Chapter 7
... Membranes are Bifacial The lipid composition of the two layers is different. The proteins have specific orientations. Carbohydrates are found only on the outer surface. ...
... Membranes are Bifacial The lipid composition of the two layers is different. The proteins have specific orientations. Carbohydrates are found only on the outer surface. ...
Oxidative phosphorylation
... • Oxidative Phosphorylation: electron transport chain and chemiosmosis • e- trasport chain embedded in INNER mito membrane • Composed of 3 transmembrane H+ pumps • Electrons flow through e- chain – Loss of energy from e-s powers H+ pump ...
... • Oxidative Phosphorylation: electron transport chain and chemiosmosis • e- trasport chain embedded in INNER mito membrane • Composed of 3 transmembrane H+ pumps • Electrons flow through e- chain – Loss of energy from e-s powers H+ pump ...
1. Name two functions of the cell membrane
... 16. Because cells are hypertonic in relation to fresh water, ___________________________ produces a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. 17. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmoti ...
... 16. Because cells are hypertonic in relation to fresh water, ___________________________ produces a net movement of water into the cell. If that happens, the cell will become ____________________________ and can even burst. 17. In plant and bacteria cells, what keeps them from bursting due to osmoti ...
Biology Name: Block: ____ Learning Targets: Membrane
... cell to maintain homeostasis given concentration gradients and different sizes of molecules. (change to send to S. Brown) I can define the terms selectively permeable or semi-permeable in relation to membranes. ...
... cell to maintain homeostasis given concentration gradients and different sizes of molecules. (change to send to S. Brown) I can define the terms selectively permeable or semi-permeable in relation to membranes. ...
Cell Membrane - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... Mosaic : because it is made of many pieces http://home.earthlink.net/~shalpine/anim/Life/memb.htm ...
... Mosaic : because it is made of many pieces http://home.earthlink.net/~shalpine/anim/Life/memb.htm ...
Your Pre AP biology final exam
... Color the polar part green Color the non polar part yellow Add in a channel (transport) protein. Add in a carbohydrate marker on one of the proteins ...
... Color the polar part green Color the non polar part yellow Add in a channel (transport) protein. Add in a carbohydrate marker on one of the proteins ...
Slide ()
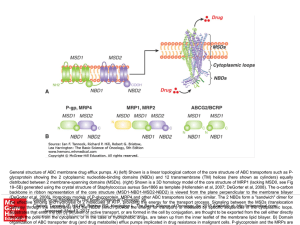
... (DeGorter et al, 2008). Homology models of P-glycoprotein, MRP4 and other ABC transporters look very similar. The 2 NBDs form a "sandwich" dimer for Source: Drug Resistance, The Basic Science of Oncology, 5e the effective binding and hydrolysis of 2 molecules of ATP, providing the energy for the tra ...
... (DeGorter et al, 2008). Homology models of P-glycoprotein, MRP4 and other ABC transporters look very similar. The 2 NBDs form a "sandwich" dimer for Source: Drug Resistance, The Basic Science of Oncology, 5e the effective binding and hydrolysis of 2 molecules of ATP, providing the energy for the tra ...
Section Slides
... • Influences transport of charged molecules • Combination of the concentration gradient and the membrane potential (charge difference across the membrane) ...
... • Influences transport of charged molecules • Combination of the concentration gradient and the membrane potential (charge difference across the membrane) ...
Cell Respiration Exam - Data Analysis and Essay Markscheme
... H+ is pumped out across membrane; more H+ outside (from electron transport chain); concentration gradient of H+ is formed / potential energy; H+ movement across membrane through protein channels in ATP synthetase; ADP is phosphorylated / picks up phosphate to ATP; ATP has more energy than ADP; chemi ...
... H+ is pumped out across membrane; more H+ outside (from electron transport chain); concentration gradient of H+ is formed / potential energy; H+ movement across membrane through protein channels in ATP synthetase; ADP is phosphorylated / picks up phosphate to ATP; ATP has more energy than ADP; chemi ...
Chapter 8: CELL MEMBRANE
... ions can use as a tunnel ● Channel proteins called AQUAPORINS ● Other transport proteins, called carrier proteins, bind to molecules and change shape to shuttle them across the membrane ● A transport protein is specific for the substance it moves! 2) RECEPTOR PROTEINS: collect & transmit information ...
... ions can use as a tunnel ● Channel proteins called AQUAPORINS ● Other transport proteins, called carrier proteins, bind to molecules and change shape to shuttle them across the membrane ● A transport protein is specific for the substance it moves! 2) RECEPTOR PROTEINS: collect & transmit information ...
Cell Membrane Structure & Function
... – 2.Take up molecules present in high concentration – 3 Part of protein extends through bilayer – 4.May be non polar helix beta-pleated sheets of non polar amino acids – 5.Non polar portion held within interior of bilayer – 6.Polar ends protrude from both sides of membrane B. Enzymes – 1. Chemical r ...
... – 2.Take up molecules present in high concentration – 3 Part of protein extends through bilayer – 4.May be non polar helix beta-pleated sheets of non polar amino acids – 5.Non polar portion held within interior of bilayer – 6.Polar ends protrude from both sides of membrane B. Enzymes – 1. Chemical r ...
Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff
... Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff ...
... Digestion and Respiration MMHS Anatomy Chitraroff ...
