_1-45723eed01d76cad9811e1514890dc2a-300x300.png)