Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by
... Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by the nervous system Functions Communication between distant parts of the body Collection and integration of stimuli (both internal and external Formation and initiation of appropriate response Responsible for very rapid responses ...
... Chapter 7 Nervous System Every conscious action is governed by the nervous system Functions Communication between distant parts of the body Collection and integration of stimuli (both internal and external Formation and initiation of appropriate response Responsible for very rapid responses ...
Slide 1
... Network (FFNN) is sufficient for realizing a broad class of input/output non-linear maps (Kolmogorov’s theorem) Disadvantages: • number of neurons in the hidden layer cannot be determined • number of neurons can be large implying expensive calculation Fainan May 2006 ...
... Network (FFNN) is sufficient for realizing a broad class of input/output non-linear maps (Kolmogorov’s theorem) Disadvantages: • number of neurons in the hidden layer cannot be determined • number of neurons can be large implying expensive calculation Fainan May 2006 ...
Reflex Arc - Cloudfront.net
... Talking Only… Which position on the soccer field do you THINK having a fast reaction time would be the greatest advantage? forward/striker, midfield, defense, goal keeper Reaction Time Drills for a Goal Keeper ...
... Talking Only… Which position on the soccer field do you THINK having a fast reaction time would be the greatest advantage? forward/striker, midfield, defense, goal keeper Reaction Time Drills for a Goal Keeper ...
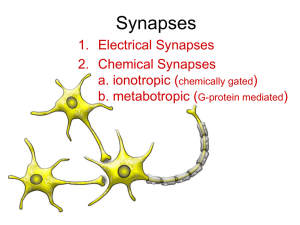
Synapses - Franklin College
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
107B exam 1 test yourself
... 2. ocular dominance columns (projects to layer ______ of V1) 3. orientation tuning map (projects to layer ______ of V1) 4. koniocellular input (to layers ______ of V1) Organized in horizontal space of cortex and vertical space (cortical column) maps 1, 2, 3 project from layer 4 to layer 2-3 where mi ...
... 2. ocular dominance columns (projects to layer ______ of V1) 3. orientation tuning map (projects to layer ______ of V1) 4. koniocellular input (to layers ______ of V1) Organized in horizontal space of cortex and vertical space (cortical column) maps 1, 2, 3 project from layer 4 to layer 2-3 where mi ...
Point Process Filters Applied to the Analysis of Spiking Neural Systems
... properties of cortical neurons in the hippocampus and deep entorhinal cortex of a rat. Using a spatio-temporal spline model, we were able to characterize and track changes in the firing properties of these neurons. The second estimation problem involves predicting an intended reaching arm movement f ...
... properties of cortical neurons in the hippocampus and deep entorhinal cortex of a rat. Using a spatio-temporal spline model, we were able to characterize and track changes in the firing properties of these neurons. The second estimation problem involves predicting an intended reaching arm movement f ...
7-4_DescendingPathways_HubaT
... 3.b We can separate three types of descending pathways, the pyramid tract, extrapyramidal tract and vegetative tract. The pyramid tracts emerge from the cerebral cortex, and most of them crossing-over in the medulla, and continue it’s way to the anterior horn of the spinal cord, where they make syna ...
... 3.b We can separate three types of descending pathways, the pyramid tract, extrapyramidal tract and vegetative tract. The pyramid tracts emerge from the cerebral cortex, and most of them crossing-over in the medulla, and continue it’s way to the anterior horn of the spinal cord, where they make syna ...
CHANGES OF THE CELL BODY OF NEURONS IN CENTRAL
... structural changes (staining of histological specimens of toluidine blue) and behavioral reactions (open field test). In morphological investigations we observed structurally modified neurons in the gray matter of the cerebrum, cerebellum and the spinal cord of all experimental groups of mice, but i ...
