ECE 593 - Southern Illinois University Carbondale
... Cells are the simplest structural units into which a complex multicellular organism can be divided and still retain the functions characteristic of life. Cells can be classified broadly into four types namely muscle cells, nerve cells, epithelial cells, connective tissue cells. Muscle cells: these a ...
... Cells are the simplest structural units into which a complex multicellular organism can be divided and still retain the functions characteristic of life. Cells can be classified broadly into four types namely muscle cells, nerve cells, epithelial cells, connective tissue cells. Muscle cells: these a ...
The History and Scope of Psychology Module 1
... Humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. ...
... Humans and animals operate similarly when processing information. ...
Cnidarians
... HYDROSTATIC SKELETON – circular muscles and longitudinal muscles that enable movement via contraction and water pressure Medusas move by jet propulsion (from muscle contractions) ...
... HYDROSTATIC SKELETON – circular muscles and longitudinal muscles that enable movement via contraction and water pressure Medusas move by jet propulsion (from muscle contractions) ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Dr. Wozniak is examining a cell from the nervous system of an animal. He notices that at one end of the cell body is a long, fibrous strand of tissue. He immediately recognizes this is an axon that is responsible for a. carrying signals away from the cell body b. receiving signals from other cells a ...
... Dr. Wozniak is examining a cell from the nervous system of an animal. He notices that at one end of the cell body is a long, fibrous strand of tissue. He immediately recognizes this is an axon that is responsible for a. carrying signals away from the cell body b. receiving signals from other cells a ...
The Nervous System
... conduction of nerve impulses is prevented due to parasthesia, leading to muscle weakness, unsteady gait & paralysis ...
... conduction of nerve impulses is prevented due to parasthesia, leading to muscle weakness, unsteady gait & paralysis ...
view - Scan. Vet. Press
... a point-to-point transmission of light intensity, as is the case for shaping a pixelated picture on a television or computer screen. Instead, analytical processing of the visual information, both in the retina and in the brain, occurs in such a way that only information about selected characteristic ...
... a point-to-point transmission of light intensity, as is the case for shaping a pixelated picture on a television or computer screen. Instead, analytical processing of the visual information, both in the retina and in the brain, occurs in such a way that only information about selected characteristic ...
Ch 27 Neurones and Neural Pathways
... reaches the synaptic knob, several vesicles fuse with the knob surface membrane and release neurotransmitter from the vesicles into the synaptic cleft ...
... reaches the synaptic knob, several vesicles fuse with the knob surface membrane and release neurotransmitter from the vesicles into the synaptic cleft ...
5 Action Potential.key
... • Voltage-gated ion channels do not only mediate the action potential. They also influence the pattern of action potentials. • Different neurons express different sets of voltageregulated ion channels – Therefore, different neurons have different firing patterns in response to the same excitatory in ...
... • Voltage-gated ion channels do not only mediate the action potential. They also influence the pattern of action potentials. • Different neurons express different sets of voltageregulated ion channels – Therefore, different neurons have different firing patterns in response to the same excitatory in ...
Information Theory and Neural Coding
... Panzeri et al (2001 Neuron Vol. 29, 769–777) recorded from the D2 barrel, stimulated D2 whisker as well as surrounding whiskers. Response PSTHs shown on right While spike counts were not very informative about which whisker was stimulated, response latency carried large amounts of information. ...
... Panzeri et al (2001 Neuron Vol. 29, 769–777) recorded from the D2 barrel, stimulated D2 whisker as well as surrounding whiskers. Response PSTHs shown on right While spike counts were not very informative about which whisker was stimulated, response latency carried large amounts of information. ...
Introduction to Neuroscience: Systems Neuroscience – Concepts
... Examples of Somatosensory receptive fields for 2 neurons in the monkey primary somatosensory cortex: Receptive field ...
... Examples of Somatosensory receptive fields for 2 neurons in the monkey primary somatosensory cortex: Receptive field ...
