Evidence for neurogenesis in the adult mammalian substantia nigra
... after initiation of BrdUrd i.c.v. infusion (Table 1). In contrast, no BrdUrd⫹ nuclei were found in nigral neurons in animals analyzed immediately after i.p. or after 2 days i.c.v. administration, arguing against DNA repair-associated incorporation. In agreement with earlier studies reporting an incr ...
... after initiation of BrdUrd i.c.v. infusion (Table 1). In contrast, no BrdUrd⫹ nuclei were found in nigral neurons in animals analyzed immediately after i.p. or after 2 days i.c.v. administration, arguing against DNA repair-associated incorporation. In agreement with earlier studies reporting an incr ...
doc GIT
... closure – impulses originate in CNS, mediated by vagus, releasing ACh, causing muscle contraction relaxation – mediated by cessation/arrest of impulses, results in muscle relaxation ...
... closure – impulses originate in CNS, mediated by vagus, releasing ACh, causing muscle contraction relaxation – mediated by cessation/arrest of impulses, results in muscle relaxation ...
PDF file
... vector that links neurons in the earlier cortex. Each neuron i in cortex L2/3 has a top-down weight vector that links neurons in the later cortex. Bottom-up connections generate the information flow starting from an input image, going through V2, branching to the ventral and dorsal pathways, and fin ...
... vector that links neurons in the earlier cortex. Each neuron i in cortex L2/3 has a top-down weight vector that links neurons in the later cortex. Bottom-up connections generate the information flow starting from an input image, going through V2, branching to the ventral and dorsal pathways, and fin ...
Correlated neuronal activity and the flow of neural information
... frequency region, far below respiration rate. There are some peaks at 0.1Hz or at a lower frequency. • Such 0.1Hz oscillations used to be attributed to so-called vaso-motion, of the sort seen in in-vivo optical measurements. Any vascular modulation could lead to CBF variations. If this is the case, ...
... frequency region, far below respiration rate. There are some peaks at 0.1Hz or at a lower frequency. • Such 0.1Hz oscillations used to be attributed to so-called vaso-motion, of the sort seen in in-vivo optical measurements. Any vascular modulation could lead to CBF variations. If this is the case, ...
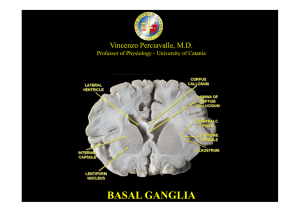
basal ganglia
... into two parts: the pars reticulata (SNpr) and pars compacta (SNpc). The SNpr bears a strong structural and functional resemblance to the internal part of the globus pallidus. The two are sometimes considered parts of the same structure, separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like th ...
... into two parts: the pars reticulata (SNpr) and pars compacta (SNpc). The SNpr bears a strong structural and functional resemblance to the internal part of the globus pallidus. The two are sometimes considered parts of the same structure, separated by the white matter of the internal capsule. Like th ...
differentiation of neuronal types and synapses in myelinating
... M. K. WOLF Differentiation of Neuronal Types and Synapses ...
... M. K. WOLF Differentiation of Neuronal Types and Synapses ...
Physiology Ch 58 p711-720 [4-25
... cerebrum needs signals from lower brain to survive -nerve signals in brainstem directly activate basal level of neuron activity in brain and activate neurohormonal systems that release specific facilitatory/inhibitory hormone neurotransmitter Control of Cerebral Activity by Continuous Excitatory Sig ...
... cerebrum needs signals from lower brain to survive -nerve signals in brainstem directly activate basal level of neuron activity in brain and activate neurohormonal systems that release specific facilitatory/inhibitory hormone neurotransmitter Control of Cerebral Activity by Continuous Excitatory Sig ...
Chapter 2: The Brain and Behavior
... scale is exaggerated here. Such measurements require ultra-small electrodes, as described later in this chapter.) The inside of an axon at rest is about -60 to -70 millivolts, compared with the outside. Electrochemical changes in a neuron generate an action potential. When positively charged sodium ...
... scale is exaggerated here. Such measurements require ultra-small electrodes, as described later in this chapter.) The inside of an axon at rest is about -60 to -70 millivolts, compared with the outside. Electrochemical changes in a neuron generate an action potential. When positively charged sodium ...
Do neurons generate monopolar current sources?
