The Nervous System
... E. Physiology of synapse • 1. action potential arrives • 2. Calcium ion channels open • 3. synaptic vesicles fuse with membrane • 4. transmitter substance released • 5. diffusion of transmitter substance • 6. binding to receptors • 7. creates a graded potential • 8. may bring postsynaptic membrane ...
... E. Physiology of synapse • 1. action potential arrives • 2. Calcium ion channels open • 3. synaptic vesicles fuse with membrane • 4. transmitter substance released • 5. diffusion of transmitter substance • 6. binding to receptors • 7. creates a graded potential • 8. may bring postsynaptic membrane ...
GABA A Receptor
... neuron and can initiate chemical results that include long-term changes in cell structure that alter long term excitability ...
... neuron and can initiate chemical results that include long-term changes in cell structure that alter long term excitability ...
bioii ch10 ppt
... gastrointestinal tract, platelets and the central nervous system. This chemical is also known as the “happiness hormone”, because it arouses feelings of pleasure and well-being. Low levels of serotonin are associated with increased carbohydrate cravings, depression, sleep deprivations and hypersensi ...
... gastrointestinal tract, platelets and the central nervous system. This chemical is also known as the “happiness hormone”, because it arouses feelings of pleasure and well-being. Low levels of serotonin are associated with increased carbohydrate cravings, depression, sleep deprivations and hypersensi ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... o E.g. warm water = low frequency, hot water = high frequency 2. Different neurons have different thresholds o E.g. water at 40°C will cause one neuron to reach threshold level, but water at 60°C may cause two or more o Brain distinguishes between neural impulses Synaptic Transmission Neurons can ...
... o E.g. warm water = low frequency, hot water = high frequency 2. Different neurons have different thresholds o E.g. water at 40°C will cause one neuron to reach threshold level, but water at 60°C may cause two or more o Brain distinguishes between neural impulses Synaptic Transmission Neurons can ...
Animal Nutrition
... It will fire completely once a stimulus is received and threshold potential is reached: “all or nothing” principle No threshold, no action potential ...
... It will fire completely once a stimulus is received and threshold potential is reached: “all or nothing” principle No threshold, no action potential ...
1) Propagated electrical signals - UW Canvas
... 2) Fast chemical transmission at chemical synapses electrical to chemical to electrical ...
... 2) Fast chemical transmission at chemical synapses electrical to chemical to electrical ...
E4 - Neurotransmitters and Synapses - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... of waves neurotransmitter from the same presynaptic neurone depolarises the post synaptic membrane (i.e. waves of depolarisation are added together to reach threshold). ...
... of waves neurotransmitter from the same presynaptic neurone depolarises the post synaptic membrane (i.e. waves of depolarisation are added together to reach threshold). ...
overview of neural f..
... that the receiving neuron will 'fire' (i.e. produce an action potential). ...
... that the receiving neuron will 'fire' (i.e. produce an action potential). ...
Neural and Hormonal Systems
... 2. refractory period – “recharging” phase of a neuron; cannot fire just yet 3. resting potential – neuron is capable and ready to generate another action potential ...
... 2. refractory period – “recharging” phase of a neuron; cannot fire just yet 3. resting potential – neuron is capable and ready to generate another action potential ...
ACh - Perkins Science
... • Stimulation causes phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of connexin proteins to open or close the channels ...
... • Stimulation causes phosphorylation or dephosphorylation of connexin proteins to open or close the channels ...
Membrane Biophysics and Synaptic Physiology
... dependence of release, two models and mechanisms? •Multivesicular release, when and where? •Synaptic ...
... dependence of release, two models and mechanisms? •Multivesicular release, when and where? •Synaptic ...
48 Nervous System PowerPoint
... the signal, axon delivers the signal away to another neuron or to the CNS Myelin sheaths (white matter) insulate the axon and are made by Schwanns cells or oligodendrocytes. Schwanns and Oligodendrocytes are both types of supporting cells called glia. What is saltatory conduction? P.970 What is a No ...
... the signal, axon delivers the signal away to another neuron or to the CNS Myelin sheaths (white matter) insulate the axon and are made by Schwanns cells or oligodendrocytes. Schwanns and Oligodendrocytes are both types of supporting cells called glia. What is saltatory conduction? P.970 What is a No ...
Nervous System - EMTStudyCenter.com
... 5. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT senses changes. analyzes changes. ...
... 5. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT senses changes. analyzes changes. ...
Synapses - UBC Zoology
... • separation between presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes is about 20 to 30 nm • a chemical transmitter is released and diffuses to bind to receptors on postsynaptic side • bind leads (directly or indirectly) to changes in the postsynaptic membrane potential (usually by opening or closing transmit ...
... • separation between presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes is about 20 to 30 nm • a chemical transmitter is released and diffuses to bind to receptors on postsynaptic side • bind leads (directly or indirectly) to changes in the postsynaptic membrane potential (usually by opening or closing transmit ...
