1. Which of the following is not a feature of scientific hypotheses? A
... C) the rough endoplasmic reticulum. D) a prokaryotic cell. E) the Golgi apparatus. ...
... C) the rough endoplasmic reticulum. D) a prokaryotic cell. E) the Golgi apparatus. ...
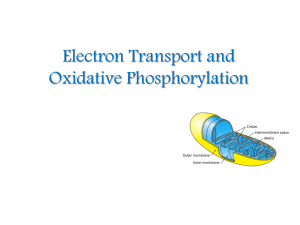
Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
... First, carbon fuels are oxidized in the citric acid cycle to yield electrons with high transfer potential. Then, this electron-motive force is converted into a ...
... First, carbon fuels are oxidized in the citric acid cycle to yield electrons with high transfer potential. Then, this electron-motive force is converted into a ...
Oxidative Phosphorylation - Study in Universal Science College
... • These function as prosthetic groups which facilitate electron transfer • Iron - sulfur protein - The iron is not present in heme but is found in association with inorganic sulfur or the cysteine residues in the protein • Rieske Iron - sulfur protein - One iron atom is coordinated to 2 Histidine re ...
... • These function as prosthetic groups which facilitate electron transfer • Iron - sulfur protein - The iron is not present in heme but is found in association with inorganic sulfur or the cysteine residues in the protein • Rieske Iron - sulfur protein - One iron atom is coordinated to 2 Histidine re ...
THE CELL
... 1) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2) Cells are the basic living units within organisms. 3) All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
... 1) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2) Cells are the basic living units within organisms. 3) All cells arise from preexisting cells. ...
Chapter 14 (Part 1)
... Chemiosmotic Theory • Electron Transport: Electrons carried by reduced coenzymes are passed through a chain of proteins and coenzymes to drive the generation of a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane ...
... Chemiosmotic Theory • Electron Transport: Electrons carried by reduced coenzymes are passed through a chain of proteins and coenzymes to drive the generation of a proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane ...
BIOL 303 Cell Biology Test preparation questionnaire # 1
... 93. What molecules represent the lowest and highest electron energy levels in the cycle of energetic conversions that take place within aerobic organisms? 94. What are the main photosynthetic organisms living on Earth? 95. How many moles of photons of red light would contain the same amount of energ ...
... 93. What molecules represent the lowest and highest electron energy levels in the cycle of energetic conversions that take place within aerobic organisms? 94. What are the main photosynthetic organisms living on Earth? 95. How many moles of photons of red light would contain the same amount of energ ...
chapter6_Sections 1
... Line color is the characteristic color of each pigment. Fig. 6.4c, p. 96 ...
... Line color is the characteristic color of each pigment. Fig. 6.4c, p. 96 ...
Chapter-4 part-2 Energy Metabolism
... • Proteins of mitochondria have 2 purposes, to – Transport electrons – Transport hydrogen atoms ...
... • Proteins of mitochondria have 2 purposes, to – Transport electrons – Transport hydrogen atoms ...
Mycolic acid export to the outer membrane of mycobacteria
... is membrane biogenesis, i.e. how a biological membrane is assembled. Membrane lipid bilayers form the basis for life, physically defining cells and organelles, and modulating the chemical environments within these compartments for optimal metabolism and growth. Despite these fundamental roles, howev ...
... is membrane biogenesis, i.e. how a biological membrane is assembled. Membrane lipid bilayers form the basis for life, physically defining cells and organelles, and modulating the chemical environments within these compartments for optimal metabolism and growth. Despite these fundamental roles, howev ...
The Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Acetyl-coenzyme A is oxidized to CO 2
... 1. As electrons pass through the ETC, protons are transported from the matrix and released into the intermembrane space. As a result, an electrical potential and proton gradient are created across the inner membrane. The electrochemical proton gradient is sometimes referred to as the proton motive f ...
... 1. As electrons pass through the ETC, protons are transported from the matrix and released into the intermembrane space. As a result, an electrical potential and proton gradient are created across the inner membrane. The electrochemical proton gradient is sometimes referred to as the proton motive f ...
hydrophilic - muhlsdk12.org
... Membrane Proteins • Proteins determine membrane’s specific functions – cell membrane & organelle membranes each have unique collections of proteins ...
... Membrane Proteins • Proteins determine membrane’s specific functions – cell membrane & organelle membranes each have unique collections of proteins ...
8C_BioReview NOTES (7C9)
... 17. Exocytosis is the process in which the membrane of the vesicle fuses with the cell’s membrane and the vesicle’s cargo is released outside the cell. (or the cargo EXITS!) 18. Cells use chemical reactions to change the chemical energy stored in food into forms of energy needed to perform activitie ...
... 17. Exocytosis is the process in which the membrane of the vesicle fuses with the cell’s membrane and the vesicle’s cargo is released outside the cell. (or the cargo EXITS!) 18. Cells use chemical reactions to change the chemical energy stored in food into forms of energy needed to perform activitie ...
4.4. INTRODUCING PROKARYOTIC CELLS
... Make far more ATP from the same compounds than prokaryotic cells Hydrogen ions released from the breakdown of organic compounds accum ulate in the inner compartment by operation of transport systems ...
