Cell Benchmark Study Guide 2013
... Plants take in __CO2__ from the atmosphere to create glucose in the process of photosynthesis. This process happens inside the ____chloroplast__ of a plant cell. _ O2__ is a waste product of photosynthes ...
... Plants take in __CO2__ from the atmosphere to create glucose in the process of photosynthesis. This process happens inside the ____chloroplast__ of a plant cell. _ O2__ is a waste product of photosynthes ...
Respiration, Lithotrophy & Photosynthesis
... 1) The substrate dehydrogenase receives a pair of electrons from an organic substrate, such as glucose, NADH, H2. 2) It donates the electrons ultimately to Flavoprotein (FMN/FMNH2) and Iron sulfur (Fe3+/Fe2+). ...
... 1) The substrate dehydrogenase receives a pair of electrons from an organic substrate, such as glucose, NADH, H2. 2) It donates the electrons ultimately to Flavoprotein (FMN/FMNH2) and Iron sulfur (Fe3+/Fe2+). ...
4-2 Parts of the Eukaryotic Cell
... Both types of proteins form channels for nutrients to travel and also give cell its selectively permeable status. Both the lipids and the proteins help in structure and support of the cell. ...
... Both types of proteins form channels for nutrients to travel and also give cell its selectively permeable status. Both the lipids and the proteins help in structure and support of the cell. ...
슬라이드 1
... - Lipid + peripheral & integral proteins (originally) + lipid anchored proteins + membrane protein-cytoskeletal interactions (recently). - Membrane fluidity involves the movement not only of lipid molecules but also of the different proteins. - The importance of protein movement in membranes a) the ...
... - Lipid + peripheral & integral proteins (originally) + lipid anchored proteins + membrane protein-cytoskeletal interactions (recently). - Membrane fluidity involves the movement not only of lipid molecules but also of the different proteins. - The importance of protein movement in membranes a) the ...
Slide ()
... activates the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor dimer, resulting in the tyrosine phosphorylation (Y-P) of the receptor's β subunits and a small number of specific substrates (yellow shapes): the Insulin Receptor Substrate (IRS) proteins, Gab-1 and SHC; within the membrane, a caveola ...
... activates the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor dimer, resulting in the tyrosine phosphorylation (Y-P) of the receptor's β subunits and a small number of specific substrates (yellow shapes): the Insulin Receptor Substrate (IRS) proteins, Gab-1 and SHC; within the membrane, a caveola ...
Unit Test: Metabolism
... 7. Which of the following statements about adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is NOT true? 8. In which of the following situations would you least expect to find anaerobic respiration occurring? 9. Glycolysis can best be described as…… 10. At the end of glycolysis, most of the energy originally found in g ...
... 7. Which of the following statements about adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is NOT true? 8. In which of the following situations would you least expect to find anaerobic respiration occurring? 9. Glycolysis can best be described as…… 10. At the end of glycolysis, most of the energy originally found in g ...
Chapter 5 Capturing and releasing Energy
... and NADPH, releasing oxygen • Occur at the thylakoid membrane in plant chloroplasts ...
... and NADPH, releasing oxygen • Occur at the thylakoid membrane in plant chloroplasts ...
Slide 1
... pumps out excess water •Plants – large, central vacuole - stores chemicals that contribute to plant growth ...
... pumps out excess water •Plants – large, central vacuole - stores chemicals that contribute to plant growth ...
Basic structure and organization of Eukaryotic cell in Comparison to
... • thylakoid membrane is impermeable to ions well suited for its role in protein translocation • thylakoids are stacked grana • stroma of chloroplasts contain enzymes for reduction of CO2 to organic material • outer chloroplast membrane is highly permeable • Although some bacteria are photosynthetic, ...
... • thylakoid membrane is impermeable to ions well suited for its role in protein translocation • thylakoids are stacked grana • stroma of chloroplasts contain enzymes for reduction of CO2 to organic material • outer chloroplast membrane is highly permeable • Although some bacteria are photosynthetic, ...
Cell Membranes CXH File
... Membranes have several functions: 1. They are partially permeable, controlling what passes through them. 2. They are involved in cell signalling (communication between cells). 3. They provide attachment sites for enzymes and other molecules involved in metabolism. 4. They can allow electrical signa ...
