Introduction to Skeletal Muscle
... Distribution of Na+-K+ pumps in skeletal muscle and muscle-nerve bundles (N). Pumps are lit from exposure to a labeled antibody ...
... Distribution of Na+-K+ pumps in skeletal muscle and muscle-nerve bundles (N). Pumps are lit from exposure to a labeled antibody ...
Neuroscience and Behavior - Bremerton School District
... A neural impulse. A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
... A neural impulse. A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon and is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon’s membrane. ...
What are the physical and perceptual dimensions of light
... of neurons: receptors, horizontal cells, bipolar cells, amacrine cells, and retinal ganglion cells. • Light reaches the receptor layer only after passing through the other four layers; for this reason, the cellular organization of the retina is described as “inside-out.” • The point at which the opt ...
... of neurons: receptors, horizontal cells, bipolar cells, amacrine cells, and retinal ganglion cells. • Light reaches the receptor layer only after passing through the other four layers; for this reason, the cellular organization of the retina is described as “inside-out.” • The point at which the opt ...
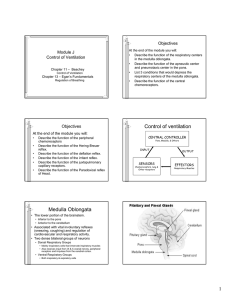
Control of ventilation Medulla Oblongata
... • Also receives input from IX & X cranial nerves, peripheral receptors and impulses from the cerebral cortex. ...
... • Also receives input from IX & X cranial nerves, peripheral receptors and impulses from the cerebral cortex. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - macomb
... • Also receives input from IX & X cranial nerves, peripheral receptors and impulses from the cerebral cortex. ...
... • Also receives input from IX & X cranial nerves, peripheral receptors and impulses from the cerebral cortex. ...
Brain Powerpoint
... called norepinephrine – One of its major functions is to stimulate the adrenal glands to release a hormone called epinephrine – The resulting hormone rush is more commonly known as adrenaline ...
... called norepinephrine – One of its major functions is to stimulate the adrenal glands to release a hormone called epinephrine – The resulting hormone rush is more commonly known as adrenaline ...
SENSORY SYSTEMS
... TOUCH, VIBRATION, PROPRIOCEPTION (AWARENESS OF POSITION AND MOVEMENTS: KINAESTHESIA) ...
... TOUCH, VIBRATION, PROPRIOCEPTION (AWARENESS OF POSITION AND MOVEMENTS: KINAESTHESIA) ...
Slide 2
... Skeletal muscle is made up of individual components known as muscle fibers. Each muscle fiber is formed of still finer fibers, myofibrils. The identifying features of these muscles are haphazard distribution of nuclei among the muscle fibers. The fibers are also transversely marked with line ...
... Skeletal muscle is made up of individual components known as muscle fibers. Each muscle fiber is formed of still finer fibers, myofibrils. The identifying features of these muscles are haphazard distribution of nuclei among the muscle fibers. The fibers are also transversely marked with line ...
Ch 15: Autonomic Division of NS
... Alpha (α-)(Smooth muscle in blood vessels) Beta (β-)(Heart, resp tract, skeletal muscle) An enormous number of drugs have their effect at these receptors ...
... Alpha (α-)(Smooth muscle in blood vessels) Beta (β-)(Heart, resp tract, skeletal muscle) An enormous number of drugs have their effect at these receptors ...
Nervous System
... The largest part of a typical neuron is the cell body. The cell body contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm. Most of the metabolic activity of the neuron takes place in the cell body. Spreading out from the cell body are short, branched extensions called dendrites. Dendrites carry impulses f ...
... The largest part of a typical neuron is the cell body. The cell body contains the nucleus and much of the cytoplasm. Most of the metabolic activity of the neuron takes place in the cell body. Spreading out from the cell body are short, branched extensions called dendrites. Dendrites carry impulses f ...
Sensory System
... largest of the sensory fibers. o Anesthesia: These fibers are the last to be blocked by anesthesia—they are the largest fibers. Class III (A-δ) Fibers: Fast Pain, crude touch, temperature sensation. o Fibers terminate in free nerve endings. o FAST PAIN: Pin-prick pain; it is the first pain you wil ...
... largest of the sensory fibers. o Anesthesia: These fibers are the last to be blocked by anesthesia—they are the largest fibers. Class III (A-δ) Fibers: Fast Pain, crude touch, temperature sensation. o Fibers terminate in free nerve endings. o FAST PAIN: Pin-prick pain; it is the first pain you wil ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis during stress, it is the “flight-or-fight” system of the body. This is done by accelerating heart rate, constricting blood vessels, and raising the blood pressure. For this information to be communicated, it uses pre/post-ganglionic neurons. -Preganglionic ...
... Plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis during stress, it is the “flight-or-fight” system of the body. This is done by accelerating heart rate, constricting blood vessels, and raising the blood pressure. For this information to be communicated, it uses pre/post-ganglionic neurons. -Preganglionic ...
