Print this Page Presentation Abstract Program#/Poster#: 532.07/GG10
... Presentation Title: How SOM+ and PV+ inhibitory neurons could differentially modulate surround suppression of cortical neurons Location: ...
... Presentation Title: How SOM+ and PV+ inhibitory neurons could differentially modulate surround suppression of cortical neurons Location: ...
PPt #2 Human Body Nervous system
... • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and their functions. • 5. I can explain how the nervous system passes information between the external environment and the many parts of the body. ...
... • 4. I can identify and explain different areas of the brain and their functions. • 5. I can explain how the nervous system passes information between the external environment and the many parts of the body. ...
NEURAL REGULATION OF BREATHING Section 4, Part A
... Section 4, Part A NEUROGENESIS OF BREATHING I. Medullary Respiratory Center A. Medulla isolated from cranial nerves and higher centers can drive respiratory muscles 1. rhythm appears "ataxic" B. Integration of neural centers 1. nucleus of the tractus solitarus (NTS) or dorsal resp. group a. appears ...
... Section 4, Part A NEUROGENESIS OF BREATHING I. Medullary Respiratory Center A. Medulla isolated from cranial nerves and higher centers can drive respiratory muscles 1. rhythm appears "ataxic" B. Integration of neural centers 1. nucleus of the tractus solitarus (NTS) or dorsal resp. group a. appears ...
Technical Definitions
... This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a certain threshold potential, the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a ...
... This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a certain threshold potential, the neuron will fire. A stimulus that substantially exceeds the threshold potential does not generate a ...
Study Guide Solutions - Elsevier: Baars and Gage
... Glutamate, the most common neurotransmitter in the brain, is known to be excitatory. GABA (gamma-amino butyric acid) is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter. 4. What role do artificial neural nets (ANNs) play in understanding how the brain works? (Give some examples). See Section 4.0. A neura ...
... Glutamate, the most common neurotransmitter in the brain, is known to be excitatory. GABA (gamma-amino butyric acid) is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter. 4. What role do artificial neural nets (ANNs) play in understanding how the brain works? (Give some examples). See Section 4.0. A neura ...
Slide ()
... B. The neural plate folds dorsally at its midline to form the neural fold. Floor plate cells (blue) differentiate at the ventral midline of the neural tube. C. The neural tube forms by fusion of the dorsal tips of the neural folds. Roof plate cells form at the dorsal midline of the neural tube. Neur ...
... B. The neural plate folds dorsally at its midline to form the neural fold. Floor plate cells (blue) differentiate at the ventral midline of the neural tube. C. The neural tube forms by fusion of the dorsal tips of the neural folds. Roof plate cells form at the dorsal midline of the neural tube. Neur ...
Somatic Sensory System
... • Fingertips have highest resolution – Due to high density of mechanoreceptors – Receptor subtypes with small receptive fields – More cortical neurons dedicated to deciphering sensory information ...
... • Fingertips have highest resolution – Due to high density of mechanoreceptors – Receptor subtypes with small receptive fields – More cortical neurons dedicated to deciphering sensory information ...
Capacity Analysis of Attractor Neural Networks with Binary Neurons and Discrete Synapses
... ABSTRACT Inspired by the delay activity observed in numerous delayed match-to-sample (DMS) experiments, the attractor states of neural network dynamics are considered to be the underlying mechanism of memory storage in neural networks. For the simplest network with binary neurons and standard asynch ...
... ABSTRACT Inspired by the delay activity observed in numerous delayed match-to-sample (DMS) experiments, the attractor states of neural network dynamics are considered to be the underlying mechanism of memory storage in neural networks. For the simplest network with binary neurons and standard asynch ...
Chapter 3: The nerve cell Multiple Choice Questions (1
... comprised of mostly two-way connections that aid in resolving ambiguous inputs comprised of mostly one-way connections in order to produce temporal encoding of sensory features ...
