muscle spindle - KIN450
... conduction (120 m/sec). These afferents increase their firing rate when there is a change in muscle length or rapid movement. They have a rapidly adapting response and therefore provide information about the velocity and direction of the muscle stretch. They also provide information about the rate o ...
... conduction (120 m/sec). These afferents increase their firing rate when there is a change in muscle length or rapid movement. They have a rapidly adapting response and therefore provide information about the velocity and direction of the muscle stretch. They also provide information about the rate o ...
PDF
... Omitting electric shocks during further odor presentations gradually restores the odor’s original hedonic valence—the aversive memory is extinguished (Quinn et al., 1974; Tully and Quinn, 1985). The fly thus keeps a record of its experience, which it uses to inform its actions. Olfactory-driven acti ...
... Omitting electric shocks during further odor presentations gradually restores the odor’s original hedonic valence—the aversive memory is extinguished (Quinn et al., 1974; Tully and Quinn, 1985). The fly thus keeps a record of its experience, which it uses to inform its actions. Olfactory-driven acti ...
Temporal Sequence Detection with Spiking Neurons: Towards
... maximizing its response to a specific spatio-temporal distribution of incoming action potentials. The learning algorithm follows recent biological evidence on synaptic plasticity. It goes beyond the current computational approaches which are based only on the relative timing between single preand po ...
... maximizing its response to a specific spatio-temporal distribution of incoming action potentials. The learning algorithm follows recent biological evidence on synaptic plasticity. It goes beyond the current computational approaches which are based only on the relative timing between single preand po ...
Retinal Ganglion Cells Can Rapidly Change Polarity from Off to On
... We recorded extracellularly from retinal ganglion cells in the isolated salamander retina. To probe how a ganglion cell responds to light, we projected a flickering spot that covered the receptive field center and slightly beyond (Figure 1A). The spot intensity was modulated in a pseudo-random fashion ...
... We recorded extracellularly from retinal ganglion cells in the isolated salamander retina. To probe how a ganglion cell responds to light, we projected a flickering spot that covered the receptive field center and slightly beyond (Figure 1A). The spot intensity was modulated in a pseudo-random fashion ...
Heterogeneous Integration of Bilateral Whisker Signals by Neurons
... barrel. That is, for some time after each stimulus the barrel columns can encode the activity of single whiskers. Similarly, Petersen et al. (2002) recently noted that the earliest evoked spike after an isolated punctate single-whisker stimulus contains most of the information about which the single ...
... barrel. That is, for some time after each stimulus the barrel columns can encode the activity of single whiskers. Similarly, Petersen et al. (2002) recently noted that the earliest evoked spike after an isolated punctate single-whisker stimulus contains most of the information about which the single ...
Regulation
... What are we going to cover? • 1. Basic terminology of regulation theory • 2. Types of feedback loops in the body (positive, negative) • 3. Origin of disturbance/disease in regulated system • 4. History of regulated systems and their description • 5. Different types of governors (automated regulator ...
... What are we going to cover? • 1. Basic terminology of regulation theory • 2. Types of feedback loops in the body (positive, negative) • 3. Origin of disturbance/disease in regulated system • 4. History of regulated systems and their description • 5. Different types of governors (automated regulator ...
Reconstructing the Engram: Neurotechnique Simultaneous, Multisite
... neuroaxis. Yet, most of the contemporary neurophysiological theories still focus on the individual properties of single neurons without much consideration given for the potential role played by the emergent properties of large neuronal ensembles. In part, this is a direct consequence of the most com ...
... neuroaxis. Yet, most of the contemporary neurophysiological theories still focus on the individual properties of single neurons without much consideration given for the potential role played by the emergent properties of large neuronal ensembles. In part, this is a direct consequence of the most com ...
Hearing in a diurnal, mute butterfly, Morpho peleides
... this study. Ribaric and Gogala (1996) described various behavioral responses, including wing flicks and taking flight, to low-frequency (⬇1 kHz) sounds in two species of diurnal wood nymphs, Erebia euryale and E. manto (Nymphalidae, Satyrinae). Response thresholds were increased when VO was covered in ...
