Volatile Solvents as Drugs of Abuse: Focus on the Cortico
... 2011). However, the intentional misuse of volatile solvents was not reported in clinical case reports or popular press until the mid-twentieth century. The first documented case was in 1946, when a boy, who was being treated for psychotic symptoms at a hospital, admitted to the attending physician t ...
... 2011). However, the intentional misuse of volatile solvents was not reported in clinical case reports or popular press until the mid-twentieth century. The first documented case was in 1946, when a boy, who was being treated for psychotic symptoms at a hospital, admitted to the attending physician t ...
Clarke`s column neurons as the focus of a corticospinal corollary circuit
... provide anatomical evidence that a subset of Clarke’s column dSC neurons in receipt of proprioceptive sensory input are also contacted by the terminals of corticospinal neurons. To assess the function of these corticospinal inputs, we analyzed the response of fluorogold-labeled Clarke’s column dSC n ...
... provide anatomical evidence that a subset of Clarke’s column dSC neurons in receipt of proprioceptive sensory input are also contacted by the terminals of corticospinal neurons. To assess the function of these corticospinal inputs, we analyzed the response of fluorogold-labeled Clarke’s column dSC n ...
Imaging Single-mRNA Localization and Translation in Live Neurons
... While local translation in dendrites is well accepted, local protein synthesis in axons has been controversial over the years. Although a few early studies reported the presence of ribosomes in axons (Bunge, 1973; Tennyson, 1970; Zelena, 1970), the low density of axonal mRNAs and ribosomes supported ...
... While local translation in dendrites is well accepted, local protein synthesis in axons has been controversial over the years. Although a few early studies reported the presence of ribosomes in axons (Bunge, 1973; Tennyson, 1970; Zelena, 1970), the low density of axonal mRNAs and ribosomes supported ...
Thomas C. Südhof - Nobel Lecture Slides
... botulinum toxins (C. Montecucco + R. Jahn laboratories; 1992/1993) 2. Synaptobrevin, SNAP-25, and syntaxin form a complex, known as SNARE complex (J. Rothman laboratory; 1993) 3. Munc18 binds to SNAREs and is homologous to Unc18 and Sec1p, proteins known to be essential for C. elegans movements and ...
... botulinum toxins (C. Montecucco + R. Jahn laboratories; 1992/1993) 2. Synaptobrevin, SNAP-25, and syntaxin form a complex, known as SNARE complex (J. Rothman laboratory; 1993) 3. Munc18 binds to SNAREs and is homologous to Unc18 and Sec1p, proteins known to be essential for C. elegans movements and ...
Spontaneous persistent activity in entorhinal cortex modulates
... Taken together, their results suggest a region-specific pattern of cortico-hippocampal interactions, whereby MECIII neurons produce a partial decoupling of the CA1 activity from neocortical UDS via their markedly delayed Down transitions and persistent Up states. Notably, the authors found that the ...
... Taken together, their results suggest a region-specific pattern of cortico-hippocampal interactions, whereby MECIII neurons produce a partial decoupling of the CA1 activity from neocortical UDS via their markedly delayed Down transitions and persistent Up states. Notably, the authors found that the ...
MECHANISMS OF CENTRAL TRANSMISSION OF RESPIRATORY
... in the opposite direction. In contrast moderate lung inflation causes more specific effects: activation of expiratory neurons, inactivation of inspiratory neurons. But if a certain degree of lung inflations is exceeded a more general inhibition of both inspiratory and expiratory neurons takes place. ...
... in the opposite direction. In contrast moderate lung inflation causes more specific effects: activation of expiratory neurons, inactivation of inspiratory neurons. But if a certain degree of lung inflations is exceeded a more general inhibition of both inspiratory and expiratory neurons takes place. ...
Developmental Changes in the Subcellular Localization of Calretinin
... because calcium levels locally govern exocytotic neurotransmitter release (Augustine et al., 1987). Because other proteins also contribute to the regulation of calcium ion concentration, one might predict that such proteins, rather than being uniformly dispersed within a cell, might also be spatiall ...
... because calcium levels locally govern exocytotic neurotransmitter release (Augustine et al., 1987). Because other proteins also contribute to the regulation of calcium ion concentration, one might predict that such proteins, rather than being uniformly dispersed within a cell, might also be spatiall ...
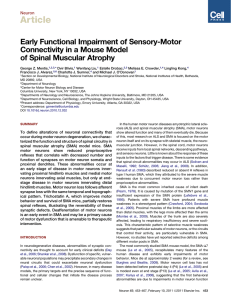
Early Functional Impairment of Sensory-Motor Connectivity in a Mouse Model of Spinal Muscular Atrophy
... show altered function and many of them eventually die. Because of this, most research on ALS and SMA is focused on the motor neuron itself and on its synapse with skeletal muscle, the neuromuscular junction. However, in the spinal cord, motor neurons receive inputs from local spinal networks, descen ...
