Morphological and Functional Types of Neurons
... Neurons in the thalamic ventral posterior (VB) nucleus of the cat were investigated by extracellular and intracellular recording and by anatomical methods involving either the retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or the intracellular injection of HRP. Two morphological types of neuro ...
... Neurons in the thalamic ventral posterior (VB) nucleus of the cat were investigated by extracellular and intracellular recording and by anatomical methods involving either the retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or the intracellular injection of HRP. Two morphological types of neuro ...
in Primate STT Cells Differentially Modulate Brief
... 1997; Pin and Duvoisin 1995; Schoepp et al. 1999). It is not clear, however, whether group II and/or group III mGluRs actually couple to inhibition of neurotransmitter-induced cAMP increases in native systems. If so, agonists at these receptors may be useful in downregulating the enhanced responses ...
... 1997; Pin and Duvoisin 1995; Schoepp et al. 1999). It is not clear, however, whether group II and/or group III mGluRs actually couple to inhibition of neurotransmitter-induced cAMP increases in native systems. If so, agonists at these receptors may be useful in downregulating the enhanced responses ...
Dendritic Signal Integration
... which typically emanates from the soma. Thus, the soma and axon are often considered to be the final site of synaptic integration. When charge enters a dendrite through synaptically activated ion channels, much of the charge is deposited onto the membrane locally, due to its capacitance, thus produc ...
... which typically emanates from the soma. Thus, the soma and axon are often considered to be the final site of synaptic integration. When charge enters a dendrite through synaptically activated ion channels, much of the charge is deposited onto the membrane locally, due to its capacitance, thus produc ...
leukodystrophy - United Leukodystrophy Foundation
... What is the nervous system? In order to understand the leukodystrophies, we need to discuss some basic facts about the nervous system. The nervous system is made up of two main components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Together, these two systems interact ...
... What is the nervous system? In order to understand the leukodystrophies, we need to discuss some basic facts about the nervous system. The nervous system is made up of two main components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Together, these two systems interact ...
“Conscious” Dorsal Stream
... The notion that spatial awareness is linked to movement is pretty old. Von Helmoltz (1896) proposed the notion that the “a-priori” nature of our representation of space depends on the fact that it is generated by active exploratory behavior. Indeed, as it has been argued elsewhere (see Rizzolatti et ...
... The notion that spatial awareness is linked to movement is pretty old. Von Helmoltz (1896) proposed the notion that the “a-priori” nature of our representation of space depends on the fact that it is generated by active exploratory behavior. Indeed, as it has been argued elsewhere (see Rizzolatti et ...
energy balance
... The BBB constitutes a large interface between the circulation and the central nervous system (CNS), consisting of: brain and spinal cord. ...
... The BBB constitutes a large interface between the circulation and the central nervous system (CNS), consisting of: brain and spinal cord. ...
The “Conscious” Dorsal Stream - Università degli Studi di Parma
... The notion that spatial awareness is linked to movement is pretty old. Von Helmoltz (1896) proposed the notion that the “a-priori” nature of our representation of space depends on the fact that it is generated by active exploratory behavior. Indeed, as it has been argued elsewhere (see Rizzolatti et ...
... The notion that spatial awareness is linked to movement is pretty old. Von Helmoltz (1896) proposed the notion that the “a-priori” nature of our representation of space depends on the fact that it is generated by active exploratory behavior. Indeed, as it has been argued elsewhere (see Rizzolatti et ...
Chapter_02 Edited
... Action Potential – An electric nerve impulse that travels through a neuron, changing the cell’s charge from negative to positive ...
... Action Potential – An electric nerve impulse that travels through a neuron, changing the cell’s charge from negative to positive ...
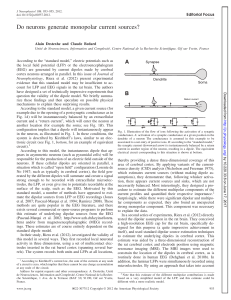
Do neurons generate monopolar current sources?
