No Slide Title
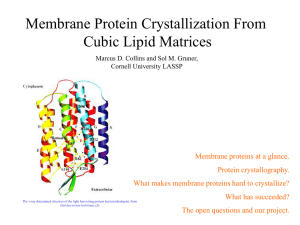
... and hydrophobic regions. Until very recently all protein crystallization techniques used an aqueous solvent for crystallization. Membrane proteins easily denature (that is, lose their structure) in this environment. In 1984 the first membrane protein, a photosynthetic reaction center, was crystalliz ...
... and hydrophobic regions. Until very recently all protein crystallization techniques used an aqueous solvent for crystallization. Membrane proteins easily denature (that is, lose their structure) in this environment. In 1984 the first membrane protein, a photosynthetic reaction center, was crystalliz ...
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... Big Idea 2: Energy - Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. Big Idea 4: Interactions - Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. ...
... Big Idea 2: Energy - Biological systems utilize free energy and molecular building blocks to grow, to reproduce and to maintain dynamic homeostasis. Big Idea 4: Interactions - Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. ...
Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting
... Light energy is used to oxidize water. Electrons are transferred to reduce NADPH and proton gradient is used to form ATP. CO2 + RuBP -- rubisco--> 2 PGA PGA --NADPH, ATP --> G3P ...
... Light energy is used to oxidize water. Electrons are transferred to reduce NADPH and proton gradient is used to form ATP. CO2 + RuBP -- rubisco--> 2 PGA PGA --NADPH, ATP --> G3P ...
Biol 178 Lecture 10
... Membrane bound compartment that contains water, organic compounds, inorganic ions, and pigments. ...
... Membrane bound compartment that contains water, organic compounds, inorganic ions, and pigments. ...
Document
... 1. Light excites an electron from photosystem I 2. Light excites an electron from photosystem II 3. Electrons reduce NADP+ to NADPH 4. Electrons pass through an electron transport chain, which generates a H+ gradient used to make ATP a. b. c. d. ...
... 1. Light excites an electron from photosystem I 2. Light excites an electron from photosystem II 3. Electrons reduce NADP+ to NADPH 4. Electrons pass through an electron transport chain, which generates a H+ gradient used to make ATP a. b. c. d. ...
HS Life Sci Standard 2.5 Cells
... what factors influence their rates? 2a. How does the direction of osmosis depend on the concentration of the solutes on both sides of a membrane? 2b. Why is it important that cell membranes are selectively permeable? 3. How do proteins act as gateways through the cell membrane and use receptors to r ...
... what factors influence their rates? 2a. How does the direction of osmosis depend on the concentration of the solutes on both sides of a membrane? 2b. Why is it important that cell membranes are selectively permeable? 3. How do proteins act as gateways through the cell membrane and use receptors to r ...
Special Guest Speaker Dr. Christopher Colbert
... Project 1: Rieske oxygenases are a diverse class of non-heme, mononuclear iron-containing enzymes capable of the stereo- and regio-selective insertion of molecular oxygen into aromatic substrates. These enzymes are important in the bioremediation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biph ...
... Project 1: Rieske oxygenases are a diverse class of non-heme, mononuclear iron-containing enzymes capable of the stereo- and regio-selective insertion of molecular oxygen into aromatic substrates. These enzymes are important in the bioremediation of polyaromatic hydrocarbons and polychlorinated biph ...
Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reactions Calvin Cycle
... • Calvin cycle (Light-Independent Reaction) – Occurs in stroma – uses carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADPH to produce sugars (aka food, glucose, carbohydrates, etc.) ...
... • Calvin cycle (Light-Independent Reaction) – Occurs in stroma – uses carbon dioxide, ATP, and NADPH to produce sugars (aka food, glucose, carbohydrates, etc.) ...
Answers - AP BIOLOGY!
... from the environment. This bilayer is what composes cell membranes. The largely nonpolar/hydrophobic interior of cell membranes keeps even small polar/hydrophilic molecules from diffusing rapidly through the membrane. Therefore, small, nonpolar molecules diffuse most easily through the membrane. 2. ...
... from the environment. This bilayer is what composes cell membranes. The largely nonpolar/hydrophobic interior of cell membranes keeps even small polar/hydrophilic molecules from diffusing rapidly through the membrane. Therefore, small, nonpolar molecules diffuse most easily through the membrane. 2. ...
