Synaptic Transmission
... message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
... message and can be inhibitory. When they bind to the post-synaptic neuron, they let potassium out instead of sodium in, which makes the neuron even more negative! ...
Neurons and how they communicate
... neuron to fire off its own message, or inhibitory, decreasing the probability that the neuron will fire The power to restrain is just as crucial as important as the power to engage in action ...
... neuron to fire off its own message, or inhibitory, decreasing the probability that the neuron will fire The power to restrain is just as crucial as important as the power to engage in action ...
Message Transmission
... don't actually touch each other. • The sender neuron is the presynaptic neuron • The receiving one is the postsynaptic neuron • Crossing the cleft is called synaptic transmission – One-way process handled by neurotransmitters released from synaptic vesicles located in the synaptic knobs and ...
... don't actually touch each other. • The sender neuron is the presynaptic neuron • The receiving one is the postsynaptic neuron • Crossing the cleft is called synaptic transmission – One-way process handled by neurotransmitters released from synaptic vesicles located in the synaptic knobs and ...
Module 4 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... understanding the rest of the course. Action potentials travel down the axon until reaching a tiny junction, the synapse. Then, the action potential stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules. They cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This allows ions ...
... understanding the rest of the course. Action potentials travel down the axon until reaching a tiny junction, the synapse. Then, the action potential stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules. They cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This allows ions ...
48 Nervous System PowerPoint
... What is saltatory conduction? P.970 What is a Node of Ranvier? What is a synapse? ...
... What is saltatory conduction? P.970 What is a Node of Ranvier? What is a synapse? ...
Brain 1
... The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the synapse occur that result in increased firing to the same stimulus. These changes in the ...
... The record indicates the rate of nerve firing measured in the postsynaptic neuron due to this initial experience. (b) After continued firing occurs due to repetitions of the experience, structural changes at the synapse occur that result in increased firing to the same stimulus. These changes in the ...
Ch. 48 - 49
... Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
... Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... • Synapse at which the neurotransmitter decreases the likelihood that an action potential will occur • NT open Cl- or K+ channel hyperpolarization • E.g. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) ...
... • Synapse at which the neurotransmitter decreases the likelihood that an action potential will occur • NT open Cl- or K+ channel hyperpolarization • E.g. GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) ...
Action Potential revisited When a stimulus reaches threshold level
... therefore, hyperpolarization occurs, and the cell is said to be in a refractory period (toilet flushing) The Sodium-Potassium pump moves ions back across the membrane against the concentration gradient, and resting potential is restored. The refractory period helps to ensure that stimulus only flows ...
... therefore, hyperpolarization occurs, and the cell is said to be in a refractory period (toilet flushing) The Sodium-Potassium pump moves ions back across the membrane against the concentration gradient, and resting potential is restored. The refractory period helps to ensure that stimulus only flows ...
PowerPoint for 9/29
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
Neural Pathways
... outside 3. channels then automatically close very quickly, but this causes the neighboring channels to open 4. it proceeds like a wave along the membrane to the tip of the axon 5. then it arrives at the synapse ...
... outside 3. channels then automatically close very quickly, but this causes the neighboring channels to open 4. it proceeds like a wave along the membrane to the tip of the axon 5. then it arrives at the synapse ...
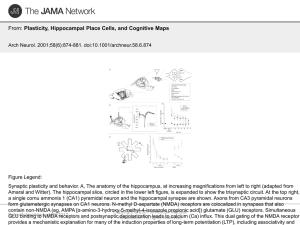
Plasticity, Hippocampal Place Cells, and Cognitive Maps
... receptors and postsynapticAssociation. depolarization leads to calcium (Ca) influx. This dual gating of the NMDA receptor All rights reserved. provides a mechanistic explanation for many of the induction properties of long-term potentiation (LTP), including associativity and ...
... receptors and postsynapticAssociation. depolarization leads to calcium (Ca) influx. This dual gating of the NMDA receptor All rights reserved. provides a mechanistic explanation for many of the induction properties of long-term potentiation (LTP), including associativity and ...
overview of neural f..