... Membranes have several functions: 1. They are partially permeable, controlling what passes through them. 2. They are involved in cell signalling (communication between cells). 3. They provide attachment sites for enzymes and other molecules involved in metabolism. 4. They can allow electrical signa ...
Amazing Cells Build-A-Membrane
... Cell membranes are made of phospholipid molecules that arrange themselves into two rows called a bilayer. Proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, through one or both layers. These proteins help other molecules cross the membrane and perform a variety of other functions. Create a model of ...
... Cell membranes are made of phospholipid molecules that arrange themselves into two rows called a bilayer. Proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer, through one or both layers. These proteins help other molecules cross the membrane and perform a variety of other functions. Create a model of ...
Name
... Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 1. How do organisms get the energy they need? a. by burning food molecules and releasing their energy as heat b. by breathing oxygen into the lungs and combining it with carbon dioxide c. by breaki ...
... Write the letter that best answers the question or completes the statement on the line provided. _____ 1. How do organisms get the energy they need? a. by burning food molecules and releasing their energy as heat b. by breathing oxygen into the lungs and combining it with carbon dioxide c. by breaki ...
ATP – P - Acpsd.net
... Chemosynthesis is a process through which some organisms use energy from chemicals in their environment to build sugars in the absence of ...
... Chemosynthesis is a process through which some organisms use energy from chemicals in their environment to build sugars in the absence of ...
Chapter 5
... from packing tightly • Most membranes also contain sterols such as cholesterol, which can either increase or decrease membrane fluidity, depending on the temperature ...
... from packing tightly • Most membranes also contain sterols such as cholesterol, which can either increase or decrease membrane fluidity, depending on the temperature ...
Cellular Respiration 2
... Many electron acceptors used released energy to pump an H+ proton into the intermembrane space – Gradient of H+ is formed outside of cristaes ...
... Many electron acceptors used released energy to pump an H+ proton into the intermembrane space – Gradient of H+ is formed outside of cristaes ...
CHAPTER 3 PHOTOSYNTHESIS
... D: outer envelope membrane (b) The mitochondrion has two membranes, with the inner membrane folded into the interior, while the chloroplast has a double membrane system with a separate third membrane system, the thylakoid membrane, that houses chlorophyll molecules. 6. The overall equation for photo ...
... D: outer envelope membrane (b) The mitochondrion has two membranes, with the inner membrane folded into the interior, while the chloroplast has a double membrane system with a separate third membrane system, the thylakoid membrane, that houses chlorophyll molecules. 6. The overall equation for photo ...
4.3 The Light Reactions
... Three turns of the cycle (which uses 3 CO2 molecules) results in 6 PGAL molecules. 5 of those PGAL are used to regenerate RuBP & the last one is available to the organism to ...
... Three turns of the cycle (which uses 3 CO2 molecules) results in 6 PGAL molecules. 5 of those PGAL are used to regenerate RuBP & the last one is available to the organism to ...
CHEM523 Exam2
... A) A specific membrane protein lowers the activation energy for movement of the solute through the membrane. B) It can increase the size of a transmembrane concentration gradient of the diffusing ...
... A) A specific membrane protein lowers the activation energy for movement of the solute through the membrane. B) It can increase the size of a transmembrane concentration gradient of the diffusing ...
SOLVING REAL WORLD PROBLEMS-
... It is a type of passive transport Cell membrane has some _________________________ in channels that allow certain substances to be carried inside cell e..g _____________, _______________ ...
... It is a type of passive transport Cell membrane has some _________________________ in channels that allow certain substances to be carried inside cell e..g _____________, _______________ ...
No Slide Title
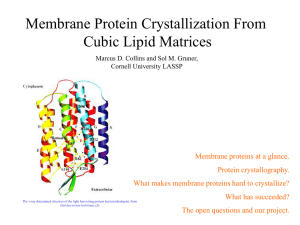
... and hydrophobic regions. Until very recently all protein crystallization techniques used an aqueous solvent for crystallization. Membrane proteins easily denature (that is, lose their structure) in this environment. In 1984 the first membrane protein, a photosynthetic reaction center, was crystalliz ...
... and hydrophobic regions. Until very recently all protein crystallization techniques used an aqueous solvent for crystallization. Membrane proteins easily denature (that is, lose their structure) in this environment. In 1984 the first membrane protein, a photosynthetic reaction center, was crystalliz ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.