... in the neuron, as illustrated in Fig. 1. In these conditions, the system is described by Kirchhoff’s laws, similar to an electronic circuit (see Fig. 1, bottom, for an example of equivalent circuit).1 According to this model, the instantaneous dipole that appears in asymmetric neurons (such as pyram ...
... in the neuron, as illustrated in Fig. 1. In these conditions, the system is described by Kirchhoff’s laws, similar to an electronic circuit (see Fig. 1, bottom, for an example of equivalent circuit).1 According to this model, the instantaneous dipole that appears in asymmetric neurons (such as pyram ...
Lesson #M1: How Your Brain Thinks Thoughts Time: 50 minutes
... The neurons in your brain are connected in a dense network, like a web. These cells communicate with each other. Each neuron is connected to between one and one million other cells. Overall in your brain, there are over a trillion connections. When you have a thought, it sends a signal from on ...
... The neurons in your brain are connected in a dense network, like a web. These cells communicate with each other. Each neuron is connected to between one and one million other cells. Overall in your brain, there are over a trillion connections. When you have a thought, it sends a signal from on ...
MECHANISMS OF VERTEBRATE SYNAPTOGENESIS
... chemical signals transmitted through connected networks of neurons. Neurons transmit these signals to one another at specialized sites of contact called synapses. In the vertebrate nervous system, most neurons communicate via chemical synapses. As the name implies, chemical synapses function by conv ...
... chemical signals transmitted through connected networks of neurons. Neurons transmit these signals to one another at specialized sites of contact called synapses. In the vertebrate nervous system, most neurons communicate via chemical synapses. As the name implies, chemical synapses function by conv ...
Lower motor neuron
... • Type I fibers (slower contraction, resistant to fatigue, little ATPase) • Type II fibers (faster contraction, more rapidly fatigued, high ATPase) ...
... • Type I fibers (slower contraction, resistant to fatigue, little ATPase) • Type II fibers (faster contraction, more rapidly fatigued, high ATPase) ...
PART IV INTEGRATION AND COORDINATION IN HUMANS
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. Transmission Across a Synapse Transmis ...
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. Transmission Across a Synapse Transmis ...
cp_kellermann_launay_17092010
... Lariboisière, Paris and the mental health network, Santé Mentale), sheds new light on the mechanisms of action of these drugs which have been used for more than 30 years and are heavily consumed in France. In particular, the researchers have revealed, for the first time, a sequence of reactions caus ...
... Lariboisière, Paris and the mental health network, Santé Mentale), sheds new light on the mechanisms of action of these drugs which have been used for more than 30 years and are heavily consumed in France. In particular, the researchers have revealed, for the first time, a sequence of reactions caus ...
Brain Areas and Topography
... ought to be that lights up for something I think it ought to light up for • Neuroanatomist’s definition of an area: A circumscribed region of the cerebral cortex in which neurons together serve a specific function, receive connections from the same regions, have a common structural arrangement, and ...
... ought to be that lights up for something I think it ought to light up for • Neuroanatomist’s definition of an area: A circumscribed region of the cerebral cortex in which neurons together serve a specific function, receive connections from the same regions, have a common structural arrangement, and ...
Poster Session Abstract Booklet - The New York Academy of Sciences
... Bioelectronic medicine has established that electrical stimulation of the nervous system offers exciting new opportunities for an incredible array of therapies. The development of optogenetics introduced the possibility of targeting specific types of neurons with phenomenal potential for therapeutic ...
... Bioelectronic medicine has established that electrical stimulation of the nervous system offers exciting new opportunities for an incredible array of therapies. The development of optogenetics introduced the possibility of targeting specific types of neurons with phenomenal potential for therapeutic ...