... The sodium-potassium pump is an active process that returns & maintains levels of Na+ and K+ ...
... The sodium-potassium pump is an active process that returns & maintains levels of Na+ and K+ ...
Threshold Stimulus
... potential • Blocks _______ channels • Sodium cannot flow into the cell, so threshold is not achieved ...
... potential • Blocks _______ channels • Sodium cannot flow into the cell, so threshold is not achieved ...
Membrane Biophysics and Synaptic Physiology
... dependence of release, two models and mechanisms? •Multivesicular release, when and where? •Synaptic ...
... dependence of release, two models and mechanisms? •Multivesicular release, when and where? •Synaptic ...
Nervous System Study Guide
... and potassium amount inside and outside of neuron cell. 6. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of sodium amount outside and inside the cell? 7. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of K+ ions inside and outside the neuron cell? 8. Functions of sodium-potassium pumps during action potentia ...
... and potassium amount inside and outside of neuron cell. 6. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of sodium amount outside and inside the cell? 7. When a neuron at rest, what is the amount of K+ ions inside and outside the neuron cell? 8. Functions of sodium-potassium pumps during action potentia ...
The Synaptic Cleft or Synapse
... A neuron’s axon ends in many small swellings called axon terminals. At the axon terminal the neuron may meet dendrites of another axon or an effector, like a muscle or gland. The space where neurons meet other neurons or effectors is called the synapse. There are presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic ...
... A neuron’s axon ends in many small swellings called axon terminals. At the axon terminal the neuron may meet dendrites of another axon or an effector, like a muscle or gland. The space where neurons meet other neurons or effectors is called the synapse. There are presynaptic neurons and postsynaptic ...
Cognitive Psychology
... Neural membrane • There are specialized structures in the neural membrane that allow various elements to cross in and out of the cell – Ion channels: Proteins that cross the cell wall, creating pores that allow ions (Na+, K+, Cl-) to pass. – Specific to particular ions; more K+ channels – Nongated ...
... Neural membrane • There are specialized structures in the neural membrane that allow various elements to cross in and out of the cell – Ion channels: Proteins that cross the cell wall, creating pores that allow ions (Na+, K+, Cl-) to pass. – Specific to particular ions; more K+ channels – Nongated ...
Lecture 2 - Nerve Impulse
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
... Potential: occurs when there is a change in polarity in the axon’s membrane. “All or none” - Depolarization - When the inside of the axon first becomes positive compared to the outside of the cell. Na+ ions move to the inside of the axon. - Repolarization - When the inside of the axon becomes negati ...
File
... K+ ions across the axonal membrane, resulting in a net positive charge outside and a negative charge inside the neuron. 2. Depolarization – an active transport process that requires ATP and protein channels. Depolarization occurs when Na+ moves into the cell, causing the charge on the axonal membran ...
... K+ ions across the axonal membrane, resulting in a net positive charge outside and a negative charge inside the neuron. 2. Depolarization – an active transport process that requires ATP and protein channels. Depolarization occurs when Na+ moves into the cell, causing the charge on the axonal membran ...
Nervous System
... One extension is different from all the others, and is called the axon. The purpose of the axon is to transmit an electro-chemical signal to other neurons, sometimes over a considerable distance. In the neurons that make up the nerves running from the spinal cord to your toes, the axons can be as lo ...
... One extension is different from all the others, and is called the axon. The purpose of the axon is to transmit an electro-chemical signal to other neurons, sometimes over a considerable distance. In the neurons that make up the nerves running from the spinal cord to your toes, the axons can be as lo ...
Slide ()
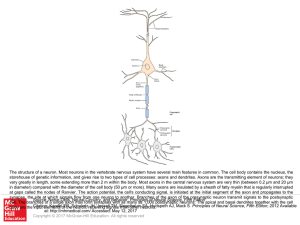
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.