Neurophysiology Neurotransmitter and Nervous System
... summation) and across the membrane (spatial summation) . The net effect of summation is reflected at the axon hillock where action potentials are generated. ...
... summation) and across the membrane (spatial summation) . The net effect of summation is reflected at the axon hillock where action potentials are generated. ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... junctions (channels that allow ion currents of action potential to flow) o Chemical synapses Synaptic cleft: narrow gap separating the presynaptic cell from postsynaptic ...
... junctions (channels that allow ion currents of action potential to flow) o Chemical synapses Synaptic cleft: narrow gap separating the presynaptic cell from postsynaptic ...
Nervous System Exam Review
... Be able to diagram how the nervous system is organized (refer to concept map). What is the fundamental unit of the nervous system? Distinguish between a neuron and a neuroglia cell. Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classific ...
... Be able to diagram how the nervous system is organized (refer to concept map). What is the fundamental unit of the nervous system? Distinguish between a neuron and a neuroglia cell. Know the 5 types of neuroglia cell --- where are they found, what do they do. Identify neurons by structural classific ...
The Nervous System - El Camino College
... Release of NT molecules: Exocytosis – the process by which NTs are ejected from the axon button • NT molecules are synthesized and packed into vesicles -- small molecule NTs right there in the terminal button and large molecule NTs in the cell soma (they have to be transported down the axon to the t ...
... Release of NT molecules: Exocytosis – the process by which NTs are ejected from the axon button • NT molecules are synthesized and packed into vesicles -- small molecule NTs right there in the terminal button and large molecule NTs in the cell soma (they have to be transported down the axon to the t ...
The Importance of the Nervous System
... • 10-100 action potentials per second • rate of conduction increases with diameter of nerve (up to 25 m/s) ...
... • 10-100 action potentials per second • rate of conduction increases with diameter of nerve (up to 25 m/s) ...
Nervous System - De Anza College
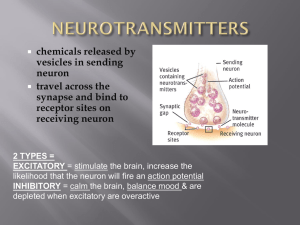
... Synaptic terminal: branch of the axon that forms the specialized connection Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that send information from the transmitting neuron (presynaptic cell) to the receiving neuron (postsynaptic cell) Synaptic terminals ...
... Synaptic terminal: branch of the axon that forms the specialized connection Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that send information from the transmitting neuron (presynaptic cell) to the receiving neuron (postsynaptic cell) Synaptic terminals ...
Excitatory and inhibitory transmission in the superior olivary complex
... Maintenance of high transmission rates is a major physiological problem since it causes severe depletion of the pool of readily releasable synaptic vesicles. Consequently, there is considerable depression in the number of vesicles released following each sequential action potential of the train. Th ...
... Maintenance of high transmission rates is a major physiological problem since it causes severe depletion of the pool of readily releasable synaptic vesicles. Consequently, there is considerable depression in the number of vesicles released following each sequential action potential of the train. Th ...
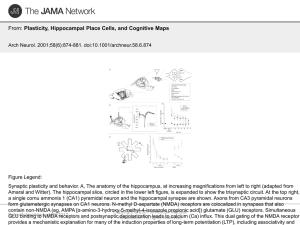
Plasticity, Hippocampal Place Cells, and Cognitive Maps
... receptors and postsynapticAssociation. depolarization leads to calcium (Ca) influx. This dual gating of the NMDA receptor All rights reserved. provides a mechanistic explanation for many of the induction properties of long-term potentiation (LTP), including associativity and ...
... receptors and postsynapticAssociation. depolarization leads to calcium (Ca) influx. This dual gating of the NMDA receptor All rights reserved. provides a mechanistic explanation for many of the induction properties of long-term potentiation (LTP), including associativity and ...
Bio70 Psychobiology Fall 2006 First Midterm October 12 Version A
... a. serotonin; dopamine b. dopamine; serotonin c. acetylcholine; norepinephrine d. norepinephrine; acetylcholine 38. The hindbrain consists of the: a. tectum, tegmentum, and reticular formation. b. thalamus and hypothalamus. c. spinal cord and cranial nerves. d. medulla, pons, and cerebellum. 39. Dam ...
