Powerpoint slides
... About -70 mV Selectively allowing certain ions in With stimulation Na+ is allowed in ...
... About -70 mV Selectively allowing certain ions in With stimulation Na+ is allowed in ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
... When a neurotransmitter binds to a receptor on the postsynaptic side of the synapse, it results in a change of the postsynaptic cell's excitability: it makes the postsynaptic cell either more or less likely to fire an action potential. If the number of excitatory postsynaptic events are large enough ...
... When a neurotransmitter binds to a receptor on the postsynaptic side of the synapse, it results in a change of the postsynaptic cell's excitability: it makes the postsynaptic cell either more or less likely to fire an action potential. If the number of excitatory postsynaptic events are large enough ...
Stochastic fluctuations of the synaptic function
... synapses. The vesicle diameter varies in a significant range. As a result we have that different spikes, arriving to the same synapse at different times, produce a variable number of ...
... synapses. The vesicle diameter varies in a significant range. As a result we have that different spikes, arriving to the same synapse at different times, produce a variable number of ...
Neurons
... Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. • In a chemical synapse chemicals from a presynaptic cell induce changes in a postsynaptic cell. • The neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells. • The motor neuron releases acetylc ...
... Neurons communicate with other neurons or target cells at synapses. • In a chemical synapse chemicals from a presynaptic cell induce changes in a postsynaptic cell. • The neuromuscular junction is a chemical synapse between motor neurons and skeletal muscle cells. • The motor neuron releases acetylc ...
Learn about synapses
... figure to the left) containing neurotransmitters toward the presynaptic membrane. The vesicle membrane will fuse with the presynaptic membrane releasing the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. Until recently, it was thought that a neuron produced and released only one type of neurotransmitter ...
... figure to the left) containing neurotransmitters toward the presynaptic membrane. The vesicle membrane will fuse with the presynaptic membrane releasing the neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft. Until recently, it was thought that a neuron produced and released only one type of neurotransmitter ...
The Nervous System
... – The gap that separates adjacent neurons – Transmission of impulse across the synapse • Presynaptic cell to postsynaptic cell • Electrical or Chemical – Most synaptic clefts are traversed by chemicals ...
... – The gap that separates adjacent neurons – Transmission of impulse across the synapse • Presynaptic cell to postsynaptic cell • Electrical or Chemical – Most synaptic clefts are traversed by chemicals ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous System – Homework – Part I
... Chapter 48 – Neurons, Synapses and Signaling – Homework 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contra ...
... Chapter 48 – Neurons, Synapses and Signaling – Homework 1. Describe the basic pathway of information flow through neurons that cause you to turn your head when you hear the sound of your name being called. 2. Compare and contrast sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons 3. Compare and contra ...
Ch 2 lec 3
... Mediated by transporter molecules on neurons and glia After it is taken up it may be degraded or recycled in vesicles ...
... Mediated by transporter molecules on neurons and glia After it is taken up it may be degraded or recycled in vesicles ...
Document
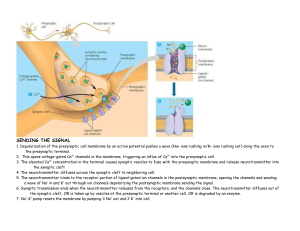
... 5. The neurotransmitter binds to the receptor portion of ligand–gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels and sending a wave of Na+ in and K+ out through ion channels depolarizing the postsynaptic membrane sending the signal. 6. Synaptic transmission ends when the neurotr ...
... 5. The neurotransmitter binds to the receptor portion of ligand–gated ion channels in the postsynaptic membrane, opening the channels and sending a wave of Na+ in and K+ out through ion channels depolarizing the postsynaptic membrane sending the signal. 6. Synaptic transmission ends when the neurotr ...
Neurotransmitters & Synapses - IB
... from multiple sources Some NT are excitatory Other NT are inhibitory Summation is the axon hillock is summative If it reaches threshold the AP is propagated ...
... from multiple sources Some NT are excitatory Other NT are inhibitory Summation is the axon hillock is summative If it reaches threshold the AP is propagated ...
No Slide Title
... the releasing point; so peptide turnover is much slower. Neurotransmitters are synthesised from precursor molecules derived form the diet, e.g acetylcholine is synthesised from choline found in cauliflower and milk. Both neurotransmitters and peptides are stored in spherical packets called synap ...
... the releasing point; so peptide turnover is much slower. Neurotransmitters are synthesised from precursor molecules derived form the diet, e.g acetylcholine is synthesised from choline found in cauliflower and milk. Both neurotransmitters and peptides are stored in spherical packets called synap ...
ppt
... Synaptic Potentials •Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) •triggered by excitatory neurotransmitters •open ligand-gated Na+ channels •allows Na+ to flow inside the cell •causing a slight depolarization of the postsynaptic cell •moves the postsynaptic cell closer to firing an action potential ...
... Synaptic Potentials •Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) •triggered by excitatory neurotransmitters •open ligand-gated Na+ channels •allows Na+ to flow inside the cell •causing a slight depolarization of the postsynaptic cell •moves the postsynaptic cell closer to firing an action potential ...
Slide 1
... them to the presynaptic element. 4. Vesicles bind to specific sites on the presynaptic element and open, spilling their contents (a neurotransmitter) into the synaptic cleft 5. Neurotransmitters (the ligand) bind to receptors at specific binding sites on the post synaptic cell membrane causing eithe ...
... them to the presynaptic element. 4. Vesicles bind to specific sites on the presynaptic element and open, spilling their contents (a neurotransmitter) into the synaptic cleft 5. Neurotransmitters (the ligand) bind to receptors at specific binding sites on the post synaptic cell membrane causing eithe ...
Mind Is Matter
... Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Recep ...
... Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Recep ...
Slide ()
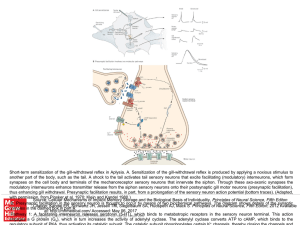
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Part 1: True/False
... C. Waking up in the middle of the night and writing unintelligible notes to himself D. Showing that 'stuff' dripping from the vagus nerve slows down the heart <––– E. Showing that heartbeat is controlled by vagus nerve 15. Neuropeptide Y is a peptide neurotransmitter. What can you say about this pep ...
... C. Waking up in the middle of the night and writing unintelligible notes to himself D. Showing that 'stuff' dripping from the vagus nerve slows down the heart <––– E. Showing that heartbeat is controlled by vagus nerve 15. Neuropeptide Y is a peptide neurotransmitter. What can you say about this pep ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.