Psychology 300 Instructor: Sylvia S. Spencer Ph.D. TEST 1 REVIEW
... 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What structures are located in the Brain Stem and what are their functions? 13. What could result if each of these structures were af ...
... 10. What is an EEG, PET, and MRI and the differences in procedures and purpose. 11. The sequence of brain regions from the evolutionarily oldest to the newest is? 12. What structures are located in the Brain Stem and what are their functions? 13. What could result if each of these structures were af ...
Evolution and analysis of minimal neural circuits for klinotaxis in
... Spatial orientation is one of the most fundamental adaptive behaviors in motile organisms. C. elegans performs a diverse set of orientation behaviors, including chemotaxis to tastants, odors, osmolarity, electrotaxis, thermotaxis, etc. Nearly all work on C. elegans chemotaxis was based on klinokines ...
... Spatial orientation is one of the most fundamental adaptive behaviors in motile organisms. C. elegans performs a diverse set of orientation behaviors, including chemotaxis to tastants, odors, osmolarity, electrotaxis, thermotaxis, etc. Nearly all work on C. elegans chemotaxis was based on klinokines ...
cogsci200
... Each region encompasses a cortical surface area of roughly 2 mm2 and possesses a total of about 200,000 neurons. ...
... Each region encompasses a cortical surface area of roughly 2 mm2 and possesses a total of about 200,000 neurons. ...
Reflexes
... -receptors are specialized muscle cells embedded within whole muscles: intrafusal muscle fibers -sensory neurons monitor the degree (type Ia fibers and type II fibers) and rate of stretch (type Ia fibers) of the intrafusal muscle fibers -the whole production (receptor cells and sensory neuron ending ...
... -receptors are specialized muscle cells embedded within whole muscles: intrafusal muscle fibers -sensory neurons monitor the degree (type Ia fibers and type II fibers) and rate of stretch (type Ia fibers) of the intrafusal muscle fibers -the whole production (receptor cells and sensory neuron ending ...
Chapter 8 - Nervous Pre-Test
... 14. Below are given the steps of the patellar reflex arc. What is the correct order of events from the time the hammer taps the patellar ligament to the knee jerk response? 1) The leg extends at the knee. 2) Sensory neurons conduct the action potentials to the spinal cord. 3) Motor neurons are stim ...
... 14. Below are given the steps of the patellar reflex arc. What is the correct order of events from the time the hammer taps the patellar ligament to the knee jerk response? 1) The leg extends at the knee. 2) Sensory neurons conduct the action potentials to the spinal cord. 3) Motor neurons are stim ...
Nervous System Period 7 - Mercer Island School District
... Function of Central and Peripheral Systems ● integrating sensory information and responding accordingly ● The spinal cord serves as a conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body ● cells that detect information like smell and vision, exclusively motor cells, like the eyeballs and ...
... Function of Central and Peripheral Systems ● integrating sensory information and responding accordingly ● The spinal cord serves as a conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body ● cells that detect information like smell and vision, exclusively motor cells, like the eyeballs and ...
Neurology - wsscience
... a neurotransmitter Transient hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane Repolarization produced by the addition of multiple stimul Reflection of the activation of an opposing transmembrane potential ...
... a neurotransmitter Transient hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane Repolarization produced by the addition of multiple stimul Reflection of the activation of an opposing transmembrane potential ...
Nervous System
... cerebrospinal fluid Adequate blood supply is needed, brain tissue will die in 4-8 min. without O2 Divided into 4 major parts: cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, brain stem ...
... cerebrospinal fluid Adequate blood supply is needed, brain tissue will die in 4-8 min. without O2 Divided into 4 major parts: cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, brain stem ...
Action Potentials
... • Sensory (afferent) neurons – _________________________ _________________________ – Transmit info to brain/spinal cord • ___________________________ – In between sensory and motor pathways in CNS – 90% of neurons are interneurons – _________________________ _________________________ • _____________ ...
... • Sensory (afferent) neurons – _________________________ _________________________ – Transmit info to brain/spinal cord • ___________________________ – In between sensory and motor pathways in CNS – 90% of neurons are interneurons – _________________________ _________________________ • _____________ ...
