The Neuron - Austin Community College
... that is still above threshold by the time it reaches the trigger zone, so an action potential results. ...
... that is still above threshold by the time it reaches the trigger zone, so an action potential results. ...
CH 12 shortened for test three nervous tissue A and P 2016
... - Na/K pump uses 70% of the energy needs of the nervous system diffusion, selective permeability, and ion concentration result in the electrical differences across the membrane which allows for nerve conduction to take place ...
... - Na/K pump uses 70% of the energy needs of the nervous system diffusion, selective permeability, and ion concentration result in the electrical differences across the membrane which allows for nerve conduction to take place ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Voltage-gated ion channels: channels that open and close in response to membrane potential changes. These ion channels are responsible the action potential Potassium channels: closed when resting, opens slowly in response to depolarization Sodium channels: (two types of gates) Activation: clos ...
... Voltage-gated ion channels: channels that open and close in response to membrane potential changes. These ion channels are responsible the action potential Potassium channels: closed when resting, opens slowly in response to depolarization Sodium channels: (two types of gates) Activation: clos ...
Nervous System - EMTStudyCenter.com
... 4. The portion of the nervous system that is considered involuntary is the somatic nervous system. sensory nervous system. autonomic nervous system. motor nervous system. 5. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT senses changes. analyzes changes. ...
... 4. The portion of the nervous system that is considered involuntary is the somatic nervous system. sensory nervous system. autonomic nervous system. motor nervous system. 5. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT senses changes. analyzes changes. ...
chapter 48
... o Gated ion channels are specialized proteins that span the membrane, and allow ions to diffuse back and forth across the membrane according to their respective gradients. o Chemically-gated ion channels respond to a chemical stimulus (ex. neurotransmitter) o Voltage-gated ion channels respond t ...
... o Gated ion channels are specialized proteins that span the membrane, and allow ions to diffuse back and forth across the membrane according to their respective gradients. o Chemically-gated ion channels respond to a chemical stimulus (ex. neurotransmitter) o Voltage-gated ion channels respond t ...
Lecture_30_2014
... • Excitatory (but sometimes inhibitory) depending on the location in the nervous system • Associated with the reward system!! • Requires a transport protein to inactivate ...
... • Excitatory (but sometimes inhibitory) depending on the location in the nervous system • Associated with the reward system!! • Requires a transport protein to inactivate ...
nervous5
... Exceptions: Peptide NTs originate in cell body, move in vesicles by fast orthograde axonal transport to axon terminal. ...
... Exceptions: Peptide NTs originate in cell body, move in vesicles by fast orthograde axonal transport to axon terminal. ...
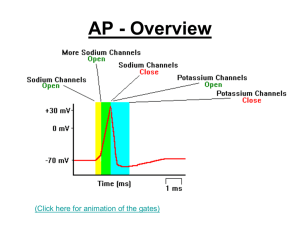
AP – All or nothing
... membrane, this is repolarisation • The membrane briefly becomes hyperpolarised (more negative on the inside than usual) • The Na+ / K+ channels close ...
... membrane, this is repolarisation • The membrane briefly becomes hyperpolarised (more negative on the inside than usual) • The Na+ / K+ channels close ...
Bio 3411 Problem Set 9 Name: (Due Monday, November 28th 2011
... b. Using the GHK equation altered to calculate relative conductances (as given in class) , calculated the relative conductances between Na+ and K+. Show your work. (1) ...
... b. Using the GHK equation altered to calculate relative conductances (as given in class) , calculated the relative conductances between Na+ and K+. Show your work. (1) ...
nervous system
... Neuron cell bodies are clustered together in the PNS= ganglia Satellite cells- surround neuron cell bodies, regulate environment Schwann cells- form a sheath around every axon, can myelinate axons ...
... Neuron cell bodies are clustered together in the PNS= ganglia Satellite cells- surround neuron cell bodies, regulate environment Schwann cells- form a sheath around every axon, can myelinate axons ...
Neurons and Neurotransmission
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
Neurons_and_Neurotranmission
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
... Neurotransmitters Acetylcholine • Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system • Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 • As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic ...
53 XIX BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O`Brien)
... 2. Membrane potential = electrical potential due to differences in concentrations of ions on either side of a neuron’s plasma membrane. 3. Action potential = electrical signal a. All-or-none change in membrane voltage at plasma membrane b. Inflow of sodium ions (Na+) is followed by outflow of potass ...
... 2. Membrane potential = electrical potential due to differences in concentrations of ions on either side of a neuron’s plasma membrane. 3. Action potential = electrical signal a. All-or-none change in membrane voltage at plasma membrane b. Inflow of sodium ions (Na+) is followed by outflow of potass ...
File
... opening of channels Depending on the ions that can pass through, channels are excitatory or inhibitory NT binds and an associated ion channel opens or closes, causing a PSP. If Na+ channels are opened, an EPSP occurs. If K+ channels are opened, an IPSP occurs ...
... opening of channels Depending on the ions that can pass through, channels are excitatory or inhibitory NT binds and an associated ion channel opens or closes, causing a PSP. If Na+ channels are opened, an EPSP occurs. If K+ channels are opened, an IPSP occurs ...
Ch 11 Part 2 - Groch Biology
... 9. Matching. a. absolute refractory period b. action potential c. depolarization d. frequency of impulses e. graded potential f. hyperpolarization g. polarized h. relative refractory period i. repolarization j. sodium-potassium pump k. subthreshold l. threshold 1. Corresponds to the period of repola ...
... 9. Matching. a. absolute refractory period b. action potential c. depolarization d. frequency of impulses e. graded potential f. hyperpolarization g. polarized h. relative refractory period i. repolarization j. sodium-potassium pump k. subthreshold l. threshold 1. Corresponds to the period of repola ...
here
... 4. What are three types of information that neurons must process? What does each type allow us to do? ...
... 4. What are three types of information that neurons must process? What does each type allow us to do? ...
Nervous System
... Nerve impulses reach the axonal terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron ...
... Nerve impulses reach the axonal terminal of the presynaptic neuron and open Ca2+ channels Neurotransmitter is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis Neurotransmitter crosses the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the postsynaptic neuron ...
File
... from the axon terminal, a skeletal muscle is triggered to contract, and the response is always ...
... from the axon terminal, a skeletal muscle is triggered to contract, and the response is always ...
The synapse.
... chemical synapses • 1) Conduction velocities are far to quick for ordinary metabolic activity (against). • Loew’s study with the two hearts ...
... chemical synapses • 1) Conduction velocities are far to quick for ordinary metabolic activity (against). • Loew’s study with the two hearts ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.