AP Psychology – Unit 3 – Biological Bases of Behavior
... b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. syna ...
... b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. syna ...
1 - My Blog
... b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. syna ...
... b. only be able to write the word key using her left hand. c. only be able to draw a picture of a key using her left hand. d. do none of the above. 31. The branching extensions of nerve cells that receive incoming signals from sensory receptors or from other neurons are called the: a. axons. b. syna ...
Everson Nervous system I. Functional/ Anatomical Divisions A
... membrane, where the inside becomes more positively charged than the outside. 4. This initial reversal of charge is propagated down the axon (saltatory conduction in myelinated axons) to the axon terminals. 5. The electrical impulse then causes the release of the _________________________ which diff ...
... membrane, where the inside becomes more positively charged than the outside. 4. This initial reversal of charge is propagated down the axon (saltatory conduction in myelinated axons) to the axon terminals. 5. The electrical impulse then causes the release of the _________________________ which diff ...
Pain Physiology
... and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage’. Pain has objective, physiological sensory aspects as well as subjective, emotional and psychological components. The term ‘nociception’ is used only to describe the neural response to tr ...
... and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage’. Pain has objective, physiological sensory aspects as well as subjective, emotional and psychological components. The term ‘nociception’ is used only to describe the neural response to tr ...
Lec 7 Lab Demo Handout
... As body temperatures decrease, shivering thermogenesis progresses from increased thermoregulatory muscle tone, to micro-vibrations, to clonic contractions of both flexor and extensor muscles. The shivering pathway begins with signals from the precentral gyrus or the premotor cortex. These impulses a ...
... As body temperatures decrease, shivering thermogenesis progresses from increased thermoregulatory muscle tone, to micro-vibrations, to clonic contractions of both flexor and extensor muscles. The shivering pathway begins with signals from the precentral gyrus or the premotor cortex. These impulses a ...
The Nervous System and Neurons
... Nervous System (PNS) Mainly nerve fibres outside the brain and spinal cord Consists of long dendrites or axons taking impulses to ...
... Nervous System (PNS) Mainly nerve fibres outside the brain and spinal cord Consists of long dendrites or axons taking impulses to ...
Sprint Adaptive Swimwear - Post
... For more information about this suit, and other creative products that address the needs of those who utilize pools for physical therapy as well as recreation, visit www.sprintaquatics.com or call 800-235-2156. s ...
... For more information about this suit, and other creative products that address the needs of those who utilize pools for physical therapy as well as recreation, visit www.sprintaquatics.com or call 800-235-2156. s ...
General Physiology
... • The entire membrane is held together by noncovalent interaction of hydrophobic tails • the structure is quite fluid and not fixed rigidly in place • The bilayer is impenetrable to water soluble molecules and ions • The right ratio of saturated to unsaturated fatty acids keeps the membrane fluid a ...
... • The entire membrane is held together by noncovalent interaction of hydrophobic tails • the structure is quite fluid and not fixed rigidly in place • The bilayer is impenetrable to water soluble molecules and ions • The right ratio of saturated to unsaturated fatty acids keeps the membrane fluid a ...
Slide ()
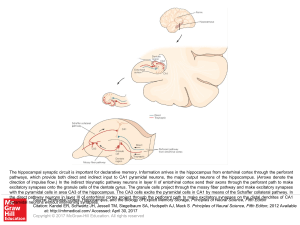
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
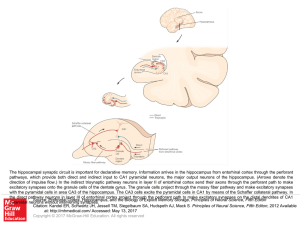
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
nn2new-02
... •We can forget all sub-threshold activity and concentrate on spikes, which are signals sent to other neurons ...
... •We can forget all sub-threshold activity and concentrate on spikes, which are signals sent to other neurons ...
Med Term Chapter 10
... cord is lined by ependymal cells which have cilia (arrows) that project into the lumen of the central canal. ...
... cord is lined by ependymal cells which have cilia (arrows) that project into the lumen of the central canal. ...
Behavioral Neuroscience
... Depolarization: Depolarization occurs when positive ions enter the neuron, making it more prone to firing an action potential. Hyperpolarization occurs when negative ions enter the neuron, making it less prone to firing an action potential. ...
... Depolarization: Depolarization occurs when positive ions enter the neuron, making it more prone to firing an action potential. Hyperpolarization occurs when negative ions enter the neuron, making it less prone to firing an action potential. ...
Neural Anatomy and Function
... This time he stimulates 460 motor units (280 slow twitch and 180 fast twitch) As the pectoralis major muscle contracts the GTO in the pectoralis major are stimulated They stimulate a sensory nerve leading to the CNS In the CNS, the sensory nerve synapses with a motor nerve that will inhibit (relax) ...
... This time he stimulates 460 motor units (280 slow twitch and 180 fast twitch) As the pectoralis major muscle contracts the GTO in the pectoralis major are stimulated They stimulate a sensory nerve leading to the CNS In the CNS, the sensory nerve synapses with a motor nerve that will inhibit (relax) ...
My Big List Thing
... Neurite: extension of cell body of neuron; can be axon or dendrite; typically used re: immature neurons due to difficulty in determining which is being observed Neuropilin: receptors in neurons which receive semaphorins and VEGF Orbit: cavity in skull for eye and its appendages; human orbit takes up ...
... Neurite: extension of cell body of neuron; can be axon or dendrite; typically used re: immature neurons due to difficulty in determining which is being observed Neuropilin: receptors in neurons which receive semaphorins and VEGF Orbit: cavity in skull for eye and its appendages; human orbit takes up ...
CASE 5
... peripheral postganglionic neurons, which then synapse onto effector cells in target organs. In the sympathetic system, the preganglionic cell bodies are in the intermediolateral column of the spinal cord between levels T1 and L3 (thoracolumbar). The postganglionic cell bodies are in either the nearb ...
... peripheral postganglionic neurons, which then synapse onto effector cells in target organs. In the sympathetic system, the preganglionic cell bodies are in the intermediolateral column of the spinal cord between levels T1 and L3 (thoracolumbar). The postganglionic cell bodies are in either the nearb ...
Perception Lecture unit6Perception
... Chemicals – chemoreceptors Pressure – mechanoreceptors Light - photoreceptors ...
... Chemicals – chemoreceptors Pressure – mechanoreceptors Light - photoreceptors ...
Chapter 5: The First Two Years
... dendrites, and synapses occur (connections are being made) • Transient Exuberance is the great increase in the number of dendrites that occurs in an infant’s brain over 1st 2 years of life • Enables neurons to become connected and communicate with other neurons within the brain – This leads to expan ...
... dendrites, and synapses occur (connections are being made) • Transient Exuberance is the great increase in the number of dendrites that occurs in an infant’s brain over 1st 2 years of life • Enables neurons to become connected and communicate with other neurons within the brain – This leads to expan ...
The Cutaneous Senses
... chemicals, severe pressure, and cold • The threshold at which nociceptors respond should be ‘just right’. Too low would cause normal activity to result in pain; too high would take away from the early warning aspect of pain (the skin would already be damaged before we sensed pain). ...
... chemicals, severe pressure, and cold • The threshold at which nociceptors respond should be ‘just right’. Too low would cause normal activity to result in pain; too high would take away from the early warning aspect of pain (the skin would already be damaged before we sensed pain). ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.