Photosynthesis occurs in 2 sets of main reactions in the chloroplast
... are known as ___. a) grana; b) stroma; c) thylakoids; d) cristae; e) matrix 19. The fluid-filled area of the chloroplast is the ___. a) grana; b) stroma; c) thylakoids; d) cristae; e) matrix 20. The chloroplast contains all of these except ___. a) grana; b) stroma; c) DNA; d) membranes; e) endoplasm ...
... are known as ___. a) grana; b) stroma; c) thylakoids; d) cristae; e) matrix 19. The fluid-filled area of the chloroplast is the ___. a) grana; b) stroma; c) thylakoids; d) cristae; e) matrix 20. The chloroplast contains all of these except ___. a) grana; b) stroma; c) DNA; d) membranes; e) endoplasm ...
L11v01a_oxy_phos_part_1.stamped_doc
... [00:00:00.86] Hi. In this video, we'll talk about oxidative phosphorylation, which is the main method that cells use to make the majority of their ATP. We'll talk about the mechanism that ATP is made, which involves the coupled vectorial processes of electron transport, establishment of a proton gra ...
... [00:00:00.86] Hi. In this video, we'll talk about oxidative phosphorylation, which is the main method that cells use to make the majority of their ATP. We'll talk about the mechanism that ATP is made, which involves the coupled vectorial processes of electron transport, establishment of a proton gra ...
Chapter 5 Handout - Prep for Bio 010-51
... carrier protein. iii. Osmosis – Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. b. Active transport is movement across a membrane of substances that travel against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy. i. Active transport – Movement of individual small molecules or i ...
... carrier protein. iii. Osmosis – Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane. b. Active transport is movement across a membrane of substances that travel against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy. i. Active transport – Movement of individual small molecules or i ...
CELL MEMBRANES LEARNING OBJECTIVES • At the end
... -ion channels allow the passage of ions (charged atoms or molecules) which are associated with water -gated channels are opened or closed in response to a stimulus -the stimulus may be chemical or electrical ACTIVE TRANSPORT Active transport -requires energy – ATP is used directly or indirectly to f ...
... -ion channels allow the passage of ions (charged atoms or molecules) which are associated with water -gated channels are opened or closed in response to a stimulus -the stimulus may be chemical or electrical ACTIVE TRANSPORT Active transport -requires energy – ATP is used directly or indirectly to f ...
Cell membrane ppt Plasma mb ppt
... • Allows cells to maintain a different environment inside vs. outside the cell ...
... • Allows cells to maintain a different environment inside vs. outside the cell ...
Chapter 8 Notes – Energy and Metabolism
... Cytochrome c transfers electrons to the cytochrome c oxidase complex. Protons are also transferred to the outside of the membrane by the cytochrome c oxidase complex. The cytochrome oxidase complex then transfers electrons from cytochrome c to oxygen, the terminal electron acceptor and water is form ...
... Cytochrome c transfers electrons to the cytochrome c oxidase complex. Protons are also transferred to the outside of the membrane by the cytochrome c oxidase complex. The cytochrome oxidase complex then transfers electrons from cytochrome c to oxygen, the terminal electron acceptor and water is form ...
Enzymes and CellMemb.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Use the graph at the right to answer questions 2-5 2. Why did the reaction rate for enzyme J drop when the temperature exceeded 50C? 3. What is the optimal temperature for enzyme J? 4. How do you know this is the optimal temperature? 5. Could enzyme J be an enzyme found in the human body? Why or wh ...
... Use the graph at the right to answer questions 2-5 2. Why did the reaction rate for enzyme J drop when the temperature exceeded 50C? 3. What is the optimal temperature for enzyme J? 4. How do you know this is the optimal temperature? 5. Could enzyme J be an enzyme found in the human body? Why or wh ...
Cell Membranes: Chapt. 6
... Cell Membrane Every cell is encircled by a membrane and most cells contain an extensive intracellular membrane system. Membranes fence off the cell's interior from its surroundings. Membranes let in water, certain ions and substrates and they excrete waste substances. They act to protect the cell. ...
... Cell Membrane Every cell is encircled by a membrane and most cells contain an extensive intracellular membrane system. Membranes fence off the cell's interior from its surroundings. Membranes let in water, certain ions and substrates and they excrete waste substances. They act to protect the cell. ...
Answer Key - TeacherWeb
... 19. The diffusion of water into or out of a cell is called osmosis. 20. Osmosis is a type of passive transport. 21. Ions move through ion channels by passive transport. P.85, Fig 3.21 22. Ion channel gates close the pores of some ion channels in response to stretching of the cell membrane, a change ...
... 19. The diffusion of water into or out of a cell is called osmosis. 20. Osmosis is a type of passive transport. 21. Ions move through ion channels by passive transport. P.85, Fig 3.21 22. Ion channel gates close the pores of some ion channels in response to stretching of the cell membrane, a change ...
Chapter 35 - What is pages.mtu.edu?
... • H,K-ATPase pumps protons from these cells into the stomach to maintain a pH difference across a single plasma membrane of 6.6! • This is the largest concentration gradient across a membrane in eukaryotic organisms! • H,K-ATPase is similar in many respects to Na,K-ATPase and CaATPase (P-type) ...
... • H,K-ATPase pumps protons from these cells into the stomach to maintain a pH difference across a single plasma membrane of 6.6! • This is the largest concentration gradient across a membrane in eukaryotic organisms! • H,K-ATPase is similar in many respects to Na,K-ATPase and CaATPase (P-type) ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.