SChapter 12
... -Presynaptic and postsynaptic cell are locked together at gap junctions -Action potentials are propagated quickly ▫Chemical synapse -Most neural synapses, all between neurons and other cells -Neurotransmitters released into synapse, picked up by receptors on postsynaptic cell -Can be excitatory or i ...
... -Presynaptic and postsynaptic cell are locked together at gap junctions -Action potentials are propagated quickly ▫Chemical synapse -Most neural synapses, all between neurons and other cells -Neurotransmitters released into synapse, picked up by receptors on postsynaptic cell -Can be excitatory or i ...
Module Worksheet - Germantown School District
... Given what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
... Given what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
PsychSim 5: NEURAL MESSAGES Name: Section: Date: ______
... • Given what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
... • Given what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
Chapter 11 Practice Questions
... 21) Neurotransmitters are chemical signals used as a means of communication. GABA and glycine are amino acid neurotransmitters; dopamine and norepinephrine are catecholamines; and endorphin and enkephalin are peptide transmitters. 22) Both excitatory and inhibitory potentials impinge on neurons. Inh ...
... 21) Neurotransmitters are chemical signals used as a means of communication. GABA and glycine are amino acid neurotransmitters; dopamine and norepinephrine are catecholamines; and endorphin and enkephalin are peptide transmitters. 22) Both excitatory and inhibitory potentials impinge on neurons. Inh ...
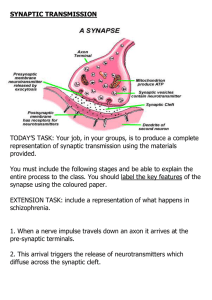
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft thus making it inactive. 4. If successfully transmitted, the nerve impulse is then carried along ...
... immediately by the post-synaptic neuron, otherwise it will either be re-absorbed by the synaptic terminals from which it was released OR it will be chemically broken down by enzymes in the synaptic cleft thus making it inactive. 4. If successfully transmitted, the nerve impulse is then carried along ...
Transmission at the Synapse and the
... Voltage-gated potassium channels can open, thus hyperpolarizing the membrane by allowing a stream of potassium to exit, and thusa decreasing the inward calcium stream upon the arrival of the action potential Direct inhibition of neurotransmitter release independent of calcium influx ...
... Voltage-gated potassium channels can open, thus hyperpolarizing the membrane by allowing a stream of potassium to exit, and thusa decreasing the inward calcium stream upon the arrival of the action potential Direct inhibition of neurotransmitter release independent of calcium influx ...
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... Neurotransmitters • Chemicals released from vesicles by exocytosis into synaptic cleft • Diffuse across synapse • Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells • Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells • Types of neurotransmitters: – Excitatory: speed up impulses ...
... Neurotransmitters • Chemicals released from vesicles by exocytosis into synaptic cleft • Diffuse across synapse • Bind to receptors on neurons, muscle cells, or gland cells • Broken down by enzymes or taken back up into surrounding cells • Types of neurotransmitters: – Excitatory: speed up impulses ...
Drugs Change the way Neurons communicate
... Cocaine blocks dopamine transporters (re-uptake pumps), causing an increase in dopamine in the synaptic cleft thus inducing euhporia ...
... Cocaine blocks dopamine transporters (re-uptake pumps), causing an increase in dopamine in the synaptic cleft thus inducing euhporia ...
Lecture #21 Date
... K+ diffuses out (Na+ in); large anions cannot follow….why not? Net negative charge of about -70mV ...
... K+ diffuses out (Na+ in); large anions cannot follow….why not? Net negative charge of about -70mV ...
Slide ()
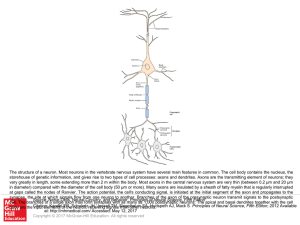
... The structure of a neuron. Most neurons in the vertebrate nervous system have several main features in common. The cell body contains the nucleus, the storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; ...
... The structure of a neuron. Most neurons in the vertebrate nervous system have several main features in common. The cell body contains the nucleus, the storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; ...
