Sxn 2 Objectives
... Define graded potential. Identify where and how a graded potential can occur on a neuron. Give examples based on specific ion movements. Define threshold and action potential. Identify where and how an action potential can occur on a neuron. Compare and contrast graded potentials with action p ...
... Define graded potential. Identify where and how a graded potential can occur on a neuron. Give examples based on specific ion movements. Define threshold and action potential. Identify where and how an action potential can occur on a neuron. Compare and contrast graded potentials with action p ...
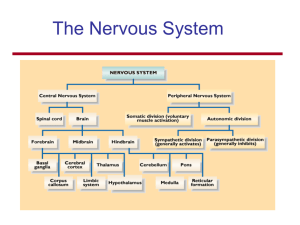
The Nervous System
... • This polarity reversal travels down the neuron • Neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminals ...
... • This polarity reversal travels down the neuron • Neurotransmitters are released at the axon terminals ...
In Pursuit of Ecstasy - Heartland Community College
... postsynaptic cell • Binding of neurotransmitter to receptors opens ion gates in membrane of postsynaptic cell ...
... postsynaptic cell • Binding of neurotransmitter to receptors opens ion gates in membrane of postsynaptic cell ...
Sensory function
... Action Potential (AP) • When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane to threshold, an action potential is generated. • An action potential consists of depolarizing and repolarizing phases. Which channels are open during depolarization? During repolarization? ...
... Action Potential (AP) • When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane to threshold, an action potential is generated. • An action potential consists of depolarizing and repolarizing phases. Which channels are open during depolarization? During repolarization? ...
Unit 2-Week 1 Notes Sheets
... - Nerve Impulse Axon Axon Terminal Release Neurotransmitter ...
... - Nerve Impulse Axon Axon Terminal Release Neurotransmitter ...
Neurons - Scott Melcher
... Neurons are intricately interwoven, but do not actually touch. The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving cell is called a synapse. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or cleft. When neurons are firing and action potent ...
... Neurons are intricately interwoven, but do not actually touch. The junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving cell is called a synapse. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or cleft. When neurons are firing and action potent ...
Slide ()
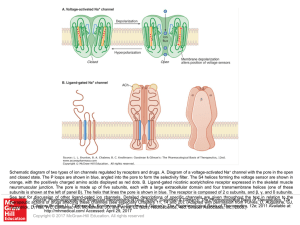
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
... Schematic diagram of two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are ...
File
... • nerve cells are surrounded by a semipermeable membrane (allows some ions to pass through and blocks the passage of other ions) ...
... • nerve cells are surrounded by a semipermeable membrane (allows some ions to pass through and blocks the passage of other ions) ...
Homeostasis Test%28CNS%29-Tawsif Hossain
... channels open and sodium ions move down the gradient into the axon. The potential difference of 40mV is reached. 2) As a result the sodium channels close and voltage gated potassium channels open. The potassium ions move down their concentration outside the axon carrying the positive charge out. Thi ...
... channels open and sodium ions move down the gradient into the axon. The potential difference of 40mV is reached. 2) As a result the sodium channels close and voltage gated potassium channels open. The potassium ions move down their concentration outside the axon carrying the positive charge out. Thi ...
lecture notes #4 membrane potentials
... and potassium ions to the inside (3Na+/2 K+), leaving a net deficit of positive ions on the inside 2. The Na+/K+ pump causes large concentrations gradient for sodium and potassium across the membrane Outside Inside Na+ 142 mEq/L 14 mEq/L K+ 4 mEq/L 140 mEq/L 3. Leakage of potassium through the nerve ...
... and potassium ions to the inside (3Na+/2 K+), leaving a net deficit of positive ions on the inside 2. The Na+/K+ pump causes large concentrations gradient for sodium and potassium across the membrane Outside Inside Na+ 142 mEq/L 14 mEq/L K+ 4 mEq/L 140 mEq/L 3. Leakage of potassium through the nerve ...
chapter 48
... • Proteins, amino acids, sulfate, and phosphate are the principal intracellular anions. ...
... • Proteins, amino acids, sulfate, and phosphate are the principal intracellular anions. ...
Biology Cells unit: LT8 Review
... Put the images in the correct order to represent the sodiumpotassium pump. The first one is already labeled #1. ...
... Put the images in the correct order to represent the sodiumpotassium pump. The first one is already labeled #1. ...
Transmission at the Synapse and the
... INDIRECT inhibition is the result of previous postsynaptic neuron discharges, eg. when the postsynaptic cell is refractory to excitation because it just fired PRESYNAPTIC INHIBITION AND FACILITATION happens when an inhibitory neuron sends a nerve ending to an excitatory synapse on another neuron, an ...
... INDIRECT inhibition is the result of previous postsynaptic neuron discharges, eg. when the postsynaptic cell is refractory to excitation because it just fired PRESYNAPTIC INHIBITION AND FACILITATION happens when an inhibitory neuron sends a nerve ending to an excitatory synapse on another neuron, an ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... membrane of another nearby neuron. Once the neurotransmitter is picked up by receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, the molecule is internalized in the neuron and the impulse continues. ...
