The Nervous System
... • 1. concentration difference of ions on either side of membrane represents potential energy-kind of like of cocked gun • 2. stacked dominoes waiting to fall over • 3. one domino falling over initiates a wave of action potentials spreading out like the ripples in a pond • 4. each action potential is ...
... • 1. concentration difference of ions on either side of membrane represents potential energy-kind of like of cocked gun • 2. stacked dominoes waiting to fall over • 3. one domino falling over initiates a wave of action potentials spreading out like the ripples in a pond • 4. each action potential is ...
Open Document - Clinton Community College
... Neuron at rest: ◦ Slightly negative charge ◦ Contains ions flowing back and forth ...
... Neuron at rest: ◦ Slightly negative charge ◦ Contains ions flowing back and forth ...
big
... Excitatory inputs at the dendrites locally depolarize the membrane, called EPSPs. Inhibitory inputs at the dendrites locally hyperpolarize the membrane, called IPSPs. – Inputs propagate toward soma, where they are integrated ...
... Excitatory inputs at the dendrites locally depolarize the membrane, called EPSPs. Inhibitory inputs at the dendrites locally hyperpolarize the membrane, called IPSPs. – Inputs propagate toward soma, where they are integrated ...
Drugs Change the way Neurons communicate
... • Alcohol binds to GABA receptors on the dendrites of neurons which release GABA as their neurotransmitter. • Alcohol is an inhibitory signal (CNS depressant) so it reduces the activity of the presynaptic neuron (which releases GABA as its neurotransmitter). • The presynaptic neuron will release les ...
... • Alcohol binds to GABA receptors on the dendrites of neurons which release GABA as their neurotransmitter. • Alcohol is an inhibitory signal (CNS depressant) so it reduces the activity of the presynaptic neuron (which releases GABA as its neurotransmitter). • The presynaptic neuron will release les ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
... Cell body: serves to integrate the inputs from the dendrites Axon: one cell has a single output which is axon. Axons may be very long (over a foot) Synaptic junction: an axon impinges on a dendrite which causes input/output signal transitions ...
... Cell body: serves to integrate the inputs from the dendrites Axon: one cell has a single output which is axon. Axons may be very long (over a foot) Synaptic junction: an axon impinges on a dendrite which causes input/output signal transitions ...
document
... cell result in a temporary hyperpolarized membrane potential. Ion channels reset and the Na+/K+ pump returns the ions to the normal gradients. ...
... cell result in a temporary hyperpolarized membrane potential. Ion channels reset and the Na+/K+ pump returns the ions to the normal gradients. ...
here
... vision, taste touch) to the CNS. Relay Neurons – Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other. Only found in brain and spinal cord. Motor Neurons – form synapses with muscles and control their contractions. ...
... vision, taste touch) to the CNS. Relay Neurons – Allow sensory and motor neurons to communicate with each other. Only found in brain and spinal cord. Motor Neurons – form synapses with muscles and control their contractions. ...
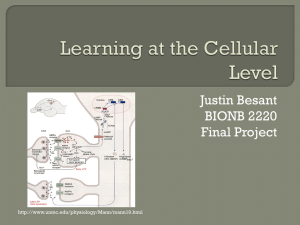
Learning at the Cellular Level
... learning can occur at the cellular level? How this be modeled and simulated quickly using the Izhikevich model? ...
... learning can occur at the cellular level? How this be modeled and simulated quickly using the Izhikevich model? ...
Lectures on mathematical neuroscience
... can encode information - place cells in hippocampus - coincidence detection for sound localization - orientation selectivity in visual cortex ...
... can encode information - place cells in hippocampus - coincidence detection for sound localization - orientation selectivity in visual cortex ...
Notes – Neurons and the nervous system
... At rest, the fluid inside a neuron has an excess of negatively charged ions. i.e. a negative resting potential When a neuron is in its resting state, sodium channels are blocked, thus keeping excess positive ions out of the cell. When a nearby neuron fires an action potential, this triggers so ...
... At rest, the fluid inside a neuron has an excess of negatively charged ions. i.e. a negative resting potential When a neuron is in its resting state, sodium channels are blocked, thus keeping excess positive ions out of the cell. When a nearby neuron fires an action potential, this triggers so ...
Lecture 6
... • Glial cells provide support to neurons: suck up the spilt-over neuro-transmitters or provide myelin sheets around axons or neurons • Neuron cells: 10^11 in our brains Neurons receive input through synapses on its dendrites; dendritic trees often receive more than 10,000 synapses Neurons communica ...
... • Glial cells provide support to neurons: suck up the spilt-over neuro-transmitters or provide myelin sheets around axons or neurons • Neuron cells: 10^11 in our brains Neurons receive input through synapses on its dendrites; dendritic trees often receive more than 10,000 synapses Neurons communica ...
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... • -Separation of charges (inside more negative) • -Caused by differences in permeability between Na+ and K+ – K+ allowed to leave, and Na+ can not enter the cell ...
... • -Separation of charges (inside more negative) • -Caused by differences in permeability between Na+ and K+ – K+ allowed to leave, and Na+ can not enter the cell ...
Ramón y Cajal, 19 th century
... Neuronal activity changes the intracellular calcium. Via changes in intra-cellular calcium, neurons change their morphology with respect to their axonal and dendritic shape. This leads to changes in neuronal connectivity which, in turn, adapts neuronal activity. The goal is that by these changes neu ...
... Neuronal activity changes the intracellular calcium. Via changes in intra-cellular calcium, neurons change their morphology with respect to their axonal and dendritic shape. This leads to changes in neuronal connectivity which, in turn, adapts neuronal activity. The goal is that by these changes neu ...
neurons
... Neurotransmitters in the synapse are reabsorbed into the sending neurons through the process of ...
... Neurotransmitters in the synapse are reabsorbed into the sending neurons through the process of ...
Myers Module Four
... electrical charge. If strong enough, this produces depolarization and an action potential. This depolarization produces another action potential a little farther along the axon. Gates in this neighbouring area are now open, and sodium ions rush in. The sodium/potassium pump in the cell membrane tran ...
... electrical charge. If strong enough, this produces depolarization and an action potential. This depolarization produces another action potential a little farther along the axon. Gates in this neighbouring area are now open, and sodium ions rush in. The sodium/potassium pump in the cell membrane tran ...
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
... Describe resting membrane potential. Explain how action potentials are generated ...
... Describe resting membrane potential. Explain how action potentials are generated ...
The Nervous Systeminofnotes
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
“The Physiology of Excitable Cells”
... magnitude of passive changes in membrane potential. Related to [ion channel]. ...
... magnitude of passive changes in membrane potential. Related to [ion channel]. ...
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... • Resting potential: membrane potential at rest; polarized – Na+ outside, K+ inside cell – Voltage-gated Na+ channel = CLOSED • Nerve impulse: stimulus causes a change in membrane potential – Action potential: neuron membrane depolarizes – All-or-nothing response ...
... • Resting potential: membrane potential at rest; polarized – Na+ outside, K+ inside cell – Voltage-gated Na+ channel = CLOSED • Nerve impulse: stimulus causes a change in membrane potential – Action potential: neuron membrane depolarizes – All-or-nothing response ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.