... this study. Ribaric and Gogala (1996) described various behavioral responses, including wing flicks and taking flight, to low-frequency (⬇1 kHz) sounds in two species of diurnal wood nymphs, Erebia euryale and E. manto (Nymphalidae, Satyrinae). Response thresholds were increased when VO was covered in ...
Neural processes underlying conscious perception
... during various paradigms including masking [24,27,36], stimuli at threshold [54] and inattention [53]. 2.2. Conscious processing affects specifically late components of sensory processing What is the timing of sensory enhancement in conscious processing? This question could not be addressed using the ...
... during various paradigms including masking [24,27,36], stimuli at threshold [54] and inattention [53]. 2.2. Conscious processing affects specifically late components of sensory processing What is the timing of sensory enhancement in conscious processing? This question could not be addressed using the ...
Finding a face in the crowd: parallel and serial neural mechanisms
... Buneo, 2002), leaving object recognition mechanisms in the temporal cortex with only a single relevant stimulus at a time (Desimone and Duncan, 1995). However, in most common visual scenes, viewers rarely know the specific location of the relevant object in advance — instead, they must search for it, ...
... Buneo, 2002), leaving object recognition mechanisms in the temporal cortex with only a single relevant stimulus at a time (Desimone and Duncan, 1995). However, in most common visual scenes, viewers rarely know the specific location of the relevant object in advance — instead, they must search for it, ...
Irregular persistent activity induced by synaptic excitatory feedback
... Most experimental papers reporting persistent activity have focused purely on changes in firing rates of the recorded neurons. Several recent studies have investigated in more detail the statistics of firing of neurons in dorsolateral PFC during such tasks (Compte et al., 2003; Shinomoto et al., 1999) ...
... Most experimental papers reporting persistent activity have focused purely on changes in firing rates of the recorded neurons. Several recent studies have investigated in more detail the statistics of firing of neurons in dorsolateral PFC during such tasks (Compte et al., 2003; Shinomoto et al., 1999) ...
Nervous System Part 4
... • Short pre-ganglionic neuron and long postganglionic neuron transmit impulse from CNS to the effector • Norepinephrine and epinephrine are neurotransmitters to the effector organs ...
... • Short pre-ganglionic neuron and long postganglionic neuron transmit impulse from CNS to the effector • Norepinephrine and epinephrine are neurotransmitters to the effector organs ...
Chapter 10
... that language did not evolve as a separate modular faculty but that it co-opted preexisting cognitive structures. Language and the brain evolved together. It would be equally true to claim that metaphor and language represent a coevolution, that language co-opted the preexisting cognitive faculty fo ...
... that language did not evolve as a separate modular faculty but that it co-opted preexisting cognitive structures. Language and the brain evolved together. It would be equally true to claim that metaphor and language represent a coevolution, that language co-opted the preexisting cognitive faculty fo ...
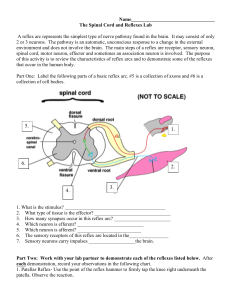
Name__________________________________ The Spinal Cord
... A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve the brain. The main steps of a reflex are receptor, sensory neuron, spi ...
... A reflex arc represents the simplest type of nerve pathway found in the brain. It may consist of only 2 or 3 neurons. The pathway is an automatic, unconscious response to a change in the external environment and does not involve the brain. The main steps of a reflex are receptor, sensory neuron, spi ...
Lesson 1 - SEL at Meigs
... To do this, we will be building our own neuron models out of food! You will be given four different types of food so that each food item can be used for a different part of the neuron. Facilitator discusses diagram: Say: The diagram in front of you has a picture of one brain cell, a neuron, with ...
... To do this, we will be building our own neuron models out of food! You will be given four different types of food so that each food item can be used for a different part of the neuron. Facilitator discusses diagram: Say: The diagram in front of you has a picture of one brain cell, a neuron, with ...
Neural Crest Cells and Axonal Specificity
... stem cell factor promotes proliferation of neural crest that enter skin ...
