Lack of response suppression follows repeated ventral tegmental
... shown a rapid desensitization of these receptors following activation of protein kinase C by 4-a-phorbol. To investigate the possible physiological correlates of this phenomenon, we have studied the effects of repeated cannabinoid treatment on ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neuronal firing in v ...
... shown a rapid desensitization of these receptors following activation of protein kinase C by 4-a-phorbol. To investigate the possible physiological correlates of this phenomenon, we have studied the effects of repeated cannabinoid treatment on ventral tegmental area dopaminergic neuronal firing in v ...
A model for experience-dependent changes in the responses of inferotemporal neurons
... excitatory IT neurons which could undergo self-organization. We use the term self-organizing to describe connections which are the primary source of excitatory input to a region (here IT cortex) and for which modification is driven entirely by intrinsic network variables (e.g. postsynaptic activity) ...
... excitatory IT neurons which could undergo self-organization. We use the term self-organizing to describe connections which are the primary source of excitatory input to a region (here IT cortex) and for which modification is driven entirely by intrinsic network variables (e.g. postsynaptic activity) ...
Solving the Distal Reward Problem through
... regular spiking type and 20% inhibitory neurons of the fast spiking type (Connors and Gutnick 1990), representing the layer 2/3 part of a cortical minicolumn. Neurons are randomly connected with 10% probability so that there are 100 synapses per averaged neuron. The connections, combined with the ra ...
... regular spiking type and 20% inhibitory neurons of the fast spiking type (Connors and Gutnick 1990), representing the layer 2/3 part of a cortical minicolumn. Neurons are randomly connected with 10% probability so that there are 100 synapses per averaged neuron. The connections, combined with the ra ...
Isodirectional Tuning of Adjacent Interneurons and Pyramidal Cells
... Isodirectional Tuning of Adjacent Interneurons and Pyramidal Cells During Working Memory: Evidence for Microcolumnar Organization in PFC SRINIVAS G. RAO, GRAHAM V. WILLIAMS, AND PATRICIA S. GOLDMAN-RAKIC Section of Neurobiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut 06510 Rao, S ...
... Isodirectional Tuning of Adjacent Interneurons and Pyramidal Cells During Working Memory: Evidence for Microcolumnar Organization in PFC SRINIVAS G. RAO, GRAHAM V. WILLIAMS, AND PATRICIA S. GOLDMAN-RAKIC Section of Neurobiology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut 06510 Rao, S ...
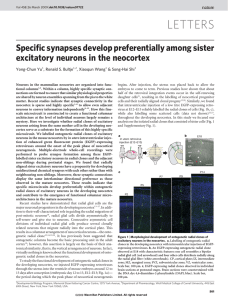
Specific synapses develop preferentially among sister excitatory
... Neurons in the mammalian neocortex are organized into functional columns1,2. Within a column, highly specific synaptic connections are formed to ensure that similar physiological properties are shared by neuron ensembles spanning from the pia to the white matter. Recent studies indicate that synapti ...
... Neurons in the mammalian neocortex are organized into functional columns1,2. Within a column, highly specific synaptic connections are formed to ensure that similar physiological properties are shared by neuron ensembles spanning from the pia to the white matter. Recent studies indicate that synapti ...
A Model of Prefrontal Cortical Mechanisms for Goal-directed Behavior Michael E. Hasselmo Abstract
... spreads over connections Wg from the goR population in the ‘‘Reward’’ minicolumn to the input population gi in the ‘‘East’’ state minicolumn. These connections were strengthened during previous exploration of the environment (as described in the Methods section below), allowing units in go to activa ...
... spreads over connections Wg from the goR population in the ‘‘Reward’’ minicolumn to the input population gi in the ‘‘East’’ state minicolumn. These connections were strengthened during previous exploration of the environment (as described in the Methods section below), allowing units in go to activa ...