Active transport - CHS Science Department Mrs. Davis
... Active Transport Larger molecules can be transported by movements of the cell membrane known as bulk transport. – Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane. • phagocytosis - cell eating • pinocytosis - cell drinking – Exocytosis is a process of re ...
... Active Transport Larger molecules can be transported by movements of the cell membrane known as bulk transport. – Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane. • phagocytosis - cell eating • pinocytosis - cell drinking – Exocytosis is a process of re ...
Cell Transport Quiz KEY
... Cell Transport Quiz KEY Directions: Write the correct word for each definition. Each word should only be used once. Osmosis ...
... Cell Transport Quiz KEY Directions: Write the correct word for each definition. Each word should only be used once. Osmosis ...
1) Where does glycolysis occur in the cell
... 8) All of the following processes occur within mitochondria except: a) the splitting of glucose b) the formation of citric acid c) the catabolism of citric acid to produce NADH, CO2, AND H+ d) the transfer of electrons form NADH to the electron transport chain e) the reduction of oxygen to form wate ...
... 8) All of the following processes occur within mitochondria except: a) the splitting of glucose b) the formation of citric acid c) the catabolism of citric acid to produce NADH, CO2, AND H+ d) the transfer of electrons form NADH to the electron transport chain e) the reduction of oxygen to form wate ...
Photosynthesis File
... H+, in the form of NADP-H, and ATP molecules made during photolysis in the thylakoids now move out into the chloroplast space, stroma CO2 is brought into plant through stomata on leaves and makes its way into the chloroplasts In the stroma, a cyclic metabolic pathway called the Calvin cycle takes pl ...
... H+, in the form of NADP-H, and ATP molecules made during photolysis in the thylakoids now move out into the chloroplast space, stroma CO2 is brought into plant through stomata on leaves and makes its way into the chloroplasts In the stroma, a cyclic metabolic pathway called the Calvin cycle takes pl ...
BioCh7-A View of the Cell
... • For all the cellular processes to happen, energy is needed • Two organelles provide that energy: – Choloroplasts (in plants) – Mitochondria (in animals and plants) ...
... • For all the cellular processes to happen, energy is needed • Two organelles provide that energy: – Choloroplasts (in plants) – Mitochondria (in animals and plants) ...
study guide
... Light-absorbing molecules called pigments capture the sun’s energy. Chlorophyll is the principal pigment in photosynthetic organisms. Chlorophyll absorbs blue-violet and red light but reflects green light. Chloroplasts have a complex internal structure that includes: thylakoids: saclike photosynth ...
... Light-absorbing molecules called pigments capture the sun’s energy. Chlorophyll is the principal pigment in photosynthetic organisms. Chlorophyll absorbs blue-violet and red light but reflects green light. Chloroplasts have a complex internal structure that includes: thylakoids: saclike photosynth ...
Ch5-Cells
... Things we will see in cells • First let’s focus on things we can see using a light microscope and ordinary stains: • Cell nucleus • Cell membrane • Cell wall • Plastids (Chloroplast, amyloplast, chromoplast) • Plant cell vacuole ...
... Things we will see in cells • First let’s focus on things we can see using a light microscope and ordinary stains: • Cell nucleus • Cell membrane • Cell wall • Plastids (Chloroplast, amyloplast, chromoplast) • Plant cell vacuole ...
S10 Key BLM 8-6 7 - Cochrane High School
... 1. A. Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis. It is used to ingest food and other solids (“cell eating”). The cell membrane forms a pocket around the substance to be transported. B. Pinocytosis is also a type of endocytosis. This process is used to ingest fluids (cell “drinking”). The cell membrane f ...
... 1. A. Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis. It is used to ingest food and other solids (“cell eating”). The cell membrane forms a pocket around the substance to be transported. B. Pinocytosis is also a type of endocytosis. This process is used to ingest fluids (cell “drinking”). The cell membrane f ...
Structure and functions
... transport two substances across the membrane in the same direction. Symporters use the potential energy of electrochemical gradients from protons (H+), that is, proton motive force to co-transport ions, glucose, and amino acids against their concentration gradient ...
... transport two substances across the membrane in the same direction. Symporters use the potential energy of electrochemical gradients from protons (H+), that is, proton motive force to co-transport ions, glucose, and amino acids against their concentration gradient ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.