Active Transport Across the Cell Membrane
... Active Transport Across the Cell Membrane Active transport is the movement of solutes against a gradient andrequires the expenditure of energy, usually in the form of ATP. Active transport is achieved through one of these two mechanisms: Protein Pumps • Transport proteins in the plasma membrane tran ...
... Active Transport Across the Cell Membrane Active transport is the movement of solutes against a gradient andrequires the expenditure of energy, usually in the form of ATP. Active transport is achieved through one of these two mechanisms: Protein Pumps • Transport proteins in the plasma membrane tran ...
Notes 9 The Cell Membrane Questions and Vocabulary
... 1. What is the cell membrane? What is it primarily composed of? 2. Besides the outer layer of the cell, where else do we find membrane? 3. Describe three functions of the cell membrane. 4. Is the membrane soluble or insoluble in water? Explain. 5. What is the primary type of lipid found in the membr ...
... 1. What is the cell membrane? What is it primarily composed of? 2. Besides the outer layer of the cell, where else do we find membrane? 3. Describe three functions of the cell membrane. 4. Is the membrane soluble or insoluble in water? Explain. 5. What is the primary type of lipid found in the membr ...
Membrane Structure & Function
... i = ionization constant (For sucrose this is 1.0 because sucrose does not ionize in water.) ...
... i = ionization constant (For sucrose this is 1.0 because sucrose does not ionize in water.) ...
Membranes and transport - part 1
... Need a way to allow their hydrophobic regions to contact each other and their hydrophilic regions to interact with surrounding water ...
... Need a way to allow their hydrophobic regions to contact each other and their hydrophilic regions to interact with surrounding water ...
Biological Membranes and Transport
... Need a way to allow their hydrophobic regions to contact each other and their hydrophilic regions to interact with surrounding water ...
... Need a way to allow their hydrophobic regions to contact each other and their hydrophilic regions to interact with surrounding water ...
Mark scheme - Biology for Life
... microvilli increase the surface of the plasma membrane exposed to the digested food; increased surface area allows for increased absorption of foods (by diffusion); lipids are absorbed by simple diffusion; hydrophilic food substances / eg fructose are absorbed by facilitated diffusion; channel prote ...
... microvilli increase the surface of the plasma membrane exposed to the digested food; increased surface area allows for increased absorption of foods (by diffusion); lipids are absorbed by simple diffusion; hydrophilic food substances / eg fructose are absorbed by facilitated diffusion; channel prote ...
Biological membranes: the basics and why they are
... and waste products (channels) • Acquired the ability to achieve these functions against a concentration gradient (transporters) • Later developments: conversion of membrane potential to do work; signalling from outside to inside; cell recognition; movement of molecules in eukaryotic vesicles; compar ...
... and waste products (channels) • Acquired the ability to achieve these functions against a concentration gradient (transporters) • Later developments: conversion of membrane potential to do work; signalling from outside to inside; cell recognition; movement of molecules in eukaryotic vesicles; compar ...
Active Transport
... Moving molecules against their concentration gradient is known as Active Transport. Energy is required because molecules are being pumped against their concentration gradient Proteins that work as pumps are called protein pumps. These protein pumps are membrane bound receptors. ...
... Moving molecules against their concentration gradient is known as Active Transport. Energy is required because molecules are being pumped against their concentration gradient Proteins that work as pumps are called protein pumps. These protein pumps are membrane bound receptors. ...
PowerPoint
... Like other membranes, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable, allowing some substances to cross more easily than others. The main macromolecules in membranes are lipids and proteins, but include some carbohydrates. ...
... Like other membranes, the plasma membrane is selectively permeable, allowing some substances to cross more easily than others. The main macromolecules in membranes are lipids and proteins, but include some carbohydrates. ...