HYPOTHALAMUS
... Plate 29 shows the relationship of troph-hormone producing cells to fenestrated capillaries in the anterior pituitary. The magno- and parvocellular cell groups producing the hypothalamic hormones receive a variety of stimuli from different parts of the brain, primarily within the hypothalamus, but ...
... Plate 29 shows the relationship of troph-hormone producing cells to fenestrated capillaries in the anterior pituitary. The magno- and parvocellular cell groups producing the hypothalamic hormones receive a variety of stimuli from different parts of the brain, primarily within the hypothalamus, but ...
Lecture #1 - University of Utah
... - ‘clamp’ (hold) membrane pot. @ desired value by delivering (injecting) current into cell to compensate for flow of ions through channels. -Record time course and magnitude of current flow @ various clamp values (‘Holding Potentials’). 2. Measuring Ion Flow and Channel Properties ...
... - ‘clamp’ (hold) membrane pot. @ desired value by delivering (injecting) current into cell to compensate for flow of ions through channels. -Record time course and magnitude of current flow @ various clamp values (‘Holding Potentials’). 2. Measuring Ion Flow and Channel Properties ...
Cuneiform Neurons Activated during
... Active sleep (AS) is a complex behavioral state that is comprised of diverse physiological processes (Steriade and McCarley, 1990; Jones, 1991) (for review, see Siegel, 1994; Rye 1997). Among the distinguishing physiological characteristics of this state are muscular atonia, EEG desynchronization, p ...
... Active sleep (AS) is a complex behavioral state that is comprised of diverse physiological processes (Steriade and McCarley, 1990; Jones, 1991) (for review, see Siegel, 1994; Rye 1997). Among the distinguishing physiological characteristics of this state are muscular atonia, EEG desynchronization, p ...
A Stereoscopic Look at Visual Cortex
... Van Essen 1991)] is far removed from the early areas (V1–V3) and receives extensive inputs from the dorsal stream (Baizer et al. 1991; Saleem et al. 2000), leaving open the possibility that the relevant processing is happening in dorsal cortex and is later relayed to ventral cortex. Three very recen ...
... Van Essen 1991)] is far removed from the early areas (V1–V3) and receives extensive inputs from the dorsal stream (Baizer et al. 1991; Saleem et al. 2000), leaving open the possibility that the relevant processing is happening in dorsal cortex and is later relayed to ventral cortex. Three very recen ...
Temporal Sequence Detection with Spiking Neurons: Towards
... active dendrites and dynamic synapses in an integrated model. For a long time, dendrites have been thought to be the structures where complex neuronal computation takes place, but only recently have we begun to understand how they operate. The dendrites do not simply collect and pass synaptic inputs ...
... active dendrites and dynamic synapses in an integrated model. For a long time, dendrites have been thought to be the structures where complex neuronal computation takes place, but only recently have we begun to understand how they operate. The dendrites do not simply collect and pass synaptic inputs ...
Understanding mirror neurons - LIRA-Lab
... of area F5: “canonical” neurons are mainly found in that sector of area F5 buried inside the arcuate sulcus, whereas “mirror” neurons are almost exclusively located in the cortical convexity of F5 (see Figure 1). 2.2. Canonical neurons Recently, the visual responses of F5 “canonical” neurons have b ...
... of area F5: “canonical” neurons are mainly found in that sector of area F5 buried inside the arcuate sulcus, whereas “mirror” neurons are almost exclusively located in the cortical convexity of F5 (see Figure 1). 2.2. Canonical neurons Recently, the visual responses of F5 “canonical” neurons have b ...
Neuronal correlates of decision
... When forming a decision based on sensory information, where and how in the brain do the neuronal responses that encode the sensory stimuli translate into responses that encode the decision? We investigated this question using a vibrotactile sequential discrimination task (Fig. 1). In this two-altern ...
... When forming a decision based on sensory information, where and how in the brain do the neuronal responses that encode the sensory stimuli translate into responses that encode the decision? We investigated this question using a vibrotactile sequential discrimination task (Fig. 1). In this two-altern ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... – These are called the paravertebral ganglia. – These ganglia are connected, forming a sympathetic chain of ganglia. ...
