Events at a chemical synapse
... volage-gated calcium channels. 2. Ca++ influx into presynaptic term. 3. Ca++ acts as intracellular messenger stimulating synaptic vesicles to fuse with membrane and release NT via exocytosis. 4. Ca++ removed from terminal by mitochondria or calcium-pumps. 5. NT diffuses across synaptic cleft and bin ...
... volage-gated calcium channels. 2. Ca++ influx into presynaptic term. 3. Ca++ acts as intracellular messenger stimulating synaptic vesicles to fuse with membrane and release NT via exocytosis. 4. Ca++ removed from terminal by mitochondria or calcium-pumps. 5. NT diffuses across synaptic cleft and bin ...
Neuronal signaling and synapses
... -disadvantages partial loss of functional individuality in coupled neurons -modulation **found in horizontal cells of the retina ...
... -disadvantages partial loss of functional individuality in coupled neurons -modulation **found in horizontal cells of the retina ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... small–diameter axon; (b) myelinated, large–diameter axon; (c) unmyelinated, small–diameter axon. ...
... small–diameter axon; (b) myelinated, large–diameter axon; (c) unmyelinated, small–diameter axon. ...
PowerPoint Slides
... •Signals are noisy “spike trains” of electrical potential •Neurons die off frequently (never replaced) •Compensates for problems by massive parallelism synapse nucleus ...
... •Signals are noisy “spike trains” of electrical potential •Neurons die off frequently (never replaced) •Compensates for problems by massive parallelism synapse nucleus ...
File
... called a terminal button which contains neurotransmitters. B. Neurotransmitters are any chemical involved in synaptic transmission. Examples of neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin. C. When an action potential reaches the terminal button of an axon, it signals synaptic tr ...
... called a terminal button which contains neurotransmitters. B. Neurotransmitters are any chemical involved in synaptic transmission. Examples of neurotransmitters include acetylcholine, dopamine, and serotonin. C. When an action potential reaches the terminal button of an axon, it signals synaptic tr ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... Norepinephrine: (NE) This compound is secreted principally from the adrenal gland. Contributes to the modulation of mood and arousal. Cocaine and amphetamines elevate activity at the NE synapses. Dopamine: (DA) Dopamine facilitates critical brain functions and voluntary movement, pleasurable emotion ...
... Norepinephrine: (NE) This compound is secreted principally from the adrenal gland. Contributes to the modulation of mood and arousal. Cocaine and amphetamines elevate activity at the NE synapses. Dopamine: (DA) Dopamine facilitates critical brain functions and voluntary movement, pleasurable emotion ...
AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 48 Neurons synapses and
... Integrate information within brain or spinal cord; connect sensory and motor neurons; located entirely within the CNS Transmit information from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland; Cause muscle contraction or gland secretion ...
... Integrate information within brain or spinal cord; connect sensory and motor neurons; located entirely within the CNS Transmit information from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland; Cause muscle contraction or gland secretion ...
File
... packaged in synaptic vesicles. E.g. Amino acids and amines are stored in synaptic vesicles • Large molecules assembled in the cell body, packaged in vesicles, and then transported to the axon terminal. E.g. Peptides are stored in and released from secretory granules Often coexist in the same axon ...
... packaged in synaptic vesicles. E.g. Amino acids and amines are stored in synaptic vesicles • Large molecules assembled in the cell body, packaged in vesicles, and then transported to the axon terminal. E.g. Peptides are stored in and released from secretory granules Often coexist in the same axon ...
NEUROPHYSIOLOGY
... 3. Synaptic vesicles fuse with the knob membrane 4. Vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft 5. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane causing the channels to open and allow sodium to leak in-thus setting up the action potential. ...
... 3. Synaptic vesicles fuse with the knob membrane 4. Vesicles release neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft 5. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane causing the channels to open and allow sodium to leak in-thus setting up the action potential. ...
CNSIntro
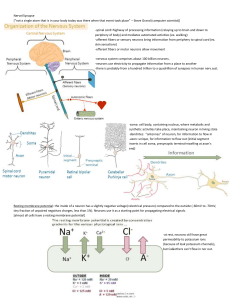
... more positively charged ions outside, more negatively charged ions inside The ions responsible for the membrane potential include ...
... more positively charged ions outside, more negatively charged ions inside The ions responsible for the membrane potential include ...
Sending Signals Notes
... taken up again by the axon terminal and recycled, or they may simply diffuse away. • NERVE GAS prevents enzymes from breaking down neurotransmitters, as a result muscles in the respiratory and nervous system becomes paralyzed. ...
... taken up again by the axon terminal and recycled, or they may simply diffuse away. • NERVE GAS prevents enzymes from breaking down neurotransmitters, as a result muscles in the respiratory and nervous system becomes paralyzed. ...
6.5 Neurons and Synapses - Mr Cartlidge`s Saigon Science Blog
... Neurons transmit electrical impulses. The myelination of nerve fibres allows for saltatory conduction. Neurons pump sodium and potassium ions across their membranes to generate a resting potential. An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of the neuron. Nerve impulses are ac ...
... Neurons transmit electrical impulses. The myelination of nerve fibres allows for saltatory conduction. Neurons pump sodium and potassium ions across their membranes to generate a resting potential. An action potential consists of depolarization and repolarization of the neuron. Nerve impulses are ac ...
PowerPoint
... taken up again by the axon terminal and recycled, or they may simply diffuse away. • NERVE GAS prevents enzymes from breaking down neurotransmitters, as a result muscles in the respiratory and nervous system becomes paralyzed. ...
... taken up again by the axon terminal and recycled, or they may simply diffuse away. • NERVE GAS prevents enzymes from breaking down neurotransmitters, as a result muscles in the respiratory and nervous system becomes paralyzed. ...
here
... Signals in the synapse are transmitted chemically. When an electrical impulse reaches the end of the neuron (the pre-synaptic terminal) it triggers the release of neurotransmitters from tiny sacs known as vesicles. These neurotransmitters diffuse across the gap and are taken up by receptors. T ...
... Signals in the synapse are transmitted chemically. When an electrical impulse reaches the end of the neuron (the pre-synaptic terminal) it triggers the release of neurotransmitters from tiny sacs known as vesicles. These neurotransmitters diffuse across the gap and are taken up by receptors. T ...
The Synaptic Cleft or Synapse
... The axon terminal at a synapse contains tiny vesicles filled with chemicals called neurotransmitters. If a nerve impulse takes place, vesicles fuse and release the neurotransmitter. A common neurotransmitter is acetylcholine. ...
... The axon terminal at a synapse contains tiny vesicles filled with chemicals called neurotransmitters. If a nerve impulse takes place, vesicles fuse and release the neurotransmitter. A common neurotransmitter is acetylcholine. ...
Document
... chemical-gated ion channels called neuroreceptors. These have specific binding sites for neurotransmitters. ...
... chemical-gated ion channels called neuroreceptors. These have specific binding sites for neurotransmitters. ...
Threshold Stimulus
... depolarization. __________ stimuli do not cause depolarization. • “_________________________ principle” - neuron depolarizes to its maximum ...
... depolarization. __________ stimuli do not cause depolarization. • “_________________________ principle” - neuron depolarizes to its maximum ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.