... show altered function and many of them eventually die. Because of this, most research on ALS and SMA is focused on the motor neuron itself and on its synapse with skeletal muscle, the neuromuscular junction. However, in the spinal cord, motor neurons receive inputs from local spinal networks, descen ...
Opposite Functions of Histamine H1 and H2 Receptors and H3
... duration (0.97 ⫾ 0.07 vs. 0.98 ⫾ 0.08 ms). The fast AHP (fAHP, 20.1 ⫾ 2.1 vs. 19.9 ⫾ 2.4 mV) and medium AHP (mAHP, 10.6 ⫾ 1.5 vs. 10.6 ⫾ 1.7 mV) were also not affected (Fig. 2B). These results indicate that histamine was not affecting voltage-gated Na⫹ and K⫹ channels or Ca2⫹-activated K⫹ channels t ...
... duration (0.97 ⫾ 0.07 vs. 0.98 ⫾ 0.08 ms). The fast AHP (fAHP, 20.1 ⫾ 2.1 vs. 19.9 ⫾ 2.4 mV) and medium AHP (mAHP, 10.6 ⫾ 1.5 vs. 10.6 ⫾ 1.7 mV) were also not affected (Fig. 2B). These results indicate that histamine was not affecting voltage-gated Na⫹ and K⫹ channels or Ca2⫹-activated K⫹ channels t ...
Table of Contents
... are mediated by the GABAA receptor, a GABA-gated chloride channel (Schofield et al., 1987). In vertebrate neurons, chloride ions are pumped out of the cell; thus, activation of GABA receptors will permit chloride to diffuse into the cell, hyperpolarize the membrane and decrease the excitability of t ...
... are mediated by the GABAA receptor, a GABA-gated chloride channel (Schofield et al., 1987). In vertebrate neurons, chloride ions are pumped out of the cell; thus, activation of GABA receptors will permit chloride to diffuse into the cell, hyperpolarize the membrane and decrease the excitability of t ...
Dendritic RNA Transport: Dynamic Spatio-Temporal Control of Neuronal Gene Expression
... strength ,in response to neurotransmission. Recent ...
... strength ,in response to neurotransmission. Recent ...
Localization of Ca2+ Channel Subtypes on Rat Spinal Motor
... Imaging Facility at the University of Washington. Double-labeling studies. Sections were fixed, sliced, rinsed, and blocked as described above. Muscle sections were then incubated in anti-C NA1 and anti-synaptotagmin or anti-C N B2 and anti-synaptotagmin at the same time for 36 hr at 4°C. Sections f ...
... Imaging Facility at the University of Washington. Double-labeling studies. Sections were fixed, sliced, rinsed, and blocked as described above. Muscle sections were then incubated in anti-C NA1 and anti-synaptotagmin or anti-C N B2 and anti-synaptotagmin at the same time for 36 hr at 4°C. Sections f ...
Direction of action is represented in the ventral premotor cortex
... highly and positively correlated with its preferred direction during the execution period (Fig. 5b). One neuron in the PMv displayed a striking inverse relationship between the preferred directions of activity during the execution and instruction periods (asterisk, Fig. 5b). Taken together, these re ...
... highly and positively correlated with its preferred direction during the execution period (Fig. 5b). One neuron in the PMv displayed a striking inverse relationship between the preferred directions of activity during the execution and instruction periods (asterisk, Fig. 5b). Taken together, these re ...
Activity of Ventral Medial Thalamic Neurons during
... Absence seizures are characterized by bilaterally synchronous spike-and-wave discharges (SWDs) in the electroencephalogram, which reflect abnormal oscillations in corticothalamic networks. Although it was suggested that basal ganglia could modulate, via their feedback circuits to the cerebral cortex ...
... Absence seizures are characterized by bilaterally synchronous spike-and-wave discharges (SWDs) in the electroencephalogram, which reflect abnormal oscillations in corticothalamic networks. Although it was suggested that basal ganglia could modulate, via their feedback circuits to the cerebral cortex ...
Module 4 Notes full - Mark Rothery`s Biology
... The initiation of an action potential and its all-or-nothing nature, explained by changes in membrane permeability leading to deplorisation. The passage of an action potential along non-myelinated and myelinated axons resulting in nerve impulses. The nature and importance of the refractory perio ...
... The initiation of an action potential and its all-or-nothing nature, explained by changes in membrane permeability leading to deplorisation. The passage of an action potential along non-myelinated and myelinated axons resulting in nerve impulses. The nature and importance of the refractory perio ...
A Physiologically Plausible Model of Action Selection
... (9) SNr and EP maintain a tonic inhibitory output over their target structures in thalamus and brainstem. Selection of an action is then encoded by suppression of the appropriate neural population (output “channel”) in SNr/EP, resulting in selective disinhibition of basal ganglia output targets (Che ...
... (9) SNr and EP maintain a tonic inhibitory output over their target structures in thalamus and brainstem. Selection of an action is then encoded by suppression of the appropriate neural population (output “channel”) in SNr/EP, resulting in selective disinhibition of basal ganglia output targets (Che ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.