CNS Brain 241North
... drinking reflexes) • Mesencephalon: Visual and Auditory reflex centers (head-turning) • Pons: Relay station for sensory info. ...
... drinking reflexes) • Mesencephalon: Visual and Auditory reflex centers (head-turning) • Pons: Relay station for sensory info. ...
Student Worksheet
... area. Model demyelination of an axon, and understand its impact on neural transmission. Background (from “Bridging Physics and Biology Using Resistance and Axons” by Joshua M. Dyer): Neurons are nerve cells that are composed of three major sections, as shown in Fig. 1: the dendrites, the cell body, ...
... area. Model demyelination of an axon, and understand its impact on neural transmission. Background (from “Bridging Physics and Biology Using Resistance and Axons” by Joshua M. Dyer): Neurons are nerve cells that are composed of three major sections, as shown in Fig. 1: the dendrites, the cell body, ...
1) Propagated electrical signals - UW Canvas
... 2) Fast chemical transmission at chemical synapses electrical to chemical to electrical ...
... 2) Fast chemical transmission at chemical synapses electrical to chemical to electrical ...
The Nervous System
... • Functions include: – Integrating center for homeostasis, movement, and almost all other body functions. – The mysterious source of those traits that we think of as setting humans apart from animals ...
... • Functions include: – Integrating center for homeostasis, movement, and almost all other body functions. – The mysterious source of those traits that we think of as setting humans apart from animals ...
the electrophysiology of photoreceptors in the nudibranch mollusc
... the dual response is fast, the second is more slowly rising and carries superimposed spikes when they are present (Text-fig. 2). Not all cells show a dual response. It is most prominent with relatively high stimulus energies and absent when the stimulus is weak. The rise time of each component also ...
... the dual response is fast, the second is more slowly rising and carries superimposed spikes when they are present (Text-fig. 2). Not all cells show a dual response. It is most prominent with relatively high stimulus energies and absent when the stimulus is weak. The rise time of each component also ...
The Nervous System - Fulton County Schools
... Left Corpus Right Visual Callosu Visual Cortex m Cortex ...
... Left Corpus Right Visual Callosu Visual Cortex m Cortex ...
Muscle
... -smooth muscle can take its time about contracting and doesn’t have to generate as much force as skeletal muscle. -activated by various way (different in uterus and in intestine or blood vessels) but still metabotropic receptors -signal to contract is an increase in calcium concentration ...
... -smooth muscle can take its time about contracting and doesn’t have to generate as much force as skeletal muscle. -activated by various way (different in uterus and in intestine or blood vessels) but still metabotropic receptors -signal to contract is an increase in calcium concentration ...
Nerves and Digestion
... What is the nervous system? What are the cells called that make up the nervous system? What are the parts of the central nervous system? What makes up the peripheral nervous system? ...
... What is the nervous system? What are the cells called that make up the nervous system? What are the parts of the central nervous system? What makes up the peripheral nervous system? ...
Brain and Neuron Quiz Key
... Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
... Fill in the blanks with the correct words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once, and some may not be used at all. 1. The frontal lobes control motor function. ...
Chapter 2 Powerpoint
... border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and ...
... border of the brainstem and cerebral hemispheres associated with emotions such as fear and aggression and drives such as those for food and sex includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and ...
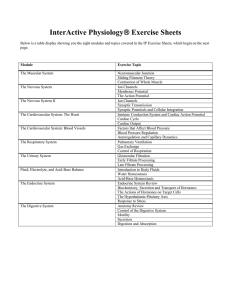
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... a. If the membrane reaches the trigger point, known as __________________, what electrical potential will be generated? __________________________________________ b. During the depolarization phase, voltage-gated __________ channels open and _______ enters the cell. ...
... a. If the membrane reaches the trigger point, known as __________________, what electrical potential will be generated? __________________________________________ b. During the depolarization phase, voltage-gated __________ channels open and _______ enters the cell. ...