... Make far more ATP from the same compounds than prokaryotic cells Hydrogen ions released from the breakdown of organic compounds accum ulate in the inner compartment by operation of transport systems ...
What is a cell Cell is the basic living, structural and
... Contains digestive enzymes that break down molecules (Eg. DNA, RNA, Carbs, Proteins) inside the cell into smaller particles that are either recycled or extruded from the cell as waste material. Lysosomes in WBC’s contains enzymes that digest foreign materials such as microbes Mitochondria Mitoch ...
... Contains digestive enzymes that break down molecules (Eg. DNA, RNA, Carbs, Proteins) inside the cell into smaller particles that are either recycled or extruded from the cell as waste material. Lysosomes in WBC’s contains enzymes that digest foreign materials such as microbes Mitochondria Mitoch ...
see lecture notes
... Chlorophyll is a large molecule with a central Magnesium atom held in a porphyrin ring (like Fe in hemoglobin) Most photosynthetic cells also contain chlorophyll b and/or carotenoids (red, orange, yellow) => most prevalent is beta-carotene, called "accessory pigments" The presence of the " secondary ...
... Chlorophyll is a large molecule with a central Magnesium atom held in a porphyrin ring (like Fe in hemoglobin) Most photosynthetic cells also contain chlorophyll b and/or carotenoids (red, orange, yellow) => most prevalent is beta-carotene, called "accessory pigments" The presence of the " secondary ...
Document
... a. Anaerobes do not lose two ATPs in glycolysis b. Anaerobes do not have an ETS c. Anaerobes do not undergo oxidative phosphorylation d. Anaerobes produces an extra FADH2 during the TCA cycle ______________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________ ...
... a. Anaerobes do not lose two ATPs in glycolysis b. Anaerobes do not have an ETS c. Anaerobes do not undergo oxidative phosphorylation d. Anaerobes produces an extra FADH2 during the TCA cycle ______________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________ ...
Active Transport
... Active Transport • Thousands of proteins are embedded in the cell's lipid bilayer. • These proteins do much of the work in active transport. • They are positioned to cross the membrane so one part is on the inside of the cell and one part is on the outside. ...
... Active Transport • Thousands of proteins are embedded in the cell's lipid bilayer. • These proteins do much of the work in active transport. • They are positioned to cross the membrane so one part is on the inside of the cell and one part is on the outside. ...
Transport Unit Study Guide
... membrane and which kind need to use a transport protein Be able to explain the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis and give examples Be able to predict the effect of a hypotonic, isotonic or hypertonic solution on a cell Be able to di ...
... membrane and which kind need to use a transport protein Be able to explain the processes of diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis and give examples Be able to predict the effect of a hypotonic, isotonic or hypertonic solution on a cell Be able to di ...
Mitochondria
... peroxide (H2O2), a poison, but the peroxisome has another enzyme that converts H2O2 to water. • Some peroxisomes break fatty acids down to smaller molecules that are transported to mitochondria for fuel. • Others detoxify alcohol and other harmful compounds. • Specialized peroxisomes, glyoxysomes, c ...
... peroxide (H2O2), a poison, but the peroxisome has another enzyme that converts H2O2 to water. • Some peroxisomes break fatty acids down to smaller molecules that are transported to mitochondria for fuel. • Others detoxify alcohol and other harmful compounds. • Specialized peroxisomes, glyoxysomes, c ...
Lec 16.
... Hydropathy Plots for Alpha Helical Proteins: Classic Method For alpha-helical membrane proteins, you can use hydropathy plots to predict the probability that a segment will be within the membrane. These are generated by measuring, for each amino acid, its partition coefficient between water and a n ...
... Hydropathy Plots for Alpha Helical Proteins: Classic Method For alpha-helical membrane proteins, you can use hydropathy plots to predict the probability that a segment will be within the membrane. These are generated by measuring, for each amino acid, its partition coefficient between water and a n ...
Electron tomography of plant thylakoid membranes
... 1999). For conventional ET, samples are embedded in plastic and sectioned by ultramicrotomy. Although this yields highcontrast images of gross cellular features including membranes, molecular detail is lost. To obtain tomograms of 4– 5nm resolution (Leis et al., 2009), the sample has to be vitrified ...
... 1999). For conventional ET, samples are embedded in plastic and sectioned by ultramicrotomy. Although this yields highcontrast images of gross cellular features including membranes, molecular detail is lost. To obtain tomograms of 4– 5nm resolution (Leis et al., 2009), the sample has to be vitrified ...
Plant Cell Anatomy
... newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body and membranes. stroma - part of the chloroplasts in plant cells, located within the inner membrane of chloroplasts, between the grana. thylakoid disk - thylakoid disks are disk-shaped membrane structures in chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll. Chlor ...
... newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body and membranes. stroma - part of the chloroplasts in plant cells, located within the inner membrane of chloroplasts, between the grana. thylakoid disk - thylakoid disks are disk-shaped membrane structures in chloroplasts that contain chlorophyll. Chlor ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.