Sympathetic - Perkins Science
... α1– causes vasoconstriction by increasing Ca2+ α2 – they are activated by norepi, but then cause a negative feedback reduction in epi levels (p. 254) clonidine (drug) - α2 receptors in the brain lowers sympathoadrenal system β(beta) -adrenergic receptors stimulate the production of cAMP in the tar ...
... α1– causes vasoconstriction by increasing Ca2+ α2 – they are activated by norepi, but then cause a negative feedback reduction in epi levels (p. 254) clonidine (drug) - α2 receptors in the brain lowers sympathoadrenal system β(beta) -adrenergic receptors stimulate the production of cAMP in the tar ...
30. Autonomic NS. Sympathetic nervous system
... – Going to the adrenal medulla – No synapse in ganglia – No synapse in collateral ganglia – YES synapse in the adrenal medulla ...
... – Going to the adrenal medulla – No synapse in ganglia – No synapse in collateral ganglia – YES synapse in the adrenal medulla ...
Nervous System - Mrs. Riggs Online
... action potential [Fig 8.11 p.128]: wave of electrical activity in which a brief (+) charge sweeps through neuron and races down axon; propagated by fast-acting, voltagesensing ion gates that quickly open and close, allowing Na and K ions to briefly flow into and out of cell; after action potential p ...
... action potential [Fig 8.11 p.128]: wave of electrical activity in which a brief (+) charge sweeps through neuron and races down axon; propagated by fast-acting, voltagesensing ion gates that quickly open and close, allowing Na and K ions to briefly flow into and out of cell; after action potential p ...
Principles of patch-‐clamp electrical recording
... • ChR2 ac4va4on of many neurons induces an “ar4ficial synchroniza4on” of the neural network. • Changes in ionic gradients occur when using light gated ion pumps. • Non-‐specific targe4ng-‐ leaky expression or ...
... • ChR2 ac4va4on of many neurons induces an “ar4ficial synchroniza4on” of the neural network. • Changes in ionic gradients occur when using light gated ion pumps. • Non-‐specific targe4ng-‐ leaky expression or ...
Elements of the nervous system
... form of heat. It depends on th size of the animals: - Heat produced by bigger animals is larger - Heat produced per body weight decreases with the size of the animal Rubner’s surface area law: heat produced by the basal metabolism of animals is proportional with their surface area rather than their ...
... form of heat. It depends on th size of the animals: - Heat produced by bigger animals is larger - Heat produced per body weight decreases with the size of the animal Rubner’s surface area law: heat produced by the basal metabolism of animals is proportional with their surface area rather than their ...
The Great Brain Drain Review - New Paltz Central School District
... When we experience extreme pain, the body releases endorphins. acetylcholine is the chemical found at neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. Therefore, the poison from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory b ...
... When we experience extreme pain, the body releases endorphins. acetylcholine is the chemical found at neuromuscular junctions. The poison of a black widow spider affects it by mimicking it. Therefore, the poison from a black widow spider is an agonist. Acetylcholine must also be involved in memory b ...
Lecture 17: Sensation
... Complex anatomy allows transfer of mechanical energy (sound waves in the air) to a nerve impulse that is interpreted as SOUND. 1. External ear A. Sound waves are “caught” by the pinna, travel through the ear canal, and run into the tympanic membrane and VIBRATE the membrane. 2. Middle ear: A. Mi ...
... Complex anatomy allows transfer of mechanical energy (sound waves in the air) to a nerve impulse that is interpreted as SOUND. 1. External ear A. Sound waves are “caught” by the pinna, travel through the ear canal, and run into the tympanic membrane and VIBRATE the membrane. 2. Middle ear: A. Mi ...
Sensory systems ppt
... – 3. The vibration causes the malleus (hammer) to hit the incus (anvil) and then the stapes (stirrup). – 4. The vibration passes to the fluid in the cochlea of the inner ear. – 5. Each part of the spiral cochlea is sensitive to different frequencies of sound. – 6. The auditory nerve takes impulses t ...
