The structure of components of a multi
... DeAngelis2, Cedric Bauvois2, Cedric Govaerts2, Jean-Marie Ruysschaert2, Guy Vandenbussche2 ...
... DeAngelis2, Cedric Bauvois2, Cedric Govaerts2, Jean-Marie Ruysschaert2, Guy Vandenbussche2 ...
Ch6 Cell homework
... e. Composed of 9 cylinders of microtubules ______________________ f. Sends secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane for exocytosis _____________ g. Site of chromosomes ______________________ h. Engages in autophagy ______________________ i. Site of cellular respiration/ATP production_______________ ...
... e. Composed of 9 cylinders of microtubules ______________________ f. Sends secretory vesicles to the plasma membrane for exocytosis _____________ g. Site of chromosomes ______________________ h. Engages in autophagy ______________________ i. Site of cellular respiration/ATP production_______________ ...
Membrane Transport notes
... into the cell 2. exocytosis – movement of materials out of the cell ...
... into the cell 2. exocytosis – movement of materials out of the cell ...
chapter 7 membranes
... actively transports H+ out of cell. By generating voltage across membranes, electrogenic pumps store energy that can be used for cellular work. o Membrane potential – voltage across a membrane, -50 -200 mv, voltage is electrical potential energy. Cytoplasm negative compared to extracellular fluid. M ...
... actively transports H+ out of cell. By generating voltage across membranes, electrogenic pumps store energy that can be used for cellular work. o Membrane potential – voltage across a membrane, -50 -200 mv, voltage is electrical potential energy. Cytoplasm negative compared to extracellular fluid. M ...
Chapter 7 Reading Guide
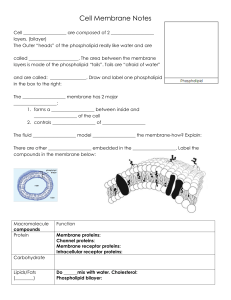
... Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why these molecules are amphipathic and how that enables them to form a lipid bilayer. ...
... Draw and label a single phospholipid molecule. Explain why these molecules are amphipathic and how that enables them to form a lipid bilayer. ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... Can you model it? Objective: Become familiar with the structure and function of the cell membrane. Use modeling clay to construct a 3D model of cell membrane structures. Use color and labels to distinguish key elements (20 pts. – 10 for model and 10 for diagram and questions) Materials: Colored mode ...
... Can you model it? Objective: Become familiar with the structure and function of the cell membrane. Use modeling clay to construct a 3D model of cell membrane structures. Use color and labels to distinguish key elements (20 pts. – 10 for model and 10 for diagram and questions) Materials: Colored mode ...
Biozentrum: Research group Martin Spiess
... mediate this. In particular, we study the pathways how proteins are transported to the cell surface and secreted. ...
... mediate this. In particular, we study the pathways how proteins are transported to the cell surface and secreted. ...
Interesting facts: • Many cells in the body use exocytosis to release
... off to form a vesicle; exocytosis forms them in order to expel things from the cell via the cell membrane and results in an increase in cell membrane, as the vesicle wall joins that of the cell membrane and is incorporated into it. Thus, the two processes also serve to balance each other. ...
... off to form a vesicle; exocytosis forms them in order to expel things from the cell via the cell membrane and results in an increase in cell membrane, as the vesicle wall joins that of the cell membrane and is incorporated into it. Thus, the two processes also serve to balance each other. ...
Slide ()
... Diagrammatic representation of the rough ER branch of protein sorting. Newly synthesized proteins are inserted into the ER membrane or lumen from membrane-bound polyribosomes (small black circles studding the cytosolic face of the ER). Proteins that are transported out of the ER are carried in COPII ...
... Diagrammatic representation of the rough ER branch of protein sorting. Newly synthesized proteins are inserted into the ER membrane or lumen from membrane-bound polyribosomes (small black circles studding the cytosolic face of the ER). Proteins that are transported out of the ER are carried in COPII ...
Slide ()
... Diagrammatic representation of the rough ER branch of protein sorting. Newly synthesized proteins are inserted into the ER membrane or lumen from membrane-bound polyribosomes (small black circles studding the cytosolic face of the ER). Proteins that are transported out of the ER are carried in COPII ...
... Diagrammatic representation of the rough ER branch of protein sorting. Newly synthesized proteins are inserted into the ER membrane or lumen from membrane-bound polyribosomes (small black circles studding the cytosolic face of the ER). Proteins that are transported out of the ER are carried in COPII ...