... – These are called the paravertebral ganglia. – These ganglia are connected, forming a sympathetic chain of ganglia. ...
Information processing in the cortex: The relevance of coherent oscillations for neuronal communication
... 1.1 Mechanisms of oscillation generation in computational modeling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 Functional role of oscillations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... 1.1 Mechanisms of oscillation generation in computational modeling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1.2 Functional role of oscillations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Striate cortex increases contrast gain of macaque LGN neurons
... jected forward (Mumford, 1992; Rao & Ballard, 1999). In discussing the latter predictive model with applicability to both corticofugal and corticocortical recurrent projections, Koch and Poggio (1999) note that “it will be critical to unravel the precise function of corticocortical feedback projecti ...
... jected forward (Mumford, 1992; Rao & Ballard, 1999). In discussing the latter predictive model with applicability to both corticofugal and corticocortical recurrent projections, Koch and Poggio (1999) note that “it will be critical to unravel the precise function of corticocortical feedback projecti ...
Spike Train SIMilarity Space (SSIMS): A Framework for Single
... trials with similar activity patterns). The proposed algorithm transforms neural data to produce a lowdimensional spike train SIMilarity space (SSIMS) that represents the relationships between activity patterns generated on individual trials. In the SSIMS projection, similar neural activity patterns ...
... trials with similar activity patterns). The proposed algorithm transforms neural data to produce a lowdimensional spike train SIMilarity space (SSIMS) that represents the relationships between activity patterns generated on individual trials. In the SSIMS projection, similar neural activity patterns ...
(Full text - MSWord file 171K)
... 2.1 Houk, Adams and Barto (1995) One of the first actor-critic models of the basal ganglia was presented by Houk et al. (1995). This model suggests that striosomal modules fulfill the main functions of the adaptive critic, whereas matrix modules function as an actor. Striosomal modules comprise of ...
... 2.1 Houk, Adams and Barto (1995) One of the first actor-critic models of the basal ganglia was presented by Houk et al. (1995). This model suggests that striosomal modules fulfill the main functions of the adaptive critic, whereas matrix modules function as an actor. Striosomal modules comprise of ...
The Interacting Neuroendocrine Network in Stress
... neurotransmitters, peptide hormones, proinflammatory cytokines and adrenal steroids from neural, neuroendocrine and immune cells which prepared the organism to alert its systems to adopt the proper behavioral responses against stressful events. Neurotransmitters, peptide hormones and cytokines act t ...
... neurotransmitters, peptide hormones, proinflammatory cytokines and adrenal steroids from neural, neuroendocrine and immune cells which prepared the organism to alert its systems to adopt the proper behavioral responses against stressful events. Neurotransmitters, peptide hormones and cytokines act t ...
Computational cognitive neuroscience: 10. Prefrontal Cortex (PFC)
... Dorsal and ventral areas on the medial PFC • The dorsal medial PFC is also known as the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), which has been shown to encode the affective aspects of motor control variables (e.g., how much effort will an action take, what is its probability of success, how much conflict ...
... Dorsal and ventral areas on the medial PFC • The dorsal medial PFC is also known as the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), which has been shown to encode the affective aspects of motor control variables (e.g., how much effort will an action take, what is its probability of success, how much conflict ...
Invited Paper Neural networks in engineering D.T. Pham Intelligent
... Neural network applications Types of applications Neural networks have been employed in a wide range of applications. These can be grouped into six general types which are [NeuralWare, 1993]:Modelling and prediction A modelling neural network essentially acts as a mapping operator or transfer functi ...
... Neural network applications Types of applications Neural networks have been employed in a wide range of applications. These can be grouped into six general types which are [NeuralWare, 1993]:Modelling and prediction A modelling neural network essentially acts as a mapping operator or transfer functi ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.