Chapter 7 1. ______ is a selectively permeable
... fatty acid tails of the phospholipid. __________ fatty acids will keep membrane more fluid while ______________ fatty acid tails will make them more viscous. ____________ will also help with stability. 5. Short carbohydrates bound to lipids are called ____________ while short carbohydrates bound to ...
... fatty acid tails of the phospholipid. __________ fatty acids will keep membrane more fluid while ______________ fatty acid tails will make them more viscous. ____________ will also help with stability. 5. Short carbohydrates bound to lipids are called ____________ while short carbohydrates bound to ...
Unit 3 Resources
... (5) ________________________ . It allows different cells to carry on different activities within the ...
... (5) ________________________ . It allows different cells to carry on different activities within the ...
The Cell Membrane
... • Steroids are a component of cell membranes in the form of cholesterol. • When present they add stability, but restrict movement of the phospholipids. • Even though high levels can clog arteries, cholesterol is crucial to the membrane stability. ...
... • Steroids are a component of cell membranes in the form of cholesterol. • When present they add stability, but restrict movement of the phospholipids. • Even though high levels can clog arteries, cholesterol is crucial to the membrane stability. ...
Huisman and Bisseling.
... membrane is driven by complex formation of the SNARE proteins. A v-SNARE component present on vesicles forms a complex with two or three t-SNAREs on the appropriate target membrane, which provides the energy to fuse the membranes. To control vesicle fusion, t-SNAREs cycle between open and closed con ...
... membrane is driven by complex formation of the SNARE proteins. A v-SNARE component present on vesicles forms a complex with two or three t-SNAREs on the appropriate target membrane, which provides the energy to fuse the membranes. To control vesicle fusion, t-SNAREs cycle between open and closed con ...
Summary
... with an -helix •Some membrane pore proteins use a ß-barrel structure •Membrane proteins can associate in “rafts” stabilized by sterols and sphingolipids •Hydrophilic molecules, including ions, cross membranes through channels and pumps •Nerve function (and other functions) depend on control of ...
... with an -helix •Some membrane pore proteins use a ß-barrel structure •Membrane proteins can associate in “rafts” stabilized by sterols and sphingolipids •Hydrophilic molecules, including ions, cross membranes through channels and pumps •Nerve function (and other functions) depend on control of ...
Plasma Membrane: Structure and Function
... phospholipid. Phospholipids are amphipathic. Write down what that means. ...
... phospholipid. Phospholipids are amphipathic. Write down what that means. ...
Section 3.2 – Moving Cellular Materials Selectively Permeable
... Section 3.2 – Moving Cellular Materials ...
... Section 3.2 – Moving Cellular Materials ...
Nanoparticle Biointerfacing via Cell Membrane Cloaking for
... promises novel treatment modalities with biomimetic functionalities. Herein I report a nanoparticle functionalization strategy that cloaks particles with natural cellular membranes derived from several cellular targets. Refinement of the technique has enabled cell membranes to conform over nanoparti ...
... promises novel treatment modalities with biomimetic functionalities. Herein I report a nanoparticle functionalization strategy that cloaks particles with natural cellular membranes derived from several cellular targets. Refinement of the technique has enabled cell membranes to conform over nanoparti ...
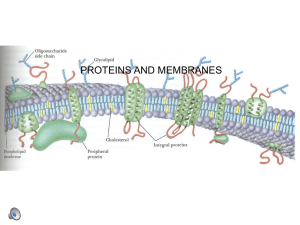
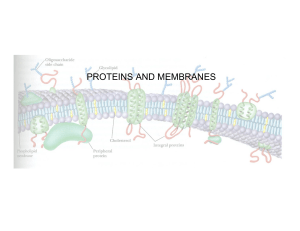
PROTEINS AND MEMBRANES
... with an α-helix •Some membrane pore proteins use a ß-barrel structure •Membrane proteins can associate in “rafts” stabilized by sterols and sphingolipids •Hydrophilic molecules, including ions, cross membranes through channels and pumps •Nerve function (and other functions) depend on control of ...
... with an α-helix •Some membrane pore proteins use a ß-barrel structure •Membrane proteins can associate in “rafts” stabilized by sterols and sphingolipids •Hydrophilic molecules, including ions, cross membranes through channels and pumps •Nerve function (and other functions) depend on control of ...