... a. serotonin; dopamine b. dopamine; serotonin c. acetylcholine; norepinephrine d. norepinephrine; acetylcholine 38. The hindbrain consists of the: a. tectum, tegmentum, and reticular formation. b. thalamus and hypothalamus. c. spinal cord and cranial nerves. d. medulla, pons, and cerebellum. 39. Dam ...
Neuron matching
... 1. __________ Cell in the nervous system that supports and assists the neurons 2. __________ Change in membrane polarity that sweeps down a neuron 3. __________ Charge difference across a membrane when the cell is not transmitting an electrical impulse 4. __________ Decrease in the polarity of the m ...
... 1. __________ Cell in the nervous system that supports and assists the neurons 2. __________ Change in membrane polarity that sweeps down a neuron 3. __________ Charge difference across a membrane when the cell is not transmitting an electrical impulse 4. __________ Decrease in the polarity of the m ...
Neurons and Glia Three basic neurons: ∼ Multipolar: Neurons by
... Autapse: Neuron synapses on itself; a negative feedback mechanism. ...
... Autapse: Neuron synapses on itself; a negative feedback mechanism. ...
Ch 48 Nervous System
... Postsynaptic cell: receiving cell 1) Electrical Synapses-via gap junctions; no delay or less in signal strength; less common; fish tail-swim away quickly from predator 2) Chemical Synapses: synaptic cleft separates pre and post-synaptic cells. Not electrically coupled ...
... Postsynaptic cell: receiving cell 1) Electrical Synapses-via gap junctions; no delay or less in signal strength; less common; fish tail-swim away quickly from predator 2) Chemical Synapses: synaptic cleft separates pre and post-synaptic cells. Not electrically coupled ...
Neurology - wsscience
... Chemical synapses differ from electric synapses because chemical synapses: Contain integral proteins Involve a neurotransmitter Involve direct physical contact between cells Propagate action potentials quickly and efficiently ...
... Chemical synapses differ from electric synapses because chemical synapses: Contain integral proteins Involve a neurotransmitter Involve direct physical contact between cells Propagate action potentials quickly and efficiently ...
Chapter 2 - Biological Basis of Behavior
... Stimulants (ex: cocaine, meds for ADD/ADHD, caffeine) cause dopamine to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
... Stimulants (ex: cocaine, meds for ADD/ADHD, caffeine) cause dopamine to be pushed into the synapse so that focus is improved BUT cause a depletion over time Acetylcholine triggers muscle contraction important role in arousal and attention Loss = linked to Alzheimer’s Disease ...
Nervous System
... • A young bird leaves the nest but does not become sexually mature until the following spring. • A male that has been hatched and reared in isolation can sing but not the species specific song. • If a young bird hears the adult song but its hearing is blocked before spring it is unable to repeat th ...
... • A young bird leaves the nest but does not become sexually mature until the following spring. • A male that has been hatched and reared in isolation can sing but not the species specific song. • If a young bird hears the adult song but its hearing is blocked before spring it is unable to repeat th ...
Widely Found and Studied Neurotransmitters
... Many types of neuropeptides; two have been extensively studied Sustance P – constriction and dilation of blood vessels Opioid types – Endorphins enkephalins ...
... Many types of neuropeptides; two have been extensively studied Sustance P – constriction and dilation of blood vessels Opioid types – Endorphins enkephalins ...
Widely Found and Studied Neurotransmitters
... • Many types of neuropeptides; two have been extensively studied • Sustance P – constriction and dilation of blood vessels • Opioid types – – Endorphins – enkephalins ...
... • Many types of neuropeptides; two have been extensively studied • Sustance P – constriction and dilation of blood vessels • Opioid types – – Endorphins – enkephalins ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... the rest are support cells called neuroglial cells Estimated 1 quadrillion synapses ...
... the rest are support cells called neuroglial cells Estimated 1 quadrillion synapses ...
Neural Pathways
... knob, neurotransmitters are released presynaptic into the synaptic cleft neuron -from vesicles ...
... knob, neurotransmitters are released presynaptic into the synaptic cleft neuron -from vesicles ...
Design a Neuron
... Cell body – Contains all organelles including the nucleus. Attached to both dendrites and axon. ...
... Cell body – Contains all organelles including the nucleus. Attached to both dendrites and axon. ...
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
... – Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) – produces a small local depolarization, pushing the cell closer to threshold – Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) – produces a small hyperpolarization, pushing the cell further away from threshold ...
... – Excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) – produces a small local depolarization, pushing the cell closer to threshold – Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP) – produces a small hyperpolarization, pushing the cell further away from threshold ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.