Q10 Describe transport mechanisms across cell membranes. Give
... ionic concentration differences of secondary molecular or ionic substances between the two sides of a cell membrane, created originally by primary active transport. Secondary active transport occurs via co-‐ transp ...
... ionic concentration differences of secondary molecular or ionic substances between the two sides of a cell membrane, created originally by primary active transport. Secondary active transport occurs via co-‐ transp ...
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE
... MEMBRANE PROTEINS • INTEGRAL or TRANS – MEMBRANE PROTEINS • LIPID-ANCHORED MEMBRANE PROTEINS • PERIPHERAL MEMBRANE PROTEINS ...
... MEMBRANE PROTEINS • INTEGRAL or TRANS – MEMBRANE PROTEINS • LIPID-ANCHORED MEMBRANE PROTEINS • PERIPHERAL MEMBRANE PROTEINS ...
MTC25 - Intracellular Processing
... More specialised secretory proteins that must be regulated are packaged in specialised secretory vesicles which mediate calcium-dependent exocytosis: o Vesicles are typically coated by clathrin proteins which exist as three-armed ‘tri-skeletons’ that attach to one another around the subject protein, ...
... More specialised secretory proteins that must be regulated are packaged in specialised secretory vesicles which mediate calcium-dependent exocytosis: o Vesicles are typically coated by clathrin proteins which exist as three-armed ‘tri-skeletons’ that attach to one another around the subject protein, ...
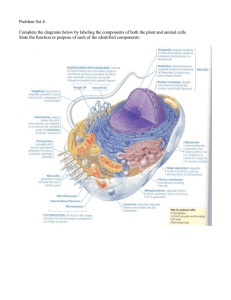
Problem Set 4:
... 8.8 Why is facilitated diffusion considered passive transport? b/c with [gradient] no E required 8.9 The Na+ -- K+ pump, the major electrogenic pump in animal cells, exchanges sodium ions for potassium ions, both of which are cations. How does this exchange generate a membrane potential? 3 Na+out fo ...
... 8.8 Why is facilitated diffusion considered passive transport? b/c with [gradient] no E required 8.9 The Na+ -- K+ pump, the major electrogenic pump in animal cells, exchanges sodium ions for potassium ions, both of which are cations. How does this exchange generate a membrane potential? 3 Na+out fo ...
Selectively Permeable Cell Membrane bellringer
... Selectively Permeable Cell Membrane Structure and Function Bellringer Need the Selectively Permeable Cell Membrane Drawing 1. What two major types of biological molecules compose the majority of the cell membrane? 2. How many different protein molecules are found in the cell membrane drawing? 3. Wha ...
... Selectively Permeable Cell Membrane Structure and Function Bellringer Need the Selectively Permeable Cell Membrane Drawing 1. What two major types of biological molecules compose the majority of the cell membrane? 2. How many different protein molecules are found in the cell membrane drawing? 3. Wha ...
CELL MEMBRANES CHAPTER 6 FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
... Plant cells with rigid cell walls build up internal pressure that keeps more water from entering—turgor pressure. FACILITATED DIFFUSION ...
... Plant cells with rigid cell walls build up internal pressure that keeps more water from entering—turgor pressure. FACILITATED DIFFUSION ...
Study Guide for Membranes and Transport
... describe the processes which allow monomers to be joined to form polymers as well as polymers to be broken down into monomers. give examples of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids including at least one location within a cell where each can be found. compare and contrast the str ...
... describe the processes which allow monomers to be joined to form polymers as well as polymers to be broken down into monomers. give examples of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids including at least one location within a cell where each can be found. compare and contrast the str ...
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
... Learning Outcomes B9 - Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane: Describe and compare endocytosis and exocytosis in terms of: Method of transport (use of vesicles) Use of energy (active vs. passive) Type / size of molecule transported ...
... Learning Outcomes B9 - Describe the structure and function of the cell membrane: Describe and compare endocytosis and exocytosis in terms of: Method of transport (use of vesicles) Use of energy (active vs. passive) Type / size of molecule transported ...
SNARE (protein)

SNARE proteins (an acronym derived from ""SNAP (Soluble NSF Attachment Protein) REceptor"") are a large protein superfamily consisting of more than 60 members in yeast and mammalian cells. The primary role of SNARE proteins is to mediate vesicle fusion, that is, the fusion of vesicles with their target membrane bound compartments (such as a lysosome). The best studied SNAREs are those that mediate docking of synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic membrane in neurons. These SNAREs are the targets of the bacterial neurotoxins responsible for botulism and tetanus.