Neurophysiology Worksheet
... ’propagate along the demyelinated axon; therefore, the muscle is not stimulated, leading to paralysis. Eventually, the muscles atrophy because of a lack of adequate activity involving contraction. ...
... ’propagate along the demyelinated axon; therefore, the muscle is not stimulated, leading to paralysis. Eventually, the muscles atrophy because of a lack of adequate activity involving contraction. ...
BOX 5.2 GOLDMAN-HODGKIN-KATZ EQUATION An equation
... describes the steady-state membrane potential for a given set of ionic concentrations inside and outside the cell and the relative permeabilities of the membrane to each of those ions: ...
... describes the steady-state membrane potential for a given set of ionic concentrations inside and outside the cell and the relative permeabilities of the membrane to each of those ions: ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
... CELL MEMBRANE: thin, porous outer covering of a neuron or other cell that separates the cell’s intracellular fluid from extracellular fluid ...
... CELL MEMBRANE: thin, porous outer covering of a neuron or other cell that separates the cell’s intracellular fluid from extracellular fluid ...
Electrical Communication #2
... making action potential possible again, though more stimulus than usual is required since the cell is farther from threshold than usual. ...
... making action potential possible again, though more stimulus than usual is required since the cell is farther from threshold than usual. ...
Physio study guide unit 2
... What two types of receptors can ACh bind to? What actions result from the binding of ACh at these two different receptors? How many ACh bind to an ACh receptor? What ion will flow through? What type of event would this trigger on a post-synaptic cell? What are Ionotropic receptors? That is, how do t ...
... What two types of receptors can ACh bind to? What actions result from the binding of ACh at these two different receptors? How many ACh bind to an ACh receptor? What ion will flow through? What type of event would this trigger on a post-synaptic cell? What are Ionotropic receptors? That is, how do t ...
A. What is a neuron? 1. A neuron is a type of cell that receives and
... 4. The amino acid tryptophan is the precursor for serotonin, another type of monoamine (indolamine). F. Release and Diffusion of Transmitters 1. Neurotransmitters are stored in vesicles (tiny nearly spherical packets) in the presynaptic terminal. (Nitric oxide is an exception to this rule, as neuro ...
... 4. The amino acid tryptophan is the precursor for serotonin, another type of monoamine (indolamine). F. Release and Diffusion of Transmitters 1. Neurotransmitters are stored in vesicles (tiny nearly spherical packets) in the presynaptic terminal. (Nitric oxide is an exception to this rule, as neuro ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
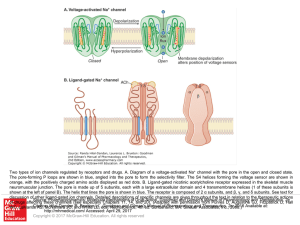
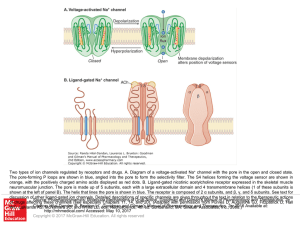
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
Slide ()
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
... Two types of ion channels regulated by receptors and drugs. A. Diagram of a voltage-activated Na+ channel with the pore in the open and closed state. The pore-forming P loops are shown in blue, angled into the pore to form the selectivity filter. The S4 helices forming the voltage sensor are shown i ...
Neuroscience in PT: Introduction and Review
... or the end-organs through fast excitatory (EPSP) or inhibitory (IPSI) postsynaptic potentials (<1 ms) – Directly opening ligand-gated ion channels on postsynaptic membrane • Slow-acting neuromodulation, occurring over 100ms to minutes – Indirect opening ion channels or activation the cellular signal ...
... or the end-organs through fast excitatory (EPSP) or inhibitory (IPSI) postsynaptic potentials (<1 ms) – Directly opening ligand-gated ion channels on postsynaptic membrane • Slow-acting neuromodulation, occurring over 100ms to minutes – Indirect opening ion channels or activation the cellular signal ...
nervous system
... • ___________ ________– space between adjacent neurons/effector cell • Presynaptic neuron - neuron bringing the depolarization wave to the ...
... • ___________ ________– space between adjacent neurons/effector cell • Presynaptic neuron - neuron bringing the depolarization wave to the ...
Functional Human Physiology for the Exercise and Sport Sciences
... post-synaptic membrane will determine if the net effect is excitatory or inhibitory. If the net effect is more excitatory than inhibitory, an action potential will be generated on the post-synaptic membrane and impulse transduction will occur The opposite is also true, a net inhibitory effect wi ...
... post-synaptic membrane will determine if the net effect is excitatory or inhibitory. If the net effect is more excitatory than inhibitory, an action potential will be generated on the post-synaptic membrane and impulse transduction will occur The opposite is also true, a net inhibitory effect wi ...
Understanding-the.. - Windsor C
... • Resting potential: resting axon has a – charge • Action potential: when excited, pores open and + ions flow through axon “firing” an electrical pathway to the terminal button – Increase in + ions is called depolarization – the # of ions necessary for “firing” is called the threshold • Once the pro ...