... – 3. The vibration causes the malleus (hammer) to hit the incus (anvil) and then the stapes (stirrup). – 4. The vibration passes to the fluid in the cochlea of the inner ear. – 5. Each part of the spiral cochlea is sensitive to different frequencies of sound. – 6. The auditory nerve takes impulses t ...
Dear Notetaker:
... phosphate, moves myosin head into a different position, tropomyosin moves via Ca binding troponin C, pulls tropomyosin out of the way, myosin head can bind to the actin, myosin releases when new ATP binds Connect NMJ to ECC (excitation coupling) Length-tension relationship of sarcomere o Resting len ...
... phosphate, moves myosin head into a different position, tropomyosin moves via Ca binding troponin C, pulls tropomyosin out of the way, myosin head can bind to the actin, myosin releases when new ATP binds Connect NMJ to ECC (excitation coupling) Length-tension relationship of sarcomere o Resting len ...
Nerves and Special Senses
... surrounds each fiber • Groups of fibers are bound into fascicles by perineurium • Fascicles are bound together by epineurium ...
... surrounds each fiber • Groups of fibers are bound into fascicles by perineurium • Fascicles are bound together by epineurium ...
Mood & Nuerotransmitters - Center for Optimal Health
... imbalances because the uptake of amino acids by the body is not selective. Foods contain an array of amino acids and no food contains just the precursors needed to specifically affect only serotonin and/or dopamine. When you eat food, your body takes up many different amino acids at random, maki ...
... imbalances because the uptake of amino acids by the body is not selective. Foods contain an array of amino acids and no food contains just the precursors needed to specifically affect only serotonin and/or dopamine. When you eat food, your body takes up many different amino acids at random, maki ...
Advanced Biology\AB U14 Nervous System
... consist of a cell body, which contains the cell nucleus, and an axon, which carries an impulse away from the cell body. Many axons in our bodies are covered by a white, fatty substance called myelin. Myelin is produced by Schwann cells and protects and insulates the nerve. The myelin sheath has gaps ...
... consist of a cell body, which contains the cell nucleus, and an axon, which carries an impulse away from the cell body. Many axons in our bodies are covered by a white, fatty substance called myelin. Myelin is produced by Schwann cells and protects and insulates the nerve. The myelin sheath has gaps ...
bupropion and the autonomic nervous system
... The nervous system comprises the brain and various types of nerves, including afferent nerves (from the Latin, ad = towards; ferro = I carry), which carry sensory impulses from all parts of the body to the brain and efferent nerves (ex = from; ferro = I carry) through which "messages" are conducted ...
... The nervous system comprises the brain and various types of nerves, including afferent nerves (from the Latin, ad = towards; ferro = I carry), which carry sensory impulses from all parts of the body to the brain and efferent nerves (ex = from; ferro = I carry) through which "messages" are conducted ...
Neuroscience and Behavior
... Neurotransmitters in the synapse are reabsorbed into the sending neurons through the process of ...
... Neurotransmitters in the synapse are reabsorbed into the sending neurons through the process of ...
Nervous system (Brain and Plexi)
... consists of brain and spinal cord, serves as information input and output control center for the body, integrates regulates and controls bodys activities and relays impulses between brain and peripheral nerves Peripheral nervous system PNS composed of neurons arranged in nerves, contains sensory and ...
... consists of brain and spinal cord, serves as information input and output control center for the body, integrates regulates and controls bodys activities and relays impulses between brain and peripheral nerves Peripheral nervous system PNS composed of neurons arranged in nerves, contains sensory and ...
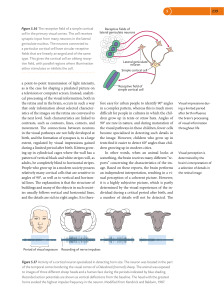
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.