... in the neuron, as illustrated in Fig. 1. In these conditions, the system is described by Kirchhoff’s laws, similar to an electronic circuit (see Fig. 1, bottom, for an example of equivalent circuit).1 According to this model, the instantaneous dipole that appears in asymmetric neurons (such as pyram ...
... in the neuron, as illustrated in Fig. 1. In these conditions, the system is described by Kirchhoff’s laws, similar to an electronic circuit (see Fig. 1, bottom, for an example of equivalent circuit).1 According to this model, the instantaneous dipole that appears in asymmetric neurons (such as pyram ...
striated.
... The elongated fibers of skeletal muscle are striated. The striations are dark and light stripes along the muscle cell due to the arrangement of the protein filaments, or myofilaments within the muscle fiber. Contractions of skeletal muscle can be regulated by conscious control, therefore, it is cons ...
... The elongated fibers of skeletal muscle are striated. The striations are dark and light stripes along the muscle cell due to the arrangement of the protein filaments, or myofilaments within the muscle fiber. Contractions of skeletal muscle can be regulated by conscious control, therefore, it is cons ...
relation between cell size and response characteristics of
... (see Fig. 3, x). The last 8 units exhibited either an increase in firing rate for both directions of stimulus orientation, thus having a predominant second harmonic of unit response or a periodic modulation but only at higher frequencies of angular tilt (see Fig. 3,0); since the results to be descri ...
... (see Fig. 3, x). The last 8 units exhibited either an increase in firing rate for both directions of stimulus orientation, thus having a predominant second harmonic of unit response or a periodic modulation but only at higher frequencies of angular tilt (see Fig. 3,0); since the results to be descri ...
Full text
... processes of the L1 and L2 vertebrae. To avoid the labeling of skin-projecting sensory and sympathetic neurons, full-thickness skin incisions (one paralleling the body long axis and situated 3 cm laterally to the midline formed by spinal processes, as well as two transverse, at Th15 and L3 spinal pr ...
... processes of the L1 and L2 vertebrae. To avoid the labeling of skin-projecting sensory and sympathetic neurons, full-thickness skin incisions (one paralleling the body long axis and situated 3 cm laterally to the midline formed by spinal processes, as well as two transverse, at Th15 and L3 spinal pr ...
The Impact of Prior Experience With Cross-Modal
... stimulus (light) presented to a subject along with a secondary stimulus (sound) will elicit enhancement or depression in the neural activation level, leading to a change in the likelihood of behavioral responses. For example, while coincident presentation of a light and sound at a target location wi ...
... stimulus (light) presented to a subject along with a secondary stimulus (sound) will elicit enhancement or depression in the neural activation level, leading to a change in the likelihood of behavioral responses. For example, while coincident presentation of a light and sound at a target location wi ...
[ 181 Dynamic Imaging of Neuronal Cytoskeleton
... processes. 15 These cultures contain very few glial cells (<5%). For studies of events such as synapse formation that require cortical neurons to survive for several weeks, plating neurons at high densities or the use of glial feeder layers is necessary. 11 Microinjection ...
... processes. 15 These cultures contain very few glial cells (<5%). For studies of events such as synapse formation that require cortical neurons to survive for several weeks, plating neurons at high densities or the use of glial feeder layers is necessary. 11 Microinjection ...
binding, internalization, and retrograde transport of `251
... rapid responses, such as the efflux of Na+ ions (Skaper cells was prevented by treatment with an antimitotic and Varon, 1980), which then give rise to other responses, agent, cytosine arabinoside. Under these conditions, rat such as the observed increased adhesivity in PC12 cells sympathetic neurons ...
... rapid responses, such as the efflux of Na+ ions (Skaper cells was prevented by treatment with an antimitotic and Varon, 1980), which then give rise to other responses, agent, cytosine arabinoside. Under these conditions, rat such as the observed increased adhesivity in PC12 cells sympathetic neurons ...
BIOLOGICAL FOUNDATIONS OF BEHAVIOR
... Huxley provided the answer. Recall that when the cell is resting, positively charged sodium ions in the salty liquid environment are kept outside the cell. When a neuron is stimulated, however, tiny protein structures on the cell membrane called ion channels are activated. Each channel can pump spec ...
... Huxley provided the answer. Recall that when the cell is resting, positively charged sodium ions in the salty liquid environment are kept outside the cell. When a neuron is stimulated, however, tiny protein structures on the cell membrane called ion channels are activated. Each channel can pump spec ...