Slide 1
... Integral - firmly anchored into the membrane by hydrophobic interactions with the hydrophobic portion of the bilayer. Transmembrane proteins - extend through membrane Lipid anchored proteins - have covalently attached lipid molecules that anchor the protein into the bilayer Peripheral - attached to ...
... Integral - firmly anchored into the membrane by hydrophobic interactions with the hydrophobic portion of the bilayer. Transmembrane proteins - extend through membrane Lipid anchored proteins - have covalently attached lipid molecules that anchor the protein into the bilayer Peripheral - attached to ...
Printing – LAB Organic Molecule – Lipid
... 3. Membranes come in various shapes depending on function and have proteins embedded in them to facilitate other molecules to pass through them. 4. Lipids are made up of closely related polar monomers called phospholipids that form a Lipid Bilayer. a. Phospholipids have Hydrophilic heads. b. Phospho ...
... 3. Membranes come in various shapes depending on function and have proteins embedded in them to facilitate other molecules to pass through them. 4. Lipids are made up of closely related polar monomers called phospholipids that form a Lipid Bilayer. a. Phospholipids have Hydrophilic heads. b. Phospho ...
Membrane Structure and Function
... 50 to 200 mV (minus sign = inside of cell is neg.) this favors passive transport of cations into the cell and anions out of the cell so: chemical force due to ion concentration gradient electrical force affects movement of ion due to membrane ...
... 50 to 200 mV (minus sign = inside of cell is neg.) this favors passive transport of cations into the cell and anions out of the cell so: chemical force due to ion concentration gradient electrical force affects movement of ion due to membrane ...
4.7-4.16
... -the golgi receives vesicles from the ER and chemically modifies them -some chemical modifications are used to mark and sort proteins for export out of the cell -one function of the shipping portion of the golgi is to package a finished protein into a vesicle to move to the plasma membrane so it ca ...
... -the golgi receives vesicles from the ER and chemically modifies them -some chemical modifications are used to mark and sort proteins for export out of the cell -one function of the shipping portion of the golgi is to package a finished protein into a vesicle to move to the plasma membrane so it ca ...
module 2 2.1.5 biological membranes student version
... Factors which increase Factors which decrease fluidity of the membrane fluidity of the membrane ...
... Factors which increase Factors which decrease fluidity of the membrane fluidity of the membrane ...
Document
... 3. Energetics of Bilayer Insertion. This last step in folding is the crucial one, but the least adequately studied because of the insolubility and aggregation of hydrophobic peptides. Direct measurement of the partitioning of a hydrophobic alpha-helix or beta-barrel across a membrane is absolutely ...
... 3. Energetics of Bilayer Insertion. This last step in folding is the crucial one, but the least adequately studied because of the insolubility and aggregation of hydrophobic peptides. Direct measurement of the partitioning of a hydrophobic alpha-helix or beta-barrel across a membrane is absolutely ...
CELLS QQ#2 (TOC#4) HW: CELLS Notes (TOC#5)
... Information center of cell Spherical shape Largest organelle, readily visible Centrally located Positioned by filaments ...
... Information center of cell Spherical shape Largest organelle, readily visible Centrally located Positioned by filaments ...
Name____________________________________________
... The diagram below shows which areas on the surface of a protein are composed of hydrophobic amino acids and which areas of hydrophilic amino acids. ...
... The diagram below shows which areas on the surface of a protein are composed of hydrophobic amino acids and which areas of hydrophilic amino acids. ...
LEARNING GOALS - Cell Membranes
... b. Active transport requires free energy to move molecules from regions of low concentration to regions of high concentration. ...
... b. Active transport requires free energy to move molecules from regions of low concentration to regions of high concentration. ...
Lh6Ch11aMembranes
... – The function of biological membranes – The structure and composition membranes and their molecules – Dynamics of membranes – Structure and function of membrane proteins – Transport across biological membranes ...
... – The function of biological membranes – The structure and composition membranes and their molecules – Dynamics of membranes – Structure and function of membrane proteins – Transport across biological membranes ...
SNARE (protein)

SNARE proteins (an acronym derived from ""SNAP (Soluble NSF Attachment Protein) REceptor"") are a large protein superfamily consisting of more than 60 members in yeast and mammalian cells. The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate vesicle fusion, that is, the fusion of vesicles with their target membrane bound compartments (such as a lysosome). The best studied SNAREs are those that mediate docking of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane in neurons. These SNAREs are the targets of the bacterial neurotoxins responsible for botulism and tetanus.