Slide ()
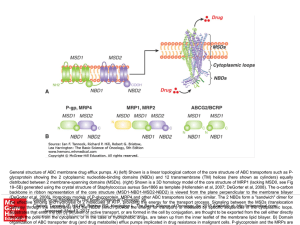
... Source: Drug Resistance, The Basic Science of Oncology, 5e the effective binding and hydrolysis of 2 molecules of ATP, providing the energy for the transport process. Signaling between the MSDs (translocation Citation: IF, Hill RG, Harrington L. The Basicfor Science of Oncology, 5e; by ...
... Source: Drug Resistance, The Basic Science of Oncology, 5e the effective binding and hydrolysis of 2 molecules of ATP, providing the energy for the transport process. Signaling between the MSDs (translocation Citation: IF, Hill RG, Harrington L. The Basicfor Science of Oncology, 5e; by ...
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... ! Empty carrier shifts to return binding site to original side of membrane. ...
... ! Empty carrier shifts to return binding site to original side of membrane. ...
Bacterial Cell Walls Contain Peptidoglycans
... • Some are partially dependent • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features ...
... • Some are partially dependent • Others are not dependent on glycans • Some are glycan-dependent in one cell type but not in another • Some glycosylation sites are more important than others – Aid in certain sorting events • In later secretory pathway of glycoproteins in Golgi – Structural features ...
Peripheral Membrane Interactions Boost the Engagement by an Anti
... immunotherapeutics. In this regard, the relevance of auto-reactivity with membrane lipids for the biological function and development of this antibody is still subject of controversy. To address this issue, here we have compared membrane-partitioning capacities of the 4E10 antibody and several of it ...
... immunotherapeutics. In this regard, the relevance of auto-reactivity with membrane lipids for the biological function and development of this antibody is still subject of controversy. To address this issue, here we have compared membrane-partitioning capacities of the 4E10 antibody and several of it ...
5.1-5.9 Study Guide
... spontaneously assemble into simple membranes ○ a critical step of evolution is formation of a membrane that encloses collections of molecules necessary for life ...
... spontaneously assemble into simple membranes ○ a critical step of evolution is formation of a membrane that encloses collections of molecules necessary for life ...
chem 240 practice lipid problems 1. True or false? Completely
... 5. List those amino acids with side chains that can be covalently attached to a fatty acid through an ester link. The most common site of fatty acylation is through a thio-ester bond with Cys. You could also imagine ester linkages with other amino acids that contain a reactive O-. 6. What property o ...
... 5. List those amino acids with side chains that can be covalently attached to a fatty acid through an ester link. The most common site of fatty acylation is through a thio-ester bond with Cys. You could also imagine ester linkages with other amino acids that contain a reactive O-. 6. What property o ...
Diffusion - Union High School
... in the membrane that act like pumps. • Many cells use protein pumps to move calcium, potassium, and sodium ions across cell membranes. ...
... in the membrane that act like pumps. • Many cells use protein pumps to move calcium, potassium, and sodium ions across cell membranes. ...
The Endomembrane System
... 2 faces: inner (directed towards ER) & outer (directed towards plasma membrane). Receives protein-filled vesicles that bud from rER & lipid-filled vesicles from sER; sorts & packages pr. & lip ...
... 2 faces: inner (directed towards ER) & outer (directed towards plasma membrane). Receives protein-filled vesicles that bud from rER & lipid-filled vesicles from sER; sorts & packages pr. & lip ...
AP Biology - Membrane Structure
... Animal cells need isotonic environment If not, cells must adapt for ...
... Animal cells need isotonic environment If not, cells must adapt for ...
SNARE (protein)

SNARE proteins (an acronym derived from ""SNAP (Soluble NSF Attachment Protein) REceptor"") are a large protein superfamily consisting of more than 60 members in yeast and mammalian cells. The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate vesicle fusion, that is, the fusion of vesicles with their target membrane bound compartments (such as a lysosome). The best studied SNAREs are those that mediate docking of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane in neurons. These SNAREs are the targets of the bacterial neurotoxins responsible for botulism and tetanus.