The following are Biology 201 terms that will be used in Biology 202
... 201 and since we stress homeostasis in both courses there will be a fair amount of information from biology 201 that is used in 202. The following terms you are expected to know and be able to use in biology 202. Anatomical position Directional terms Body planes and sections Body cavities Homeostasi ...
... 201 and since we stress homeostasis in both courses there will be a fair amount of information from biology 201 that is used in 202. The following terms you are expected to know and be able to use in biology 202. Anatomical position Directional terms Body planes and sections Body cavities Homeostasi ...
nervous system
... K+ pump to reestablish resting potential Nerves can’t be stimulated during repolarization unless a huge stimulus occurs, “you stick your wet finger into an electrical outlet Ready to fire again in .001 sec ...
... K+ pump to reestablish resting potential Nerves can’t be stimulated during repolarization unless a huge stimulus occurs, “you stick your wet finger into an electrical outlet Ready to fire again in .001 sec ...
Cai, D.; Tao, L.; Rangan, A.; McLaughlin, D. Kinetic Theory for Neuronal Network Dynamics. Comm. Math. Sci 4 (2006), no. 1, 97-12.
... conductance-based integrate-and-fire (I&F) neurons, a full kinetic description without introduction of new parameters is derived. After a brief description of the dynamics of conductance - based I&F neural networks, for the dynamics of a single I&F neuron with an infinitely fast conductance driven b ...
... conductance-based integrate-and-fire (I&F) neurons, a full kinetic description without introduction of new parameters is derived. After a brief description of the dynamics of conductance - based I&F neural networks, for the dynamics of a single I&F neuron with an infinitely fast conductance driven b ...
Nervous System Nervous System
... organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
... organization of cells into tissues, and tissues into organs. The structure and function of organs determine their relationships within body systems of an organism. Homeostasis allows the body to perform its normal functions. ...
Brainstem*s involvement in Motor process
... • Mediates motor (and sensation) control of the head, neck and face. • Influences parasympathetic reflexes • Contains ascending and descending pathways that carry motor (and sensory) information to other divisions of the central nervous system ...
... • Mediates motor (and sensation) control of the head, neck and face. • Influences parasympathetic reflexes • Contains ascending and descending pathways that carry motor (and sensory) information to other divisions of the central nervous system ...
BIOLOGY & BEHAVIOR
... because it is the basis of all behavior The NEURON is the fundamental unit of the nervous system ...
... because it is the basis of all behavior The NEURON is the fundamental unit of the nervous system ...
Neural Networks.Chap..
... A set of input-output pairs, with each pair consisting of an input signal and the corresponding desired response, is referred to as a set of training data or ...
... A set of input-output pairs, with each pair consisting of an input signal and the corresponding desired response, is referred to as a set of training data or ...
Slide ()
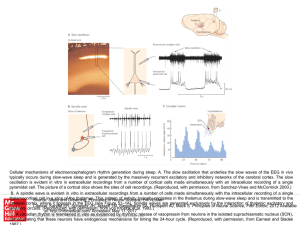
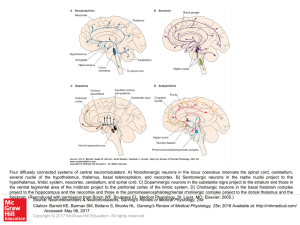
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
GAIT AND LOCOMOTION
... the travel path or is constrained to place its paws on a specific location (such as rungs of a ladder) the intensity (but not the phase) of the activity in the corticospinal tract increases dramatically (Bronstein et al 2003) ...
... the travel path or is constrained to place its paws on a specific location (such as rungs of a ladder) the intensity (but not the phase) of the activity in the corticospinal tract increases dramatically (Bronstein et al 2003) ...
An octopaminergic system in the CNS of the snails, Lymnaea
... the neuronal transmission. However, the synaptic connections formed by either OC neurons or N3p interneurons are not identical, as they make different synaptic connections with both motoneurons (B3) and feeding interneurons (N2). CGC: The cerebral, serotonergic CGC neurons excite the OC cells, but t ...
... the neuronal transmission. However, the synaptic connections formed by either OC neurons or N3p interneurons are not identical, as they make different synaptic connections with both motoneurons (B3) and feeding interneurons (N2). CGC: The cerebral, serotonergic CGC neurons excite the OC cells, but t ...
Modeling Synaptic Plasticity
... change, as a function of the history of the activity of these two neurons. Many experiments have documented the phenomenology of synaptic plasticity in the last four decades, but the precise ‘learning rule’ used by synapses and the mechanisms of plasticity still elude us. In this talk, I will first ...
... change, as a function of the history of the activity of these two neurons. Many experiments have documented the phenomenology of synaptic plasticity in the last four decades, but the precise ‘learning rule’ used by synapses and the mechanisms of plasticity still elude us. In this talk, I will first ...
Human Biology Human Body Systems Nervous System
... Relay information from sensory neurons to motor neurons . Motor Neuron Stimulate muscles or glands in effector organs to cause a response. ...
... Relay information from sensory neurons to motor neurons . Motor Neuron Stimulate muscles or glands in effector organs to cause a response. ...