overview of neural f..
... The sodium-potassium pump is an active process that returns & maintains levels of Na+ and K+ ...
... The sodium-potassium pump is an active process that returns & maintains levels of Na+ and K+ ...
Learning Objectives
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
Nerve Impulse Transmission
... If a stimulus (e.g. pressure, sound, etc.) is strong enough, a nerve impulse is initiated => action potential ...
... If a stimulus (e.g. pressure, sound, etc.) is strong enough, a nerve impulse is initiated => action potential ...
Chapter 17 Part A
... - sodium gates open (membrane suddenly permeable to Na+ ions) - charge inside changes to positive as Na+ ions flood interior - increases until rising voltage opposes inward flow of Na+ (peak of the graph) - repolarization from +40 mV to –65 mV - sodium gates close and potassium gates (in addition to ...
... - sodium gates open (membrane suddenly permeable to Na+ ions) - charge inside changes to positive as Na+ ions flood interior - increases until rising voltage opposes inward flow of Na+ (peak of the graph) - repolarization from +40 mV to –65 mV - sodium gates close and potassium gates (in addition to ...
Neural Control II
... that crosses the synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber – This type of synapse is known as a neuromuscular junction – Ach binds to its receptor proteins in the postsynaptic membrane, causing ligand-gated ion channels to open ...
... that crosses the synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber – This type of synapse is known as a neuromuscular junction – Ach binds to its receptor proteins in the postsynaptic membrane, causing ligand-gated ion channels to open ...
Neuromuscular Blockade - Health Education East Midlands VLE
... Safe use of Neuromuscular Blockade ...
... Safe use of Neuromuscular Blockade ...
Chapter 2
... Ionotropic – direct method; contains binding site for neurotransmitter, which when activated, opens an ion channel to allow ions into cell to produce postsynaptic potential (see Fig 2.33 in text); effects do not last long Metabotropic – indirect method, long-lasting effects; contain neurotransmitter ...
... Ionotropic – direct method; contains binding site for neurotransmitter, which when activated, opens an ion channel to allow ions into cell to produce postsynaptic potential (see Fig 2.33 in text); effects do not last long Metabotropic – indirect method, long-lasting effects; contain neurotransmitter ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors proteins and open the ion channels of the new neuron cell. • If enough ion channels are opened, the action potential will continue through the new neuron. If not, the nervous signal will be terminated. • After the n ...
... neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors proteins and open the ion channels of the new neuron cell. • If enough ion channels are opened, the action potential will continue through the new neuron. If not, the nervous signal will be terminated. • After the n ...
Action_ Resting_Potential
... resting state. In the resting state, the inside of a neuron has a slightly higher concentration of negatively charged ions than the outside does. This situation creates a slight negative charge inside the neuron, which acts as a store of potential energy called the resting potential. The resting pot ...
... resting state. In the resting state, the inside of a neuron has a slightly higher concentration of negatively charged ions than the outside does. This situation creates a slight negative charge inside the neuron, which acts as a store of potential energy called the resting potential. The resting pot ...
7. Describe what membrane potential is, and how
... • EPSP excitatory postsynaptic potentials - occur when excitatory synapses release a neurotransmitter that opens gated channels allowing Na+ to enter the cell and K+ to leave (depolarization) • IPSP inhibitory postsynaptic potentials - occur when neurotransmitters released from inhibitory synaps ...
... • EPSP excitatory postsynaptic potentials - occur when excitatory synapses release a neurotransmitter that opens gated channels allowing Na+ to enter the cell and K+ to leave (depolarization) • IPSP inhibitory postsynaptic potentials - occur when neurotransmitters released from inhibitory synaps ...
NEUROCHEMISTRY & NEUROTRANSMITTERS
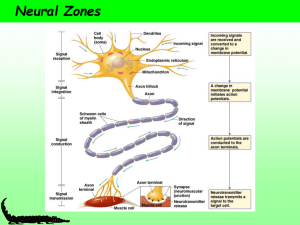
... INFORMATION BY ELECTRICAL AND CHEMICAL MEANS. THE INFORMATION, TYPICALLY (BUT WITH EXCEPTIONS), TRAVELS FROM THE DENDRITE THROUGH THE CELL BODY AND THE AXON TO THE AXON TERMINALS. JUST LIKE HORMONES, THE COMMUNICATION (OR SIGNALLING) IS MEANT TO COORDINATE THE ACTIONS OF HIGHER ORGANISMS, BUT IN A M ...
... INFORMATION BY ELECTRICAL AND CHEMICAL MEANS. THE INFORMATION, TYPICALLY (BUT WITH EXCEPTIONS), TRAVELS FROM THE DENDRITE THROUGH THE CELL BODY AND THE AXON TO THE AXON TERMINALS. JUST LIKE HORMONES, THE COMMUNICATION (OR SIGNALLING) IS MEANT TO COORDINATE THE ACTIONS OF HIGHER ORGANISMS, BUT IN A M ...
week4am
... see depolarization (change from negative inside neuron to more positive) ◦ “threshold” – if a great enough depolarization occurs, an action potential will occur ◦ action potential – very quick – milliseconds Other terms – spike, firing, generating an AP ...
... see depolarization (change from negative inside neuron to more positive) ◦ “threshold” – if a great enough depolarization occurs, an action potential will occur ◦ action potential – very quick – milliseconds Other terms – spike, firing, generating an AP ...
