view - Queen`s University
... which form connections with the motor neurons after the synapse, and permit substantial processing of signals. But the direct projection from sensory afferents to motor neurons precludes such processing. Instead, the activity of these synapses (and other afferent synapses in the spinal cord) is regu ...
... which form connections with the motor neurons after the synapse, and permit substantial processing of signals. But the direct projection from sensory afferents to motor neurons precludes such processing. Instead, the activity of these synapses (and other afferent synapses in the spinal cord) is regu ...
The Brain and Behavior
... • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One axon communicates with the spinal cord; one with either the skin ...
... • Motoneurons or Multipolar neurons carry signals from the CNS muscles and glands. • Interneurons or Pseudopolare (Spelling) cells form all the neural wiring within the CNS. These have two axons (instead of an axon and a dendrite). One axon communicates with the spinal cord; one with either the skin ...
Funkcje ruchowe
... organization underlie this function. First, the cerebellum is provided with extensive information about the goals, commands, and feedback signals associated with movement. There are 40 times more axons project into the cerebellum than exit from it. Second, the output of the cerebellum is sent to the ...
... organization underlie this function. First, the cerebellum is provided with extensive information about the goals, commands, and feedback signals associated with movement. There are 40 times more axons project into the cerebellum than exit from it. Second, the output of the cerebellum is sent to the ...
Mirror Neurons & You
... behavior, internally firing/activating the motor neurons of the corresponding behavior. They perform a kind of simulation of any observed ...
... behavior, internally firing/activating the motor neurons of the corresponding behavior. They perform a kind of simulation of any observed ...
Slide ()
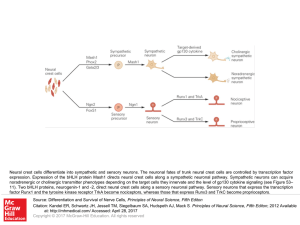
... Neural crest cells differentiate into sympathetic and sensory neurons. The neuronal fates of trunk neural crest cells are controlled by transcription factor expression. Expression of the bHLH protein Mash1 directs neural crest cells along a sympathetic neuronal pathway. Sympathetic neurons can acqui ...
... Neural crest cells differentiate into sympathetic and sensory neurons. The neuronal fates of trunk neural crest cells are controlled by transcription factor expression. Expression of the bHLH protein Mash1 directs neural crest cells along a sympathetic neuronal pathway. Sympathetic neurons can acqui ...
Document
... • it controls hunger, body temperature, aggression and other aspects of behaviour and metabolism. • the hypothalamus controls the endocrine hormone system because attached to it is the pituitary gland. • the pituitary gland produces hormones that control many of the endocrine glands. • the midbrain ...
... • it controls hunger, body temperature, aggression and other aspects of behaviour and metabolism. • the hypothalamus controls the endocrine hormone system because attached to it is the pituitary gland. • the pituitary gland produces hormones that control many of the endocrine glands. • the midbrain ...
CNS
... • it controls hunger, body temperature, aggression and other aspects of behaviour and metabolism. • the hypothalamus controls the endocrine hormone system because attached to it is the pituitary gland. • the pituitary gland produces hormones that control many of the endocrine glands. • the midbrain ...
... • it controls hunger, body temperature, aggression and other aspects of behaviour and metabolism. • the hypothalamus controls the endocrine hormone system because attached to it is the pituitary gland. • the pituitary gland produces hormones that control many of the endocrine glands. • the midbrain ...
Slide ()
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
Understanding-the.. - Windsor C
... 1. Sensory- afferent- receives messages from sense organs 2. Motor- efferent- sends messages to other parts of the body 3. Inter- communicates between sensory and motor neurons ...
... 1. Sensory- afferent- receives messages from sense organs 2. Motor- efferent- sends messages to other parts of the body 3. Inter- communicates between sensory and motor neurons ...
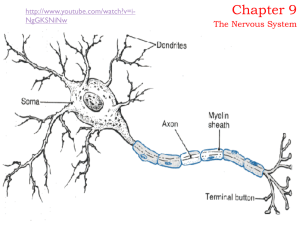
Neurons, nerves and glia
... Oligodendrocytes – form the myelin sheath which protects neurons in the CNS Microglia – as phagocytes protect neurons in response to inflammation ...
... Oligodendrocytes – form the myelin sheath which protects neurons in the CNS Microglia – as phagocytes protect neurons in response to inflammation ...
Slide ()
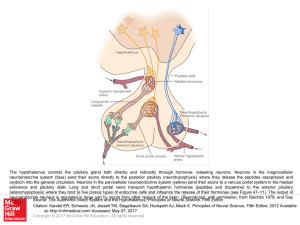
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...
... neuroendocrine system (blue) send their axons directly to the posterior pituitary (neurohypophysis) where they release the peptides vasopressin and oxytocin into the general circulation. Neurons in the parvicellular neuroendocrine system (yellow) send their axons to a venous portal system in the med ...