Glial Signaling Take Home Messages
... i. REM is characterized by high frequency, low amplitude EEG waves 1. Rapid Eye Movement 2. Sleep paralysis ii. NREM is characterized by low frequency, high amplitude EEG waves 1. Slow wave sleep = Slow Oscillation a. Up state – when action potential firing occurs b. Down state – absence of synaptic ...
... i. REM is characterized by high frequency, low amplitude EEG waves 1. Rapid Eye Movement 2. Sleep paralysis ii. NREM is characterized by low frequency, high amplitude EEG waves 1. Slow wave sleep = Slow Oscillation a. Up state – when action potential firing occurs b. Down state – absence of synaptic ...
PDF
... It is widely perceived that there is a problem in giving a naturalistic account of mental representation that deals adequately with the issue of meaning, interpretation, or significance (semantic content). It is suggested here that this problem may arise partly from the conflation of two vernacular ...
... It is widely perceived that there is a problem in giving a naturalistic account of mental representation that deals adequately with the issue of meaning, interpretation, or significance (semantic content). It is suggested here that this problem may arise partly from the conflation of two vernacular ...
The response of cat visual cortex to flicker stimuli of variable frequency
... between recording sites for a given flicker frequency. Typically, the number of additional peaks ranged from one to three, indicating that grouped discharges had not only occurred at intervals corresponding to the flicker frequency, but also at shorter intervals, corresponding to the first, second a ...
... between recording sites for a given flicker frequency. Typically, the number of additional peaks ranged from one to three, indicating that grouped discharges had not only occurred at intervals corresponding to the flicker frequency, but also at shorter intervals, corresponding to the first, second a ...
神经系统传导通路
... organ of Corti →bipolar cell (exchange neuron) →cochlear nerve →ventral cochlear nucleusdorsal and cochlear nucleus (exchange neuron) →trapezoid body of pons overlaps to the opposite side →lateral lemniscus →the dorsi-lateral part of tegmentum of midbrain →inferior colliculus (exchange neuron) →brac ...
... organ of Corti →bipolar cell (exchange neuron) →cochlear nerve →ventral cochlear nucleusdorsal and cochlear nucleus (exchange neuron) →trapezoid body of pons overlaps to the opposite side →lateral lemniscus →the dorsi-lateral part of tegmentum of midbrain →inferior colliculus (exchange neuron) →brac ...
Contextual modulation and stimulus selectivity in extrastriate cortex
... better understood, in part because the space of relevant stimuli is more easily parameterized. Since the eyes themselves are almost never still (Otero-Millan et al., 2008), and objects are typically stationary (Stocker & Simoncelli, 2006), most motion encountered by the visual system is due to displ ...
... better understood, in part because the space of relevant stimuli is more easily parameterized. Since the eyes themselves are almost never still (Otero-Millan et al., 2008), and objects are typically stationary (Stocker & Simoncelli, 2006), most motion encountered by the visual system is due to displ ...
Poster No: 1064 - Orthopaedic Research Society
... MATERALS AND METHODS. In mongrel dogs, the sixth and seventh lumbar laminae were removed, and the seventh lumbar nerve root was exposed widely on one side under general anesthesia. The nerve root was clamped with a clip for microvascular suturing at the midpoint between the dural sac and dorsal root ...
... MATERALS AND METHODS. In mongrel dogs, the sixth and seventh lumbar laminae were removed, and the seventh lumbar nerve root was exposed widely on one side under general anesthesia. The nerve root was clamped with a clip for microvascular suturing at the midpoint between the dural sac and dorsal root ...
8 Renal Physo Overview Flashcards
... It cuts angiotensin-1 (A1) into angiotensin-2 (A2). It causes blood vessel constriction in the afferent arterioles of the nephron. It also stimulates the hypothalamus to secrete aldosterone releasing hormone, which causes the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone, which also increases blood pressure ...
... It cuts angiotensin-1 (A1) into angiotensin-2 (A2). It causes blood vessel constriction in the afferent arterioles of the nephron. It also stimulates the hypothalamus to secrete aldosterone releasing hormone, which causes the adrenal cortex to release aldosterone, which also increases blood pressure ...
A lineage-related reciprocal inhibition circuitry for sensory
... + – Present address: University of Exeter Medical School, Hatherly Laboratories, Prince of Wales Road, Exeter EX4 4PS, UK ...
... + – Present address: University of Exeter Medical School, Hatherly Laboratories, Prince of Wales Road, Exeter EX4 4PS, UK ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.