The functional role of GABA and glycine in monaural and binaural
... ascending auditory pathway. It is the target site of multiple ascending pathways from the lower brain stem, which carry monaural as well as binaural information and terminate in either segregated or overlapping fashion in the central nucleus (reviews: Irvine 1986; Oliver and Shneiderman 1991). Many ...
... ascending auditory pathway. It is the target site of multiple ascending pathways from the lower brain stem, which carry monaural as well as binaural information and terminate in either segregated or overlapping fashion in the central nucleus (reviews: Irvine 1986; Oliver and Shneiderman 1991). Many ...
May 21, 04.doc
... Measures of relative optical density were obtained from all the tangential α1-GABAAimmunostained sections, from cortical layer I (whenever possible) to layer IV. Samples were taken within a computer-generated circle over each barrel column, allowing for comparisons between deprived and intact rows. ...
... Measures of relative optical density were obtained from all the tangential α1-GABAAimmunostained sections, from cortical layer I (whenever possible) to layer IV. Samples were taken within a computer-generated circle over each barrel column, allowing for comparisons between deprived and intact rows. ...
A Gaussian Approach to Neural Nets with Multiple Memory Domains
... behaviour of isolated and non-isolated neural that of isolated networks [4]. Neural nets are nets with chemical markers and high assumed to be constructed of discrete sets of connectivity, and the relationship between randomly interconnected neurons with similar structure, as expressed in patterns o ...
... behaviour of isolated and non-isolated neural that of isolated networks [4]. Neural nets are nets with chemical markers and high assumed to be constructed of discrete sets of connectivity, and the relationship between randomly interconnected neurons with similar structure, as expressed in patterns o ...
Introduction: Biology Today Chapter 1
... Since slow pain is generally spread over a large area, it cannot be as readily localized—often it is experienced as a diffuse, throbbing sensation. ...
... Since slow pain is generally spread over a large area, it cannot be as readily localized—often it is experienced as a diffuse, throbbing sensation. ...
ARTICLES
... levels in the presence or absence of OMgp. Only COS-7 cells coexpressing LINGO-1, NgR1 and p75 showed increased RhoA-GTP levels in response to AP-OMgp (Fig. 5a); other binary combinations of these three components were ineffective (NgR1/p75, LINGO-1/NgR1 and LINGO-1/p75, Fig. 4a). MAG-Fc and Nogo-66 ...
... levels in the presence or absence of OMgp. Only COS-7 cells coexpressing LINGO-1, NgR1 and p75 showed increased RhoA-GTP levels in response to AP-OMgp (Fig. 5a); other binary combinations of these three components were ineffective (NgR1/p75, LINGO-1/NgR1 and LINGO-1/p75, Fig. 4a). MAG-Fc and Nogo-66 ...
13 Nervous System
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. Transmission Across a Synapse Transmis ...
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. Transmission Across a Synapse Transmis ...
Sensory responses and movement-related activities in extrinsic
... opened window was then covered with wax. About 30%, 40% and 30% of the units reported in this study were using wires of 14, 17 and 20 lm in diameter, respectively. For mechanical support, recording electrodes were formed into bundles around a coated copper wire with a diameter of 60 lm that was inse ...
... opened window was then covered with wax. About 30%, 40% and 30% of the units reported in this study were using wires of 14, 17 and 20 lm in diameter, respectively. For mechanical support, recording electrodes were formed into bundles around a coated copper wire with a diameter of 60 lm that was inse ...
Rhetorical Mimic: Using Empathy to Persuade
... their states, then we introspect. We no longer think directly about other people but about their reflection on the mirror of our own states” (Keysers, Loc 3241). So what does this do for rhetoric? Iacoboni suggests that mirror cells break down the action between perception and action—our reactions a ...
... their states, then we introspect. We no longer think directly about other people but about their reflection on the mirror of our own states” (Keysers, Loc 3241). So what does this do for rhetoric? Iacoboni suggests that mirror cells break down the action between perception and action—our reactions a ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.