Slide 1
... receptor channel or voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC), which may be located on the spine head or dendritic shaft. Calcium pumps (P), located on the spine head, neck, and dendritic shaft, are hypothesized to help isolate Ca2+ concentration changes in the spine head from those in the dendritic sha ...
... receptor channel or voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC), which may be located on the spine head or dendritic shaft. Calcium pumps (P), located on the spine head, neck, and dendritic shaft, are hypothesized to help isolate Ca2+ concentration changes in the spine head from those in the dendritic sha ...
Nervous System Student Notes File
... neurotransmitters that open Na+ gates triggering depolarization c) _________________________________________________ (IPSP) are caused by neurotransmitters which open K+ or Cl- gates causing hyperpolarization d) A single EPSP is rarely strong enough to trigger an action potential, although and addit ...
... neurotransmitters that open Na+ gates triggering depolarization c) _________________________________________________ (IPSP) are caused by neurotransmitters which open K+ or Cl- gates causing hyperpolarization d) A single EPSP is rarely strong enough to trigger an action potential, although and addit ...
A4a - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... neuron; instead, stimulation produces transient postsynaptic membrane potential change: A. EXCITATORY synapses – postsinaptinė membrana depoliarizuojama (excitatory postsynaptic potential). ...
... neuron; instead, stimulation produces transient postsynaptic membrane potential change: A. EXCITATORY synapses – postsinaptinė membrana depoliarizuojama (excitatory postsynaptic potential). ...
Functional Human Physiology for the Exercise and Sport Sciences
... The net effect of EPSPs and IPSPs on the post-synaptic membrane will determine if the net effect is excitatory or inhibitory. If the net effect is more excitatory than inhibitory, an action potential will be generated on the post-synaptic membrane and impulse transduction will occur The opposi ...
... The net effect of EPSPs and IPSPs on the post-synaptic membrane will determine if the net effect is excitatory or inhibitory. If the net effect is more excitatory than inhibitory, an action potential will be generated on the post-synaptic membrane and impulse transduction will occur The opposi ...
The Nervous System
... I. Propagation of action potentials • 1. concentration difference of ions on either side of membrane represents potential energy-kind of like of cocked gun • 2. stacked dominoes waiting to fall over • 3. one domino falling over initiates a wave of action potentials spreading out like the ripples in ...
... I. Propagation of action potentials • 1. concentration difference of ions on either side of membrane represents potential energy-kind of like of cocked gun • 2. stacked dominoes waiting to fall over • 3. one domino falling over initiates a wave of action potentials spreading out like the ripples in ...
Nervous System Quiz Answers
... and the action potential skips from node to node (Nodes of Ranvier). Unmyelinated lacks the insulator and nodes so the action potential travels the entire length of the axon which decreases the rate of conduction. 4. What is a synapse? How does it work? (4pts) A synapse is a gap or junction between ...
... and the action potential skips from node to node (Nodes of Ranvier). Unmyelinated lacks the insulator and nodes so the action potential travels the entire length of the axon which decreases the rate of conduction. 4. What is a synapse? How does it work? (4pts) A synapse is a gap or junction between ...
Madison Pejsa Pd.4
... Brain Stem- The portion of the brain that is continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and parts of the hypothalamus, functioning in the control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion ...
... Brain Stem- The portion of the brain that is continuous with the spinal cord and comprises the medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain, and parts of the hypothalamus, functioning in the control of the reflexes and such essential internal mechanisms as respiration and heartbeat. Cerebellum- A large portion ...
How Neurons Talk to Each Other
... The presynaptic nerve endings contain signal molecules known as neurotransmitters, which are stored in small membrane-enclosed vesicles. Each nerve ending in the central nervous system contains an average of several hundred synaptic vesicles. However, synapses vary significantly. For example, some s ...
... The presynaptic nerve endings contain signal molecules known as neurotransmitters, which are stored in small membrane-enclosed vesicles. Each nerve ending in the central nervous system contains an average of several hundred synaptic vesicles. However, synapses vary significantly. For example, some s ...
Structure of a Neuron
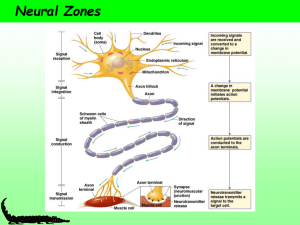
... Soma or Cell body - contains cytoplasm and the nucleus, which includes the chromosomes. Mitochondria in the cell body perform metabolism. Ribosomes synthesize proteins. Dendrites – receive input from previous neurons. Axon – Carries the electrical impulse (action potential) to the terminal buttons. ...
... Soma or Cell body - contains cytoplasm and the nucleus, which includes the chromosomes. Mitochondria in the cell body perform metabolism. Ribosomes synthesize proteins. Dendrites – receive input from previous neurons. Axon – Carries the electrical impulse (action potential) to the terminal buttons. ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.