CH 12 shortened for test three nervous tissue A and P 2016
... neuropeptides = cholecystokinin, sub P, enkephalins, endorphins neuromodulating hormones = long term effectors = NO, dopa, serotonin, histamine ...
... neuropeptides = cholecystokinin, sub P, enkephalins, endorphins neuromodulating hormones = long term effectors = NO, dopa, serotonin, histamine ...
Neurons - World of Teaching
... This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This further creates a charge differen ...
... This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This further creates a charge differen ...
Biology 3201 - s3.amazonaws.com
... This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This further creates a charge differen ...
... This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside. This is helped by the (-) proteins etc. The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This further creates a charge differen ...
Nervous System - Westminster College
... distribute ions differentially between the inside and outside of the cell. • Ion pumps: For every two positively charged potassium ions pumped into cell, three positively charged sodium ions are pumped out • This creates an voltage difference of 70 mV across cell membrane (more positive charges are ...
... distribute ions differentially between the inside and outside of the cell. • Ion pumps: For every two positively charged potassium ions pumped into cell, three positively charged sodium ions are pumped out • This creates an voltage difference of 70 mV across cell membrane (more positive charges are ...
Developer Notes
... messages. These “messages” are actually electrical. We can use our knowledge of physics to understand how they are transmitted! Different types of neurons respond to different stimuli. A stimulus is anything that generates a nerve response. For example, light is a stimulus that generates a response ...
... messages. These “messages” are actually electrical. We can use our knowledge of physics to understand how they are transmitted! Different types of neurons respond to different stimuli. A stimulus is anything that generates a nerve response. For example, light is a stimulus that generates a response ...
A neuron receives input from other neurons
... This link is called a synapse. The extent to which the signal from one neuron is passed on to the next depends on many factors, e.g. the amount of neurotransmittor available, the number and arrangement of receptors, amount of neurotransmittor reabsorbed, etc. ...
... This link is called a synapse. The extent to which the signal from one neuron is passed on to the next depends on many factors, e.g. the amount of neurotransmittor available, the number and arrangement of receptors, amount of neurotransmittor reabsorbed, etc. ...
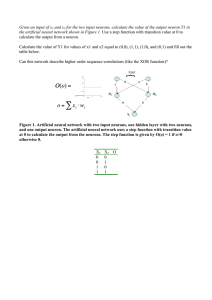
Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the
... Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the value of the output neuron Y1 in the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0 ...
... Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the value of the output neuron Y1 in the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0 ...
Your Nervous System
... sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after depolarization; the neuron cannot be stimulated ...
... sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after depolarization; the neuron cannot be stimulated ...
Human Body Systems - Whitehall District Schools
... stable, internal condition within narrow limits ...
... stable, internal condition within narrow limits ...
Supervised learning
... ei stimulus wi coefficient / synaptic weight v soma potential t transfer function (usually a sigmoïd) s answer The neuron can be in two states • excited, if s = 1 • not excited, if s = 0 Thus, a neuron is going to separate the space of inputs with an hyperplan. This is why a neural network is good a ...
... ei stimulus wi coefficient / synaptic weight v soma potential t transfer function (usually a sigmoïd) s answer The neuron can be in two states • excited, if s = 1 • not excited, if s = 0 Thus, a neuron is going to separate the space of inputs with an hyperplan. This is why a neural network is good a ...
PIPE CLEANER NEURON LESSON PLAN Part A
... Students will form a circle and “send” the message around the room. Each student will be a different part of the neuron and do a different dance to represent the function of that part. 1s – cell body – thinking motion (thinking face—finger tapping lips?) 2s – dendrites – reach out hands, wiggle fing ...
... Students will form a circle and “send” the message around the room. Each student will be a different part of the neuron and do a different dance to represent the function of that part. 1s – cell body – thinking motion (thinking face—finger tapping lips?) 2s – dendrites – reach out hands, wiggle fing ...
Chapter 11: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... 8. Three diagrams of neurons are shown below. On the lines below each diagram, indicate the neuron’s structural (unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar) and functional (sensory, motor, or interneuron/association) classification. ...
... 8. Three diagrams of neurons are shown below. On the lines below each diagram, indicate the neuron’s structural (unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar) and functional (sensory, motor, or interneuron/association) classification. ...
Increased leak conductance alters ISI variability.
... an action potential May occur before (early) or after (delayed) full repolarization Common in cardiac muscles Sometimes occurs in tissues not normally excitable ...
... an action potential May occur before (early) or after (delayed) full repolarization Common in cardiac muscles Sometimes occurs in tissues not normally excitable ...
Slayt 1 - Department of Information Technologies
... The dendrites are tree-like receptive networks of nerve fibers that carry electrical signals into the cell body The cell body effectively sums and thresholds these incoming signals. The axon is a single long fiber that carries the signal from the cell body out to other neurons. The point of contact ...
... The dendrites are tree-like receptive networks of nerve fibers that carry electrical signals into the cell body The cell body effectively sums and thresholds these incoming signals. The axon is a single long fiber that carries the signal from the cell body out to other neurons. The point of contact ...
Chapter 3: The nerve cell Multiple Choice Questions (1
... a. Neurons will fire when they receive any type of information from the neuron before it b. The strength of the action potential fired is dependent upon the strength of the signal the neuron receives c. Graded voltage inputs are summed, and if a threshold point is crossed, the neuron will fire an al ...
... a. Neurons will fire when they receive any type of information from the neuron before it b. The strength of the action potential fired is dependent upon the strength of the signal the neuron receives c. Graded voltage inputs are summed, and if a threshold point is crossed, the neuron will fire an al ...
download
... intended as an invitation to play with the programs and explore the possibilities of different algorithms. The aim of the applets is to illustrate the dynamics of different artificial neural networks. Emphasis has been put on visualization and interactive interfaces. The Java Applets are not intende ...
... intended as an invitation to play with the programs and explore the possibilities of different algorithms. The aim of the applets is to illustrate the dynamics of different artificial neural networks. Emphasis has been put on visualization and interactive interfaces. The Java Applets are not intende ...
The synapse.
... • Adherents of the electrical synapse have no circuit of neurons, in real anatomy, that can account for the irreducible delay. ...
... • Adherents of the electrical synapse have no circuit of neurons, in real anatomy, that can account for the irreducible delay. ...
ch. 48 Nervous System notes
... Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
... Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
Neuron Notes Neuron- Cells that carry messages throughout the
... 3. axons: (transmit/send signals) long fiber that carries impulses away from cell body. 4. myelin sheath: (lipids) insulating membrane around axon. There are small gaps in the myelin sheath along an axon called _nodes_____ Schwann Cells – individual cells of the myelin sheath 5. Axon Terminal- the e ...
... 3. axons: (transmit/send signals) long fiber that carries impulses away from cell body. 4. myelin sheath: (lipids) insulating membrane around axon. There are small gaps in the myelin sheath along an axon called _nodes_____ Schwann Cells – individual cells of the myelin sheath 5. Axon Terminal- the e ...
Slide ()
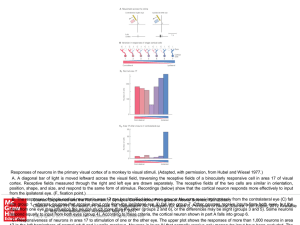
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
Types of neurons
... Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...
... Not present on all cells When present increases the speed of neural signals down the axon. ...