... • Resting potential: resting axon has a – charge • Action potential: when excited, pores open and + ions flow through axon “firing” an electrical pathway to the terminal button – Increase in + ions is called depolarization – the # of ions necessary for “firing” is called the threshold • Once the pro ...
Powerpoint version
... diffusion of Na+ in K+ would diffuse until it is balanced by its electrical gradient EK+ = –90 mV ...
... diffusion of Na+ in K+ would diffuse until it is balanced by its electrical gradient EK+ = –90 mV ...
Action Potentials
... _______________________________ • Voltage-gated channels needed for APs – fewer than 25 per m2 in myelin-covered regions – up to 12,000 per m2 in nodes of Ranvier ...
... _______________________________ • Voltage-gated channels needed for APs – fewer than 25 per m2 in myelin-covered regions – up to 12,000 per m2 in nodes of Ranvier ...
Synapse - MBBS Students Club
... • Let’s consider a stimulus at the dendrite of a neuron. The stimulus reaches the dendrite (postsynaptic neuron) from the axon (presynaptic neuron) with the help of a NT. • The NT leads to opening of simple ligand-gated channels that are present in the postsynaptic membrane, either Na+ or K+ channel ...
... • Let’s consider a stimulus at the dendrite of a neuron. The stimulus reaches the dendrite (postsynaptic neuron) from the axon (presynaptic neuron) with the help of a NT. • The NT leads to opening of simple ligand-gated channels that are present in the postsynaptic membrane, either Na+ or K+ channel ...
Synapse
... • Let’s consider a stimulus at the dendrite of a neuron. The stimulus reaches the dendrite (postsynaptic neuron) from the axon (presynaptic neuron) with the help of a NT. • The NT leads to opening of simple ligand-gated channels that are present in the postsynaptic membrane, either Na+ or K+ channel ...
... • Let’s consider a stimulus at the dendrite of a neuron. The stimulus reaches the dendrite (postsynaptic neuron) from the axon (presynaptic neuron) with the help of a NT. • The NT leads to opening of simple ligand-gated channels that are present in the postsynaptic membrane, either Na+ or K+ channel ...
Name:
... 2. Next do the exercise to see how a cell membrane becomes repolarized. Draw a cell membrane below that is repolarized showing all ions along with all gates. Show which gates are closed and which are opened. What gate(s ) did you manipulate and how? ...
... 2. Next do the exercise to see how a cell membrane becomes repolarized. Draw a cell membrane below that is repolarized showing all ions along with all gates. Show which gates are closed and which are opened. What gate(s ) did you manipulate and how? ...
Neural Tissue – Chapter 12
... Step One: Sodium ions enter the cell and are attracted to the negative charges along the inner surface of the membrane. The arrival of positive charges shifts the transmembrane potential toward 0 mV. This is called depolarization. Step Two: At the resting potential, sodium ions are drawn to the oute ...
... Step One: Sodium ions enter the cell and are attracted to the negative charges along the inner surface of the membrane. The arrival of positive charges shifts the transmembrane potential toward 0 mV. This is called depolarization. Step Two: At the resting potential, sodium ions are drawn to the oute ...
Syllabus
... to complex networks to higher brain functions. First half of the introductory 160-‐ 161 sequence. ...
... to complex networks to higher brain functions. First half of the introductory 160-‐ 161 sequence. ...
Physio Lab 5 PhysioEx 3
... All cells have a resting membrane potential (RMP). Intracellular fluid is rich in negatively charged proteins that are balanced mainly by positively charge potassium ions. As the cell membrane is permeable or “leaky” to potassium but not to protein, the excess unbalanced negative charge leads to the ...
... All cells have a resting membrane potential (RMP). Intracellular fluid is rich in negatively charged proteins that are balanced mainly by positively charge potassium ions. As the cell membrane is permeable or “leaky” to potassium but not to protein, the excess unbalanced negative charge leads to the ...
nervous tissue organization neurons neuroglia action potentials
... synaptic plasticity = the ability of a synapse to change synaptic potentiation = ability to make transmission easier immediate = able to hold for a few seconds short term = remember for a few sec to hours, then forgotten working = stored in brain & can be recalled by new input, facilitated synapses ...
... synaptic plasticity = the ability of a synapse to change synaptic potentiation = ability to make transmission easier immediate = able to hold for a few seconds short term = remember for a few sec to hours, then forgotten working = stored in brain & can be recalled by new input, facilitated synapses ...
Neurotransmission Notes
... The sending neuron reabsorbs any excess NT’s left in the synapse. This is called reuptake. Neurotransmitters can be excitatory (causing EPSP’s or excitatory post-synaptic potential) or inhibitory (causing IPSPs or inhibitory post-synaptic potential). Excitatory NTs bring the dendrite closer to thres ...
... The sending neuron reabsorbs any excess NT’s left in the synapse. This is called reuptake. Neurotransmitters can be excitatory (causing EPSP’s or excitatory post-synaptic potential) or inhibitory (causing IPSPs or inhibitory post-synaptic potential). Excitatory NTs bring the dendrite closer to thres ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.