BLoA Neurotransmission
... chemicals are in the synapse. They float across the tiny space in a random way, and in the process, bump into receptors on the other side. The receptors here are important. This is because there tend to be many different types of receptor for one type of neurotransmitter. Depending on which receptor ...
... chemicals are in the synapse. They float across the tiny space in a random way, and in the process, bump into receptors on the other side. The receptors here are important. This is because there tend to be many different types of receptor for one type of neurotransmitter. Depending on which receptor ...
Nerve Impulse Transmission
... • The nerve impulse needs to cross this gap and it does so by the release of special chemicals called neurotransmitters. ...
... • The nerve impulse needs to cross this gap and it does so by the release of special chemicals called neurotransmitters. ...
Signal transmission at synapses
... 2. Hydrolysis: in the synaptict cleft (restores the resting potential in the postsynaptic membrane) ...
... 2. Hydrolysis: in the synaptict cleft (restores the resting potential in the postsynaptic membrane) ...
PsychSim 5 neural messages
... Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ___ Axon ...
... Match the part of the neuron identified with its description: o ___ Axon ...
PharmacologyLec 1 Central nervous system pharmacology
... There are two reasons why understanding the action of drugs act on the central nervous system, the first is that centrally acting drugs are of therapeutic importance,the second reason is that the CNS is functionally far more complex than any other system in the body, and this makes the understanding ...
... There are two reasons why understanding the action of drugs act on the central nervous system, the first is that centrally acting drugs are of therapeutic importance,the second reason is that the CNS is functionally far more complex than any other system in the body, and this makes the understanding ...
Getting on your Nerves
... correct output. This allows for procedural learning, where each time an action is performed, it becomes somewhat more accurate since the "right synapses" are contributing to the response. ...
... correct output. This allows for procedural learning, where each time an action is performed, it becomes somewhat more accurate since the "right synapses" are contributing to the response. ...
An Introduction to Neurophysiology
... A. Types of Synapses 1. Electrical Synapses - gap junctions → direct electrical connection between cells - uncommon in the nervous system 2. Chemical Synapses - most common type in the nervous system - release a chemical neurotransmitter which binds to a receptor presynaptic cell (neuron) axon termi ...
... A. Types of Synapses 1. Electrical Synapses - gap junctions → direct electrical connection between cells - uncommon in the nervous system 2. Chemical Synapses - most common type in the nervous system - release a chemical neurotransmitter which binds to a receptor presynaptic cell (neuron) axon termi ...
Synapses and neurotransmitters
... Glutamate (universally excitatory) GABA (universally inhibitory) Glycine Proline ...
... Glutamate (universally excitatory) GABA (universally inhibitory) Glycine Proline ...
PsychSim - Stamford High School
... what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
... what you know about synaptic transmission, how do you think a message jumps across the synaptic gap and is passed to the next neuron? ...
Nerve Junctions
... • Synapses are the junctions between two or more neurones. • Here, neurones are able to signal to the next neurone in the sequence. • The synaptic cleft the gap between two neurons and is only 20nm wide. • Action potentials cannot cross the gap between two neurons so instead they release chemicals ( ...
... • Synapses are the junctions between two or more neurones. • Here, neurones are able to signal to the next neurone in the sequence. • The synaptic cleft the gap between two neurons and is only 20nm wide. • Action potentials cannot cross the gap between two neurons so instead they release chemicals ( ...
neuro5
... Some ion Channels that allow flux of Na+ and K+ simultaneously e.g. nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor (nAChR) ...
... Some ion Channels that allow flux of Na+ and K+ simultaneously e.g. nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor (nAChR) ...
Is Neuronatin mRNA Dendritically localized in Hippocampal Neurons
... Synaptic plasticity is the capacity of neurons to alter the strength of their connections, and has been shown to occur in a synapse-specific fashion. Alterations in synaptic strength occur during late stages of brain development and in response to a variety of stimuli in the adult brain, including i ...
... Synaptic plasticity is the capacity of neurons to alter the strength of their connections, and has been shown to occur in a synapse-specific fashion. Alterations in synaptic strength occur during late stages of brain development and in response to a variety of stimuli in the adult brain, including i ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.