... structural changes (staining of histological specimens of toluidine blue) and behavioral reactions (open field test). In morphological investigations we observed structurally modified neurons in the gray matter of the cerebrum, cerebellum and the spinal cord of all experimental groups of mice, but i ...
CHAPTER 7 Nervous system Notes
... matter of the brainstem and sacral segments of the spinal cord. Function: dominates control of many visceral effectors under normal everyday conditions (bladder, intestines, lung) ...
... matter of the brainstem and sacral segments of the spinal cord. Function: dominates control of many visceral effectors under normal everyday conditions (bladder, intestines, lung) ...
Cognitive Psychology
... neurons behave. Use these models to try and better understand cognitive processing in the brain. ...
... neurons behave. Use these models to try and better understand cognitive processing in the brain. ...
Central Nervous System - Home Page of Ken Jones
... Motor areas involved with the control • Frontal of voluntary muscles (moves to itch • Parietal toe) • Temporal • Occipital Motor speech area (Broca’s • Insula area) Occipital lobe, vision from retina ...
... Motor areas involved with the control • Frontal of voluntary muscles (moves to itch • Parietal toe) • Temporal • Occipital Motor speech area (Broca’s • Insula area) Occipital lobe, vision from retina ...
Guided Notes for the Nervous System-
... system from sensory receptors located in various parts of the body. The motor, or efferent, division carries impulses from the CNS to effector organs, the muscles and glands. ...
... system from sensory receptors located in various parts of the body. The motor, or efferent, division carries impulses from the CNS to effector organs, the muscles and glands. ...
Supporting Information S1.
... MEA recording system with an inter-node spacing of 200 m. Consequently, here we show that neurites can extend significantly from the soma over multiple nodes, up to 800 m (4 nodes). (Right) The same culture was counterstained with an antibody against βTubIII to show the whole network development. ...
... MEA recording system with an inter-node spacing of 200 m. Consequently, here we show that neurites can extend significantly from the soma over multiple nodes, up to 800 m (4 nodes). (Right) The same culture was counterstained with an antibody against βTubIII to show the whole network development. ...
Behavioral Neuroscience: The NeuroPsychological approach
... Together with John Langley, supported the “localization of function” theory for the brain. Mapped dorsal and ventral roots; opposing muscles, reciprocal innervations. “reflexes are the simplest expressions of the interactive action of the nervous system” ...
... Together with John Langley, supported the “localization of function” theory for the brain. Mapped dorsal and ventral roots; opposing muscles, reciprocal innervations. “reflexes are the simplest expressions of the interactive action of the nervous system” ...
Nervous System PPT - Effingham County Schools
... Most common disease of the nervous system Loss of myelin sheath ...
... Most common disease of the nervous system Loss of myelin sheath ...
Document
... Networks in the brain stem of vertebrates responsible for maintaining eye position appear to act as integrators. Eye position changes in response to bursts of ocular motor neurons in brain stem. Neurons in the brainstem integrate these signals. Their activity is approximately proportional to horizon ...
... Networks in the brain stem of vertebrates responsible for maintaining eye position appear to act as integrators. Eye position changes in response to bursts of ocular motor neurons in brain stem. Neurons in the brainstem integrate these signals. Their activity is approximately proportional to horizon ...
sheets DA 7
... Networks in the brain stem of vertebrates responsible for maintaining eye position appear to act as integrators. Eye position changes in response to bursts of ocular motor neurons in brain stem. Neurons in the brainstem integrate these signals. Their activity is approximately proportional to horizon ...
... Networks in the brain stem of vertebrates responsible for maintaining eye position appear to act as integrators. Eye position changes in response to bursts of ocular motor neurons in brain stem. Neurons in the brainstem integrate these signals. Their activity is approximately proportional to horizon ...
The Nervous System
... 2. Motor neurons: stimulate muscle cells throughout the body includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder ...
... 2. Motor neurons: stimulate muscle cells throughout the body includes muscles of the heart, diaphragm, intestines, and bladder ...