Text S2: Conflicting demands of localization and pattern
... However, in order to achieve invariance with respect to x and µ in the central pattern neuron, we can make use of the subtraction of the peripheries. For any given ∆x this means that rper(x+µ+∆x) - rper(x+µ-∆x) = rdir(∆x). After differentiating this equation with respect to (x+µ) and rearranging we ...
... However, in order to achieve invariance with respect to x and µ in the central pattern neuron, we can make use of the subtraction of the peripheries. For any given ∆x this means that rper(x+µ+∆x) - rper(x+µ-∆x) = rdir(∆x). After differentiating this equation with respect to (x+µ) and rearranging we ...
Neurocognition Cognitive Neuroscience/neuropsychology
... information; an electrochemical transmission along length of neuron Synapse - site of “connection” between adjacent neurons or between neurons and muscle fibers – Terminal buttons of presynaptic neuron @ dendrites/soma of postsynaptic neuron (or muscle fibres) ...
... information; an electrochemical transmission along length of neuron Synapse - site of “connection” between adjacent neurons or between neurons and muscle fibers – Terminal buttons of presynaptic neuron @ dendrites/soma of postsynaptic neuron (or muscle fibres) ...
TABLE OF CONTENTS
... exits the cell body). 2. The action potential is regenerated due to sodium ions moving down the axon, depolarizing adjacent areas of the membrane. 3. Propagation of the action potential: Transmission (movement) of an action potential down an axon. The action potential moves down the axon by regenera ...
... exits the cell body). 2. The action potential is regenerated due to sodium ions moving down the axon, depolarizing adjacent areas of the membrane. 3. Propagation of the action potential: Transmission (movement) of an action potential down an axon. The action potential moves down the axon by regenera ...
Objective 1 | Explain why psychologists are concerned with human
... encased in a myelin sheath. Neurons receive signals from other cells through their branching dendrites and their cell body. If the combined signals are strong enough, the neuron fires, transmitting an electrical impulse (the action potential) down its axon, by means of a chemistry-to-electricity pro ...
... encased in a myelin sheath. Neurons receive signals from other cells through their branching dendrites and their cell body. If the combined signals are strong enough, the neuron fires, transmitting an electrical impulse (the action potential) down its axon, by means of a chemistry-to-electricity pro ...
E.2 Perception of Stimuli
... • Mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical energy in the form of movement, sound, pressure or gravity EX. Hair cells in inner ear move due to sound waves and conduct impulse to brain. • Chemoreceptors response to chemical substance EX. Nerve cells in tongue send impulses to brain when specific chemica ...
... • Mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical energy in the form of movement, sound, pressure or gravity EX. Hair cells in inner ear move due to sound waves and conduct impulse to brain. • Chemoreceptors response to chemical substance EX. Nerve cells in tongue send impulses to brain when specific chemica ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... One of the body’s homeostatic control systems Contains sensors, integrating centers, and output pathways More interneurons in a pathways greater ability to integrate information ...
... One of the body’s homeostatic control systems Contains sensors, integrating centers, and output pathways More interneurons in a pathways greater ability to integrate information ...
Exam 2 2008 - student.ahc.umn.edu
... Pain is provoked only with firm palpation pressure Mild to moderate paroxysmal stabbing shock-like pain Nerve blocks to the trigger area do NOT eliminate their pain All of the above None of the above ...
... Pain is provoked only with firm palpation pressure Mild to moderate paroxysmal stabbing shock-like pain Nerve blocks to the trigger area do NOT eliminate their pain All of the above None of the above ...
FinalStudyGuide
... What is a threshold stimulus? What is the all or none response? Does it occur with muscular contraction? With nerve impulses? Which muscle type causes peristalsis? Nervous How do motor neurons interact with the motor end plate of a muscle to initiate a muscle contraction? What are the func ...
... What is a threshold stimulus? What is the all or none response? Does it occur with muscular contraction? With nerve impulses? Which muscle type causes peristalsis? Nervous How do motor neurons interact with the motor end plate of a muscle to initiate a muscle contraction? What are the func ...
BIOPSYCHOLOGY notes
... • Sensory (afferent) vs. Motor (efferent) neurons: • Sensory/afferent neurons take messages away from sensory organs to the brain. • Motor/efferent neurons take messages from the brain to the muscles resulting in motor tasks. ...
... • Sensory (afferent) vs. Motor (efferent) neurons: • Sensory/afferent neurons take messages away from sensory organs to the brain. • Motor/efferent neurons take messages from the brain to the muscles resulting in motor tasks. ...
neuromuscular transmission neuromuscular junction
... current sink created by this local potential depolarizes the adjacent muscle membrane to its firing level. Action potentials are generated on either side of the end plate and are conducted away from the end plate in both directions along the muscle fiber. The muscle action potential, in turn, initia ...
... current sink created by this local potential depolarizes the adjacent muscle membrane to its firing level. Action potentials are generated on either side of the end plate and are conducted away from the end plate in both directions along the muscle fiber. The muscle action potential, in turn, initia ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.