Slide ()
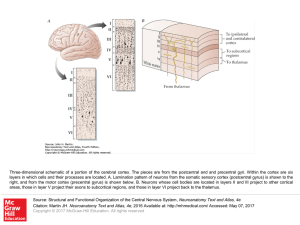
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
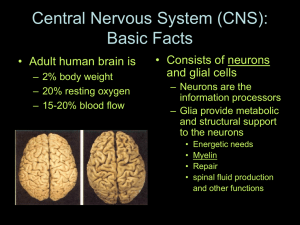
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
... Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
... Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
• Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to It releases
... movement. An impulse begins when one neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the sense organs. • The impulse travels down the axons of Sensory neurons to the brain cells called ...
... movement. An impulse begins when one neuron is stimulated by another neuron or by the sense organs. • The impulse travels down the axons of Sensory neurons to the brain cells called ...
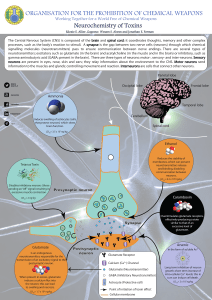
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
Chapter 2, section 2
... Identify the brain part: • Connects to your spinal cord • Controls involuntary processes: body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure ...
... Identify the brain part: • Connects to your spinal cord • Controls involuntary processes: body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure ...
The effects of electrical microstimulation on cortical signal propagation
... • The correspondence between the actual and predicted hand position decreased in sessions BCWH (Wilcoxon signed-rank test). • The R for X-position decreased 28.1% and 17.2% in Monkey 2. The R for Yposition decreased 16.7% and 15.6% in Monkeys 1 and 2, respectively. • This decrease indicates that the ...
... • The correspondence between the actual and predicted hand position decreased in sessions BCWH (Wilcoxon signed-rank test). • The R for X-position decreased 28.1% and 17.2% in Monkey 2. The R for Yposition decreased 16.7% and 15.6% in Monkeys 1 and 2, respectively. • This decrease indicates that the ...
document
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
Lecture ppt 1 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... • White matter surrounds gray matter (white: ascending and descending tracts of axons) • “H” shaped on cross section • Dorsal half of “H”: cell bodies of interneurons • Ventral half of “H”: cell bodies of motor neurons • No cortex ...
... • White matter surrounds gray matter (white: ascending and descending tracts of axons) • “H” shaped on cross section • Dorsal half of “H”: cell bodies of interneurons • Ventral half of “H”: cell bodies of motor neurons • No cortex ...
1-nervous_system
... Major functions of the nervous system-the 3 C’s Control Communicate Coordinate Receive stimuli Process information and decide output Direct response ...
... Major functions of the nervous system-the 3 C’s Control Communicate Coordinate Receive stimuli Process information and decide output Direct response ...
Activity of Spiking Neurons Stimulated by External Signals of
... Spiking neuron systems gained increasing interest in recent years because they represent spatio-temporal relations within simulated systems, unlike the spatial simple neuron models found in artificial neural systems. They are also closer to biophysical models of neurons, synapses, and related elemen ...
... Spiking neuron systems gained increasing interest in recent years because they represent spatio-temporal relations within simulated systems, unlike the spatial simple neuron models found in artificial neural systems. They are also closer to biophysical models of neurons, synapses, and related elemen ...
The Scientific Method - Northwest ISD Moodle
... The Scientific Method and Neurobiology Chapter 1: (and the Introduction) Background terms from the book intro: ...
... The Scientific Method and Neurobiology Chapter 1: (and the Introduction) Background terms from the book intro: ...
Review Sheet 1 scientific method and neurobiology
... The Scientific Method and Neurobiology Chapter 1: (and the Introduction) Background terms from the book intro: ...
... The Scientific Method and Neurobiology Chapter 1: (and the Introduction) Background terms from the book intro: ...
sensory overload - Saint Michael`s College
... with an almost empty fuel tank and no oil at full speed. The engine will eventually stop working; so do neurons. The only difference is that we can fix car engines, but usually not the central nervous system.” What we don’t see, but experience in the form of various brain disorders, is that during o ...
... with an almost empty fuel tank and no oil at full speed. The engine will eventually stop working; so do neurons. The only difference is that we can fix car engines, but usually not the central nervous system.” What we don’t see, but experience in the form of various brain disorders, is that during o ...