Effects of attention on orientation-tuning functions of single neurons
... Data anal ysis. We measured neuronal responses during the presentation of the sample stimulus. We collected at least eight repetitions of twelve orientations in each of the two task modes, in which task mode is defined by whether the animal attended to the stimulus inside (attended mode) or outside ...
... Data anal ysis. We measured neuronal responses during the presentation of the sample stimulus. We collected at least eight repetitions of twelve orientations in each of the two task modes, in which task mode is defined by whether the animal attended to the stimulus inside (attended mode) or outside ...
PDF reprint - UC Davis Mathematics
... Recently investigations have revealed that many local interneuronal networks throughout the brain display electrical coupling through gap junctions (see Galarreta and Hestrin, 2001a). There are different subpopulations of interneurons, and it has been found that the electrical coupling is predominan ...
... Recently investigations have revealed that many local interneuronal networks throughout the brain display electrical coupling through gap junctions (see Galarreta and Hestrin, 2001a). There are different subpopulations of interneurons, and it has been found that the electrical coupling is predominan ...
Muscarinic Activation of a Cation Current and Associated Current
... et al. 1986; Celesia and Jasper 1966) and cholinergic mechanisms mediated through muscarinic receptors have been implicated in different modalities of cortical plasticity (Dykes 1997; Richardson and DeLong 1988; Shulz et al. 2000) and memory function (Hasselmo and Bower 1993; Y. Tang et al. 1997). I ...
... et al. 1986; Celesia and Jasper 1966) and cholinergic mechanisms mediated through muscarinic receptors have been implicated in different modalities of cortical plasticity (Dykes 1997; Richardson and DeLong 1988; Shulz et al. 2000) and memory function (Hasselmo and Bower 1993; Y. Tang et al. 1997). I ...
Intraflagellar transport molecules in ciliary and nonciliary cells of the
... 2003; Follit et al., 2006). These experiments verified the expression of all five IFT proteins in the murine retina (Fig. S1, A and B). The antibodies to four IFT proteins each recognized a single band of expected size in retinal protein extracts, which implied that these antibodies are monospecific ...
... 2003; Follit et al., 2006). These experiments verified the expression of all five IFT proteins in the murine retina (Fig. S1, A and B). The antibodies to four IFT proteins each recognized a single band of expected size in retinal protein extracts, which implied that these antibodies are monospecific ...
Contribution of Pedunculopontine Tegmental Nucleus Neurons to
... The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. The article must therefore be hereby marked ‘‘advertisement’’ in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact. ...
... The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. The article must therefore be hereby marked ‘‘advertisement’’ in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact. ...
PDF-document - homepage.ruhr-uni-bochum.de - Ruhr
... neurons in the NOT/DTN prefer horizontal stimulus movements and receive an inhibitory input from ipsilateral MTN. Our results indicate that this input is mediated by GABAergic cells in the ventral part of MTN, which to a large extent prefer downward directed stimulus movements, and that the great ma ...
... neurons in the NOT/DTN prefer horizontal stimulus movements and receive an inhibitory input from ipsilateral MTN. Our results indicate that this input is mediated by GABAergic cells in the ventral part of MTN, which to a large extent prefer downward directed stimulus movements, and that the great ma ...
THE REGULATION OF SLEEP AND WAKEFULNESS BY THE
... The physiological importance of the orexin system in sleep is clearly demonstrated in genetically modulated mice. Prepro-orexin knockout mice2), OX2R knockout mice3), and orexin neuron-ablated transgenic mice (orexin/ataxin-3 mice)1) show severe sleep fragmentation similar to narcolepsy. Additionall ...
... The physiological importance of the orexin system in sleep is clearly demonstrated in genetically modulated mice. Prepro-orexin knockout mice2), OX2R knockout mice3), and orexin neuron-ablated transgenic mice (orexin/ataxin-3 mice)1) show severe sleep fragmentation similar to narcolepsy. Additionall ...
Specific Innervation of Neurons in the Paravertebral
... following paper (Yip, 1986b), I describe the formation of sympathetic ganglia in the chick and examine whether position along the neural tube prior to neural crest migration is a basis for recognition between pre- and postganglionic neurons. ...
... following paper (Yip, 1986b), I describe the formation of sympathetic ganglia in the chick and examine whether position along the neural tube prior to neural crest migration is a basis for recognition between pre- and postganglionic neurons. ...
Selective Coupling of T-Type Calcium Channels to SK Potassium
... Onn, 1989; Wolfart et al., 2001). Thus, it generally is assumed that a particular type of synaptic activity, which is present only in vivo, is necessary for DA neurons to switch into burst mode. In this context NMDA receptor activation (Johnson et al., 1992), GABAA receptor-mediated disinhibitory pr ...
... Onn, 1989; Wolfart et al., 2001). Thus, it generally is assumed that a particular type of synaptic activity, which is present only in vivo, is necessary for DA neurons to switch into burst mode. In this context NMDA receptor activation (Johnson et al., 1992), GABAA receptor-mediated disinhibitory pr ...