Chapter 12 Notes - Las Positas College
... B. Neurons are composed of three main parts: the cell body (soma), dendrites, and an axon. (Figs. 12.4–12.5) 1. The cytoplasm of the cell body contains all the usual organelles and chromatophilic bodies. Most neuronal cell bodies are located within the CNS; those in the PNS are termed ganglia. 2. De ...
... B. Neurons are composed of three main parts: the cell body (soma), dendrites, and an axon. (Figs. 12.4–12.5) 1. The cytoplasm of the cell body contains all the usual organelles and chromatophilic bodies. Most neuronal cell bodies are located within the CNS; those in the PNS are termed ganglia. 2. De ...
與細胞核內受器蛋白結合的激素Hormones That Bind to Nuclear
... Actions are mediated by 2nd messengers (signal-transduction mechanisms). ...
... Actions are mediated by 2nd messengers (signal-transduction mechanisms). ...
Biology Nervous System - Educational Research Center
... − an axon is linked to consecutive neurons or to effector cells by synapses. − an action potential is a sudden and rapid reversal of voltage across the plasma membrane. − an action potential results in release of neurotransmitters from the axon terminals into the synapse.the nervous message propagat ...
... − an axon is linked to consecutive neurons or to effector cells by synapses. − an action potential is a sudden and rapid reversal of voltage across the plasma membrane. − an action potential results in release of neurotransmitters from the axon terminals into the synapse.the nervous message propagat ...
principles and techniques of the examination of the trigeminal nerve
... of cotton or the edge of a tissue. One may also use a light brush of the fingertips against the skin of the face. If reliability is in doubt, the patient should be asked to close the eyes and then indicate each touch. Although the most sensitive test is to compare the sense of light touch on one sid ...
... of cotton or the edge of a tissue. One may also use a light brush of the fingertips against the skin of the face. If reliability is in doubt, the patient should be asked to close the eyes and then indicate each touch. Although the most sensitive test is to compare the sense of light touch on one sid ...
Synapse formation
... has been produced only in laboratory settings, where presynaptic neurons that are electrically stimulated will increase the tendency of a group of neighbouring postsynaptic neurons to fire. • That is… that neurons which have been stimulated will have a greater ‘potential’ to fire when they are stimu ...
... has been produced only in laboratory settings, where presynaptic neurons that are electrically stimulated will increase the tendency of a group of neighbouring postsynaptic neurons to fire. • That is… that neurons which have been stimulated will have a greater ‘potential’ to fire when they are stimu ...
Reading Part 5: The Nervous System
... mechanically gated channel to open or close. Depending on the type of ion channel opened, the membrane can become more negative (hyperpolarized) or more positive (depolarized). ...
... mechanically gated channel to open or close. Depending on the type of ion channel opened, the membrane can become more negative (hyperpolarized) or more positive (depolarized). ...
Diapositive 1 - Andrei Gorea, Ph
... the same region of the left eye's image). The algorithm requires matches to be made between dots of the same colour, which gives rise to possible correspondences at all the nodes in the network marked by an open circle. Neighbouring matches with the same disparity support one another in the network, ...
... the same region of the left eye's image). The algorithm requires matches to be made between dots of the same colour, which gives rise to possible correspondences at all the nodes in the network marked by an open circle. Neighbouring matches with the same disparity support one another in the network, ...
Anatomy of Brain Functions
... also removes waste products that form as byproducts of cellular metabolism within nervous tissue. ...
... also removes waste products that form as byproducts of cellular metabolism within nervous tissue. ...
Clinicals - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Acute loss of cerebral function with symptoms lasting under 24 hours. Origin presumed to be a disorder of cerebral circulation that leaves parts of the brain with an inadequate blood supply. Full Recovery ...
... Acute loss of cerebral function with symptoms lasting under 24 hours. Origin presumed to be a disorder of cerebral circulation that leaves parts of the brain with an inadequate blood supply. Full Recovery ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.