Neurophysiology,Dr Sravanti
... EPSP – when the change causes depolarization, this is called an excitatory post synaptic potential. ...
... EPSP – when the change causes depolarization, this is called an excitatory post synaptic potential. ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 05 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System
... • These cells have many functions, both during development and in supporting the function of the mature nervous system. • They may also constitute a separate, slow signal system. • Oligodendrocytes: produce myelin sheaths for neuron axons (white ...
... • These cells have many functions, both during development and in supporting the function of the mature nervous system. • They may also constitute a separate, slow signal system. • Oligodendrocytes: produce myelin sheaths for neuron axons (white ...
Neurons, Neurons, Neurons!
... as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spinal cord cannot reach other parts of the body. Damage, or scarring, occurs in many places throughout the central nervous system, hence the term "Mult ...
... as sclerosis, plaques, or lesions, can slow down or completely prevent the transmission of signals between nerve cells. Messages from the brain and spinal cord cannot reach other parts of the body. Damage, or scarring, occurs in many places throughout the central nervous system, hence the term "Mult ...
Slide ()
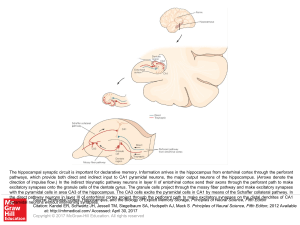
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
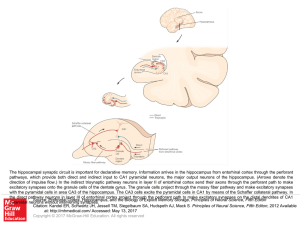
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
ap ch 48 49 powerpoint - Pregitzersninjascienceclasses
... Nerve Communication at the Synapses • If Na+ gates open, membrane becomes depolarized (more +) and results in excitatory postsynaptic potential. It may generate an action potential if strong enough. • If K+ gates open, membrane becomes polarized and results in inhibitory postsynaptic potential (mo ...
... Nerve Communication at the Synapses • If Na+ gates open, membrane becomes depolarized (more +) and results in excitatory postsynaptic potential. It may generate an action potential if strong enough. • If K+ gates open, membrane becomes polarized and results in inhibitory postsynaptic potential (mo ...
phys chapter 45 [10-24
... Excitation – opening of Na+ channels allow large numbers of cations into postsynaptic cell; raises intracellular membrane potential in positive direction (depolarization) o Depressed conduction through Cl- or K+ channels or both; decreases diffusion of Cl- to inside of postsynaptic neuron or decreas ...
... Excitation – opening of Na+ channels allow large numbers of cations into postsynaptic cell; raises intracellular membrane potential in positive direction (depolarization) o Depressed conduction through Cl- or K+ channels or both; decreases diffusion of Cl- to inside of postsynaptic neuron or decreas ...
Chapter 12 - FacultyWeb
... between cells/electrical synapses Chemical synapses involve direct connection between cells/chemical synapses Electrical synapses always use ACh/both are equally abundant ...
... between cells/electrical synapses Chemical synapses involve direct connection between cells/chemical synapses Electrical synapses always use ACh/both are equally abundant ...
Inner Hair Cells
... • INNER HAIR CELLS > Multiple (10 to 20) Afferent synapses > (Efferents synapse on afferent dendrites) • OUTER HAIR CELLS: > Large Efferent synapses engulf base of cell > Small (& not very active) Afferent synapses ...
... • INNER HAIR CELLS > Multiple (10 to 20) Afferent synapses > (Efferents synapse on afferent dendrites) • OUTER HAIR CELLS: > Large Efferent synapses engulf base of cell > Small (& not very active) Afferent synapses ...
Activity of Spiking Neurons Stimulated by External Signals of
... deliver signals and act like an “input device”. Soma is the “central processing unit” that generates a signal if the total input exceeds a certain threshold (about -30 mV) and the axon transmits the signals to other neurons. Synapses are the contact points for transferring information between neuron ...
... deliver signals and act like an “input device”. Soma is the “central processing unit” that generates a signal if the total input exceeds a certain threshold (about -30 mV) and the axon transmits the signals to other neurons. Synapses are the contact points for transferring information between neuron ...
9.2 - 4ubiology
... greater the frequency of impulses. Intense stimuli excite more neurons. Different ...
... greater the frequency of impulses. Intense stimuli excite more neurons. Different ...
Concepts of Neurobiology
... Electrical impulses begins the process Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic: Dominates in stressful situations, prepares body for fight or flight Parasympathic: Dominates when person is relaxed Neurotransmitters Play an important role in human emotions and behavior Are the target for the m ...
... Electrical impulses begins the process Autonomic Nervous System Sympathetic: Dominates in stressful situations, prepares body for fight or flight Parasympathic: Dominates when person is relaxed Neurotransmitters Play an important role in human emotions and behavior Are the target for the m ...
Neuron Function 2
... Electrical synapse - rare found only in a few places in the body Chemical synapse - most frequently found type ...
... Electrical synapse - rare found only in a few places in the body Chemical synapse - most frequently found type ...
The Nervous Systeminofnotes
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
Nerve
... its to collaterals the working presynaptic neuron. into together several neuron(s). is postsynaptic less than the 4-Synaptic Acetylcholine: potentials In neuromuscular are either excitatory junction (NMJ), (EPSP) Myelin prevents leak, nodes of Ranvier act as AP triggered in axon hillock, presence of ...
... its to collaterals the working presynaptic neuron. into together several neuron(s). is postsynaptic less than the 4-Synaptic Acetylcholine: potentials In neuromuscular are either excitatory junction (NMJ), (EPSP) Myelin prevents leak, nodes of Ranvier act as AP triggered in axon hillock, presence of ...
SBI 4U Homeostasis 2
... • Chemical messengers called neurotransmitters carry the neural signal from one neuron to the next neuron or effector. ...
... • Chemical messengers called neurotransmitters carry the neural signal from one neuron to the next neuron or effector. ...
Lecture-08-2013-Bi
... . . . dendrites are not passive. They have Na channels Now break the patch, to fill the cell with dye: ...
... . . . dendrites are not passive. They have Na channels Now break the patch, to fill the cell with dye: ...
Ch. 48 - 49
... Name the three types of neurons and their functions. Which make up the CNS and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
... Name the three types of neurons and their functions. Which make up the CNS and the PNS? Describe the main parts of a neuron. Describe what happens in a Reflex Arc. How are Nodes of Ranvier and Saltatory conduction related? What occurs at the synapse? ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.