Temporal control of neuronal diversity: common
... neurons (Cleary and Doe, 2006; Pearson and Doe, 2003). In addition, some progenitors appear to express a second endogenous burst of the same TTF, as has been observed for Kr and Cas in neuroblasts at late embryonic stages and for Cas (and also Seven up) during larval stages (Fig. 1C) (Cleary and Doe ...
... neurons (Cleary and Doe, 2006; Pearson and Doe, 2003). In addition, some progenitors appear to express a second endogenous burst of the same TTF, as has been observed for Kr and Cas in neuroblasts at late embryonic stages and for Cas (and also Seven up) during larval stages (Fig. 1C) (Cleary and Doe ...
IRK-1 Potassium Channels Mediate Peptidergic Inhibition
... cell surface receptors for diverse small molecules and peptides. In neurons, GPCRs act as receptors for most neurotransmitters and neuromodulators. Accordingly, GPCRs have critical functions in brain circuits, and they are targets of therapeutics used for the treatment of numerous psychiatric disord ...
... cell surface receptors for diverse small molecules and peptides. In neurons, GPCRs act as receptors for most neurotransmitters and neuromodulators. Accordingly, GPCRs have critical functions in brain circuits, and they are targets of therapeutics used for the treatment of numerous psychiatric disord ...
Lesion of the perforant path triggers a biphasic neurogenic response
... w ith intact post-synaptic d ensities still form , d espite the absence of glutamatergic nerve term inals. Follow ing entorhinal lesion, n ew born neurons, but not m ature granule cells, have a higher d ensity of d end ritic spines in the non -d enervated inner m olecular layer, accom panied by an i ...
... w ith intact post-synaptic d ensities still form , d espite the absence of glutamatergic nerve term inals. Follow ing entorhinal lesion, n ew born neurons, but not m ature granule cells, have a higher d ensity of d end ritic spines in the non -d enervated inner m olecular layer, accom panied by an i ...
Document
... Neurotransmitters bind to specific receptor molecules in the membrane of a postsynaptic neuron, opening ion channels and thereby stimulating impulse conduction by the membrane Names of neurotransmitters—acetylcholine, catecholamines (norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin), and other compounds ...
... Neurotransmitters bind to specific receptor molecules in the membrane of a postsynaptic neuron, opening ion channels and thereby stimulating impulse conduction by the membrane Names of neurotransmitters—acetylcholine, catecholamines (norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin), and other compounds ...
ATP as a Signaling Molecule: the Exocrine Focus
... export, the most established stimuli of ATP release are shear stress, stretch, hypoxia, inflammation, osmotic swelling, and, of course, cell death, as well as cholinergic stimulation, as shown below for pancreas (see Fig. 4). Several mechanisms for ATP release have been proposed, but it is unclear w ...
... export, the most established stimuli of ATP release are shear stress, stretch, hypoxia, inflammation, osmotic swelling, and, of course, cell death, as well as cholinergic stimulation, as shown below for pancreas (see Fig. 4). Several mechanisms for ATP release have been proposed, but it is unclear w ...
Genes That Control Ray Sensory Neuron Axon
... L. Jia and S. W. Emmons Figure 1.—Ray axon pathways in wild type. (A) Lateral view of the L4 larval male tail, showing the positions of the nine neurons of one type before they migrate into the lumbar ganglion during remodeling of the tail. (B) Lateral (top) and ventral (bottom) views of the adult m ...
... L. Jia and S. W. Emmons Figure 1.—Ray axon pathways in wild type. (A) Lateral view of the L4 larval male tail, showing the positions of the nine neurons of one type before they migrate into the lumbar ganglion during remodeling of the tail. (B) Lateral (top) and ventral (bottom) views of the adult m ...
Article
... mammals, sharing many similarities [4, 5]. CPG networks underlying locomotion exhibit features common to many neural circuits, such as spatio-temporal coordination and flexibility. Each cycle of motor output involves sequences of muscle contraction and relaxation in multiple parts of the body, and c ...
... mammals, sharing many similarities [4, 5]. CPG networks underlying locomotion exhibit features common to many neural circuits, such as spatio-temporal coordination and flexibility. Each cycle of motor output involves sequences of muscle contraction and relaxation in multiple parts of the body, and c ...
Document
... • Synaptic cleft (or gap) (Cholinesterase) • Postsynaptic membrane ( neurotransmitter’s receptors) ...
... • Synaptic cleft (or gap) (Cholinesterase) • Postsynaptic membrane ( neurotransmitter’s receptors) ...
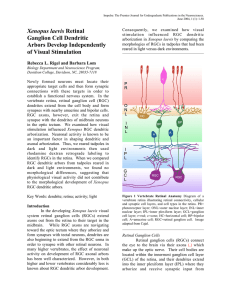
Xenopus laevis Retinal Ganglion Cell Dendritic Arbors Develop
... spontaneously released both throughout the neuron and locally within small dendritic segments. Ca+2 release helps stabilize RGC dendritic structure and blockade of local Ca+2 release causes immediate dendritic retraction. This work suggests that Ca+2 release may be a way in which afferent activity r ...
... spontaneously released both throughout the neuron and locally within small dendritic segments. Ca+2 release helps stabilize RGC dendritic structure and blockade of local Ca+2 release causes immediate dendritic retraction. This work suggests that Ca+2 release may be a way in which afferent activity r ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.