biopsychology-2-synaptic-transmission
... AQA A Specification:The structure and function of sensory, relay and motor neurons. The process of synaptic transmission, including reference to neurotransmitters, excitation and inhibition. ...
... AQA A Specification:The structure and function of sensory, relay and motor neurons. The process of synaptic transmission, including reference to neurotransmitters, excitation and inhibition. ...
Activity of Spiking Neurons Stimulated by External Signals of
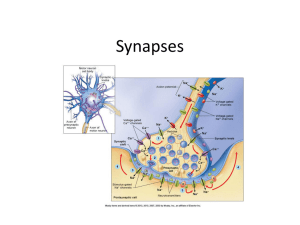
... deliver signals and act like an “input device”. Soma is the “central processing unit” that generates a signal if the total input exceeds a certain threshold (about -30 mV) and the axon transmits the signals to other neurons. Synapses are the contact points for transferring information between neuron ...
... deliver signals and act like an “input device”. Soma is the “central processing unit” that generates a signal if the total input exceeds a certain threshold (about -30 mV) and the axon transmits the signals to other neurons. Synapses are the contact points for transferring information between neuron ...
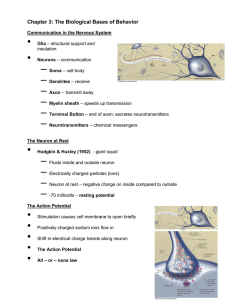
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... Voltage change at receptor site – postsynaptic potential (PSP) ...
... Voltage change at receptor site – postsynaptic potential (PSP) ...
Special Seminar Dynamic Control of Dentritic Excitability During Hippocampal Rhythmic Activity
... Dendrites of pyramidal neurons receive about 50000 excitatory and inhibitory synapses. Our lab studies how dendrites integrate synaptic input and transform it into action potential output. Hippocampal theta rhythm is important for encoding and retrieval of memories. During hippocampal theta episodes ...
... Dendrites of pyramidal neurons receive about 50000 excitatory and inhibitory synapses. Our lab studies how dendrites integrate synaptic input and transform it into action potential output. Hippocampal theta rhythm is important for encoding and retrieval of memories. During hippocampal theta episodes ...
here
... 4. What are three types of information that neurons must process? What does each type allow us to do? ...
... 4. What are three types of information that neurons must process? What does each type allow us to do? ...
LTP
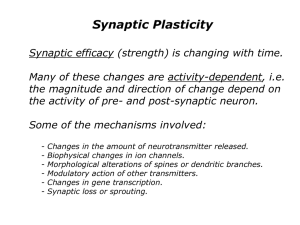
... Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
... Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
steps in nerve impulse transmission
... 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarizati ...
... 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarizati ...
Ca 2+
... strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a finely tuned regulation of synaptic tran ...
... strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a finely tuned regulation of synaptic tran ...
Brainsignals, Synaptic Transmission and Short
... strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a finely tuned regulation of synaptic tran ...
... strength changes constantly, depending upon use of a synapse Plasticity of synaptic connections underlies the complex information processing of the CNS Plasticity occurs on time scales of milliseconds to years Nature uses all possible mechanisms, to achieve a finely tuned regulation of synaptic tran ...
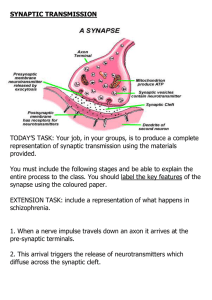
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... Synaptic transmission: Additional Information Neurotransmitters include: dopamine, acetylcholine and serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, ...
... Synaptic transmission: Additional Information Neurotransmitters include: dopamine, acetylcholine and serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, ...
Chapter 48 Reading Guide and Key Terms
... In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. How would this affect nervous system function? ...
... In the disease multiple sclerosis, myelin sheaths gradually harden and deteriorate. How would this affect nervous system function? ...
drugs and neuronal plasticity summary
... of learning processes drug-associated cues can trigger craving and compulsive drugseeking behaviour voluntary control is lost. Abused drugs can also modulate long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) in neuronal circuits associated with the addiction process, suggesting a way f ...
... of learning processes drug-associated cues can trigger craving and compulsive drugseeking behaviour voluntary control is lost. Abused drugs can also modulate long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) in neuronal circuits associated with the addiction process, suggesting a way f ...
Nerve cells - Spark (e
... In biology are defined dendrites the minor fibers branching from the neuron, they carry nerve signals in centripetal direction. The dendrites are shorter and thinner than the axon. ...
... In biology are defined dendrites the minor fibers branching from the neuron, they carry nerve signals in centripetal direction. The dendrites are shorter and thinner than the axon. ...
Mind Is Matter
... Terminal endings Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmit ...
... Terminal endings Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmit ...
Neurons - Seung Lab
... • Thin and often long. • A single axon leaves the soma, but may later branch, usually at right angles. • Action potentials travel from the soma to the presynaptic terminals. ...
... • Thin and often long. • A single axon leaves the soma, but may later branch, usually at right angles. • Action potentials travel from the soma to the presynaptic terminals. ...
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
... several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
PNS and Transmission
... in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through synaptic cleft neurotransmitters bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane. • Depending on t ...
... in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through synaptic cleft neurotransmitters bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane. • Depending on t ...
Actin , Synaptic plasticity in Parallel fibre-Purkinje Neuron
... Calcium current from cells injected with Latrunculin . It was observed that the Calcium current amplitude is decreasing after Latrunculin injection over a time period. This has been reported in many other cells even though not well documented in neurons. To study the possibility of the variations in ...
... Calcium current from cells injected with Latrunculin . It was observed that the Calcium current amplitude is decreasing after Latrunculin injection over a time period. This has been reported in many other cells even though not well documented in neurons. To study the possibility of the variations in ...
Powerpoint slides
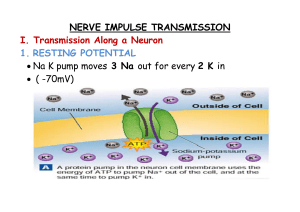
... About -70 mV Selectively allowing certain ions in With stimulation Na+ is allowed in ...
... About -70 mV Selectively allowing certain ions in With stimulation Na+ is allowed in ...
Understanding-the.. - Windsor C
... • Resting potential: resting axon has a – charge • Action potential: when excited, pores open and + ions flow through axon “firing” an electrical pathway to the terminal button – Increase in + ions is called depolarization – the # of ions necessary for “firing” is called the threshold • Once the pro ...
... • Resting potential: resting axon has a – charge • Action potential: when excited, pores open and + ions flow through axon “firing” an electrical pathway to the terminal button – Increase in + ions is called depolarization – the # of ions necessary for “firing” is called the threshold • Once the pro ...
Lecture #21 Date
... Intracellular/extracellular ionic concentration difference K+ diffuses out (Na+ in); large anions cannot follow….why not? Net negative charge of about -70mV ...
... Intracellular/extracellular ionic concentration difference K+ diffuses out (Na+ in); large anions cannot follow….why not? Net negative charge of about -70mV ...
Developmental plasticity: Pruning
... Studies of GM maturation show a loss in cortical GM density over time, which temporally correlates with postmortem findings of increased synaptic pruning during adolescence and early adulthood. The primary cause for loss of GM density is unknown. It may be driven at least partially by the process of ...
... Studies of GM maturation show a loss in cortical GM density over time, which temporally correlates with postmortem findings of increased synaptic pruning during adolescence and early adulthood. The primary cause for loss of GM density is unknown. It may be driven at least partially by the process of ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.