... membrane of another nearby neuron. Once the neurotransmitter is picked up by receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, the molecule is internalized in the neuron and the impulse continues. ...
Summary Sodium pump.
... Vessicles • Arrival of the action potential causes some of the vesicles to move to the end of the axon and discharge their contents into the synaptic cleft. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft, and bind to receptors on the other cell's membrane, causing ion channels on that cell to ...
... Vessicles • Arrival of the action potential causes some of the vesicles to move to the end of the axon and discharge their contents into the synaptic cleft. Released neurotransmitters diffuse across the cleft, and bind to receptors on the other cell's membrane, causing ion channels on that cell to ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CH 48 AND 49
... D. How the nerve impulse moves from one cell to another • The space between two nerve cells is called a synapse • Two nerves communicate with each other by synaptic signaling • How: – When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, it stimulates the release of neurotransmitters into the syna ...
... D. How the nerve impulse moves from one cell to another • The space between two nerve cells is called a synapse • Two nerves communicate with each other by synaptic signaling • How: – When the action potential reaches the end of the axon, it stimulates the release of neurotransmitters into the syna ...
ch 48 clicker questions
... The use of organophosphate pesticides that inhibit acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine, could cause skeletal muscle cells to a) undergo more graded depolarizations, because acetylcholine would remain in the synaptic cleft longer. b) undergo more graded hyperpolarizations, ...
... The use of organophosphate pesticides that inhibit acetylcholinesterase, an enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine, could cause skeletal muscle cells to a) undergo more graded depolarizations, because acetylcholine would remain in the synaptic cleft longer. b) undergo more graded hyperpolarizations, ...
Document
... concentration gradients and electrical potentials across the membranes • The resting membrane potential of a neuron is negative and is said to be polarized • These gradients are maintained by the sodium potassium pump ...
... concentration gradients and electrical potentials across the membranes • The resting membrane potential of a neuron is negative and is said to be polarized • These gradients are maintained by the sodium potassium pump ...
Communication between Neurons
... Golgi bodies and sent along the axons down the microtubules at the hair raising speeds of between 1 -100mm per day. The majority of neurotransmitters are synthesised in the cytoplasm of the terminal button and from products obtained the diet. Acetylcholine for instance, a common neurotransmitter, is ...
... Golgi bodies and sent along the axons down the microtubules at the hair raising speeds of between 1 -100mm per day. The majority of neurotransmitters are synthesised in the cytoplasm of the terminal button and from products obtained the diet. Acetylcholine for instance, a common neurotransmitter, is ...
ACTION POTENTIALS
... it. Sodium ions want to enter the neuron from outside (due to polarity differences) but cannot, due to the semipermeable neural membrane. When the sodium channels open, sodium rushes into the neuron, causing the neuron to become very positively charged (up to +40 millevolts). This is depolarization. ...
... it. Sodium ions want to enter the neuron from outside (due to polarity differences) but cannot, due to the semipermeable neural membrane. When the sodium channels open, sodium rushes into the neuron, causing the neuron to become very positively charged (up to +40 millevolts). This is depolarization. ...
Nervous Systems
... • The plasma membrane is more permeable (more membrane channels) to K+ than to Na+. – Therefore, large amounts of K+ are transferred out of the cell (down the concentration gradient) – Small amounts of Na+ are transferred into the cell (down the concentration gradient) ...
... • The plasma membrane is more permeable (more membrane channels) to K+ than to Na+. – Therefore, large amounts of K+ are transferred out of the cell (down the concentration gradient) – Small amounts of Na+ are transferred into the cell (down the concentration gradient) ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology - University of British Columbia
... resulting hyperpolarization is called an Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential (IPSP All these potentials are additive. ...
... resulting hyperpolarization is called an Inhibitory Post Synaptic Potential (IPSP All these potentials are additive. ...
Nervous Systems - Groupfusion.net
... • The plasma membrane is more permeable (more membrane channels) to K+ than to Na+. – Therefore, large amounts of K+ are transferred out of the cell (down the concentration gradient) – Small amounts of Na+ are transferred into the cell (down the concentration gradient) ...
... • The plasma membrane is more permeable (more membrane channels) to K+ than to Na+. – Therefore, large amounts of K+ are transferred out of the cell (down the concentration gradient) – Small amounts of Na+ are transferred into the cell (down the concentration gradient) ...
EQ2.3 - nerve cells communicate-
... the membrane due to two phenomenas: electrical and chemical movement. Next, special proteins move ions back and forth across the membrane. Nerves tend to be interconnected by forming electrical activities. They communicate through neurotransmitters with another an nerve cell or a tissue of some kind ...
... the membrane due to two phenomenas: electrical and chemical movement. Next, special proteins move ions back and forth across the membrane. Nerves tend to be interconnected by forming electrical activities. They communicate through neurotransmitters with another an nerve cell or a tissue of some kind ...
action potential presen - Westgate Mennonite Collegiate
... Found in brain, spinal cord and nervous system Electrically excitable Communicate via electrical and chemical synapses Made up of a soma (cell body), dendritic tree and an axon ...
... Found in brain, spinal cord and nervous system Electrically excitable Communicate via electrical and chemical synapses Made up of a soma (cell body), dendritic tree and an axon ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.