... comprised of mostly two-way connections that aid in resolving ambiguous inputs comprised of mostly one-way connections in order to produce temporal encoding of sensory features ...
Nervous System - Lemon Bay High School
... Protection of the CNS • Blood-brain barrier – What is It? A tight network of capillary beds that are both SELECTIVE - Keeps some things out and other allows other things in. DIRECTIONAL - Moves INTO the brain not OUT OF the brain – How Does it Work? Acts as a successively smaller filters to keep su ...
... Protection of the CNS • Blood-brain barrier – What is It? A tight network of capillary beds that are both SELECTIVE - Keeps some things out and other allows other things in. DIRECTIONAL - Moves INTO the brain not OUT OF the brain – How Does it Work? Acts as a successively smaller filters to keep su ...
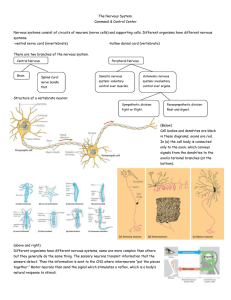
SBI4U Nervous System
... – Sensory neurons (aka afferent neurons): relay info from the environment to CNS. – Interneurons: link neurons, located in the brain and spinal cord usually; short length – Motor neurons (aka efferent neurons): relay information to the effectors which produce responses. ...
... – Sensory neurons (aka afferent neurons): relay info from the environment to CNS. – Interneurons: link neurons, located in the brain and spinal cord usually; short length – Motor neurons (aka efferent neurons): relay information to the effectors which produce responses. ...
nervesendocrine ppttwo
... spinal cord not the brain. Reflexes protect the body before the brain knows what is going on. ...
... spinal cord not the brain. Reflexes protect the body before the brain knows what is going on. ...
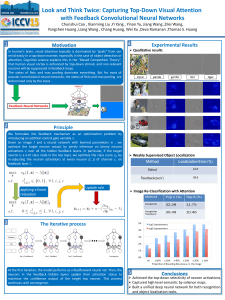
feedback-poster
... attention. Cognitive science explains this in the “Biased Competition Theory”, that human visual cortex is enhanced by top-down stimuli, and non-relevant neurons will be suppressed in feedback loops. The states of Relu and max pooling dominate everything. But for most of popular convolutional neural ...
... attention. Cognitive science explains this in the “Biased Competition Theory”, that human visual cortex is enhanced by top-down stimuli, and non-relevant neurons will be suppressed in feedback loops. The states of Relu and max pooling dominate everything. But for most of popular convolutional neural ...
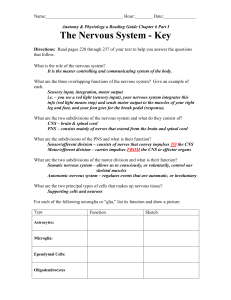
E1 – Stimulus and response - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... E.1.2 Explain the role of receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, senso ...
... E.1.2 Explain the role of receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, senso ...
File
... to, make sure to read this section so you have a better understanding of its parts and its responsibilities. What does MS stand for and what is it? Multiple sclerosis – this is an autoimmune disease where the myelin sheaths around the fibers are gradually destroyed and converted to hardened sheaths ...
... to, make sure to read this section so you have a better understanding of its parts and its responsibilities. What does MS stand for and what is it? Multiple sclerosis – this is an autoimmune disease where the myelin sheaths around the fibers are gradually destroyed and converted to hardened sheaths ...
Vocab: Unit 3 Handout made by: Jessica Jones and Hanna Cho
... Glial Cells: (glia) cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons, they may also play a role in learning and thinking Temporal lobes: lies roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information from the opposite ear. Motor cortex: an area at the rear ...
... Glial Cells: (glia) cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons, they may also play a role in learning and thinking Temporal lobes: lies roughly above the ears; includes the auditory areas, each receiving information from the opposite ear. Motor cortex: an area at the rear ...