Neuro2
... receive many simultaneous stimuli because of their many dendrites. As one, long continuous fiber pseudounipolar neurons can conduct impulses through the body very rapidly. 5) Vesicles full of fun stuff like adrenaline and acetylcholine (or maybe just peptides) are formed at trans Golgi network. Thes ...
... receive many simultaneous stimuli because of their many dendrites. As one, long continuous fiber pseudounipolar neurons can conduct impulses through the body very rapidly. 5) Vesicles full of fun stuff like adrenaline and acetylcholine (or maybe just peptides) are formed at trans Golgi network. Thes ...
Q1 (from chapter 1)
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
Neurophysiology Neurotransmitter and Nervous System
... activation of a receptor site is called the post synaptic potential (PSP). IPSP – when the change causes hyperpolarization or makes the cell harder to fire, this is called an inhibitory post synaptic potential. EPSP – when the change causes depolarization, this is called an excitatory post synap ...
... activation of a receptor site is called the post synaptic potential (PSP). IPSP – when the change causes hyperpolarization or makes the cell harder to fire, this is called an inhibitory post synaptic potential. EPSP – when the change causes depolarization, this is called an excitatory post synap ...
Brains, Synapses and Neurotransmitters
... Axons transmit information Dendrites receive information Dendrites can grow and change • Make connections to more axons • Might be the basis of learning ...
... Axons transmit information Dendrites receive information Dendrites can grow and change • Make connections to more axons • Might be the basis of learning ...
Slide 1
... 1. Neurons are electrically active; They have a resting voltage, and can undergo electrical changes ...
... 1. Neurons are electrically active; They have a resting voltage, and can undergo electrical changes ...
Structure of a Neuron Transmission of “Information” Nerve Impulse
... Unbranched except at its end Terminal part – swellings ...
... Unbranched except at its end Terminal part – swellings ...
Nervous System
... o Domino affect = one Na+ opening triggers the next and so on… causes membrane potential increases to +35 mV (outside = - ; inside = +) • all or none principle: all the way to +35 mV or not o So long as they can reach the threshold of the cell, strong stimuli produce no stronger action potentials ...
... o Domino affect = one Na+ opening triggers the next and so on… causes membrane potential increases to +35 mV (outside = - ; inside = +) • all or none principle: all the way to +35 mV or not o So long as they can reach the threshold of the cell, strong stimuli produce no stronger action potentials ...
Ch.10
... inside the cell. • There is a higher concentration of Na+ outside the membrane and higher K+ concentration inside. The Na+/ K+ pumps, three sodium ions out for every two potassium ions it pumps in. • When voltage-gated channels open and close the concentration of ions change, causing a change in mem ...
... inside the cell. • There is a higher concentration of Na+ outside the membrane and higher K+ concentration inside. The Na+/ K+ pumps, three sodium ions out for every two potassium ions it pumps in. • When voltage-gated channels open and close the concentration of ions change, causing a change in mem ...
Synapses - UBC Zoology
... • electrical signal in the presynaptic cell is communicated to the postsynaptic cell by a chemical (the neurotransmitter) • separation between presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes is about 20 to 30 nm • a chemical transmitter is released and diffuses to bind to receptors on postsynaptic side • bin ...
... • electrical signal in the presynaptic cell is communicated to the postsynaptic cell by a chemical (the neurotransmitter) • separation between presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes is about 20 to 30 nm • a chemical transmitter is released and diffuses to bind to receptors on postsynaptic side • bin ...
Action Potential Webquest
... Watch this animation. It shows how membrane potential (resting potential) develops in the neuron cell. 1. What causes the inside of the cell to be more negative compared to the outside of the cell? ...
... Watch this animation. It shows how membrane potential (resting potential) develops in the neuron cell. 1. What causes the inside of the cell to be more negative compared to the outside of the cell? ...
Action Potential Webquest
... Go to http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YP_P6bYvEjE Watch this video. It shows how membrane potential (resting potential) develops in the neuron cell. 1. What causes the inside of the cell to be more negative compared to the outside of the cell? ...
... Go to http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YP_P6bYvEjE Watch this video. It shows how membrane potential (resting potential) develops in the neuron cell. 1. What causes the inside of the cell to be more negative compared to the outside of the cell? ...
SChapter 12
... -Action potentials are propagated quickly ▫Chemical synapse -Most neural synapses, all between neurons and other cells -Neurotransmitters released into synapse, picked up by receptors on postsynaptic cell -Can be excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitters ▪Cholinergic synapses- release of ACh at syn ...
... -Action potentials are propagated quickly ▫Chemical synapse -Most neural synapses, all between neurons and other cells -Neurotransmitters released into synapse, picked up by receptors on postsynaptic cell -Can be excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitters ▪Cholinergic synapses- release of ACh at syn ...
End-plate potential

End plate potentials (EPPs) are the depolarizations of skeletal muscle fibers caused by neurotransmitters binding to the postsynaptic membrane in the neuromuscular junction. They are called ""end plates"" because the postsynaptic terminals of muscle fibers have a large, saucer-like appearance. When an action potential reaches the axon terminal of a motor neuron, vesicles carrying neurotransmitters (mostly acetylcholine) are exocytosed and the contents are released into the neuromuscular junction. These neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane and lead to its depolarization. In the absence of an action potential, acetylcholine vesicles spontaneously leak into the neuromuscular junction and cause very small depolarizations in the postsynaptic membrane. This small response (~0.5mV) is called a miniature end plate potential (MEPP) and is generated by one acetylcholine-containing vesicle. It represents the smallest possible depolarization which can be induced in a muscle.