... stem cell factor promotes proliferation of neural crest that enter skin ...
spinal nerves - Coastal Bend College
... tendon the sensory neurons of the GTO are stimulated AP carried to SC and an Inhibitory Interneuron wh/ are stimulated to release inhibitory NT’s These NT’s inhibit the a motor neurons of the associated muscle causing relaxation. • **Purpose??** To protect both muscles & tendons from XSV tension ...
... tendon the sensory neurons of the GTO are stimulated AP carried to SC and an Inhibitory Interneuron wh/ are stimulated to release inhibitory NT’s These NT’s inhibit the a motor neurons of the associated muscle causing relaxation. • **Purpose??** To protect both muscles & tendons from XSV tension ...
04/20 PPT
... 1. Initial clustering of AChR activity-independent (by unknown factor) 2. Activity-dependent processes at developing synapses -- Increased AChR lifetime (from 1 day to 1 week) -- Down-regulation of extrasynaptic AChRs -- Maturation of AChR clusters (pretzel-shaped) -- Switch of AChR subunit from α2β ...
... 1. Initial clustering of AChR activity-independent (by unknown factor) 2. Activity-dependent processes at developing synapses -- Increased AChR lifetime (from 1 day to 1 week) -- Down-regulation of extrasynaptic AChRs -- Maturation of AChR clusters (pretzel-shaped) -- Switch of AChR subunit from α2β ...
Chapter 12 - Coastal Bend College
... tendon the sensory neurons of the GTO are stimulated AP carried to SC and an Inhibitory Interneuron wh/ are stimulated to release inhibitory NT’s These NT’s inhibit the α motor neurons of the associated muscle causing relaxation. • **Purpose??** To protect both muscles & tendons from XSV tension ...
... tendon the sensory neurons of the GTO are stimulated AP carried to SC and an Inhibitory Interneuron wh/ are stimulated to release inhibitory NT’s These NT’s inhibit the α motor neurons of the associated muscle causing relaxation. • **Purpose??** To protect both muscles & tendons from XSV tension ...
UNIT II - Elsevier Health
... in the neuronal cells in the nervous system. The concentration gradient of each of these ions across the membrane helps determine the voltage of the membrane potential. Second, the degree of importance of each of the ions in determining the voltage is proportional to the membrane permeability for th ...
... in the neuronal cells in the nervous system. The concentration gradient of each of these ions across the membrane helps determine the voltage of the membrane potential. Second, the degree of importance of each of the ions in determining the voltage is proportional to the membrane permeability for th ...
Developmental biology 2008 Lecture 3
... the aqueous humor. The inner layer of the cornea derives from cranial neural crest cells. The iris (a pigmented muscular tissue responsible for controlling pupil size) develops from the outer rim of the optic cup (i.e., the iris is an ectodermally derived muscle!). ...
... the aqueous humor. The inner layer of the cornea derives from cranial neural crest cells. The iris (a pigmented muscular tissue responsible for controlling pupil size) develops from the outer rim of the optic cup (i.e., the iris is an ectodermally derived muscle!). ...
The Neurally Controlled Animat: Biological Brains Acting
... Over the course of the run many different patterns of neural activity emerged. The bottom right panel of Figure 3 shows the total number of patterns detected as the session progressed. Over the first few minutes the clustering algorithm quickly learned to recognize many of the patterns of activity o ...
... Over the course of the run many different patterns of neural activity emerged. The bottom right panel of Figure 3 shows the total number of patterns detected as the session progressed. Over the first few minutes the clustering algorithm quickly learned to recognize many of the patterns of activity o ...
see p. D20 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... b) concentric needle electrode (most popular) - fine silver (or platinum) wire, insulated except at its tip, that is contained within pointed steel shaft - potential difference between outer shaft and inner wire is recorded. upward deflection indicates that active electrode is negative with respect ...
... b) concentric needle electrode (most popular) - fine silver (or platinum) wire, insulated except at its tip, that is contained within pointed steel shaft - potential difference between outer shaft and inner wire is recorded. upward deflection indicates that active electrode is negative with respect ...
Neuropathic Pain (excluding headache)
... • “...unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage…” • Neuropathic pain caused by direct lesions or ...
... • “...unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage…” • Neuropathic pain caused by direct lesions or ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.