2014 chemical signal..
... - It balances the brain by inhibiting over-excitation. GABA contributes to motor control, vision, and many other cortical functions. -Anxiety is also regulated by GABA. Some drugs that increase the level of GABA in the brain are used to treat epilepsy. ...
... - It balances the brain by inhibiting over-excitation. GABA contributes to motor control, vision, and many other cortical functions. -Anxiety is also regulated by GABA. Some drugs that increase the level of GABA in the brain are used to treat epilepsy. ...
15-1 Section Summary
... he nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps in maintaining stable internal conditions. A stimulus is any change or signal in the enviro ...
... he nervous system receives information about what is happening both inside and outside your body. It also directs the way in which your body responds to this information. In addition, the nervous system helps in maintaining stable internal conditions. A stimulus is any change or signal in the enviro ...
AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 48 Neurons synapses and
... 24. There are many different types of neurotransmitters. Each neuron secretes only one type of neurotransmitter. Some neurotransmitters hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane. Are these excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitters? ...
... 24. There are many different types of neurotransmitters. Each neuron secretes only one type of neurotransmitter. Some neurotransmitters hyperpolarize the postsynaptic membrane. Are these excitatory or inhibitory neurotransmitters? ...
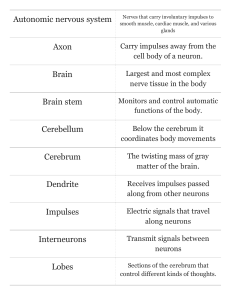
Module 4 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... understanding the rest of the course. Action potentials travel down the axon until reaching a tiny junction, the synapse. Then, the action potential stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules. They cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This allows ions ...
... understanding the rest of the course. Action potentials travel down the axon until reaching a tiny junction, the synapse. Then, the action potential stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules. They cross the synaptic gap and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. This allows ions ...
Nerve cells - Spark (e
... synapses; the cell that sends the signal is the presynaptic cell while which receives it is the postsynaptic one. The space that separates the cells is said synaptic gap or synaptic cleft. ...
... synapses; the cell that sends the signal is the presynaptic cell while which receives it is the postsynaptic one. The space that separates the cells is said synaptic gap or synaptic cleft. ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an _______________________. 11. Indentations between the Schwann cells/myelin sheaths are called the _________ of ______________. 12. Nerve cells are also known as _________________ ...
... 10. A self-propagating wave of electrical negativity that travels along the surface of the neuron membrane is called a/an _______________________. 11. Indentations between the Schwann cells/myelin sheaths are called the _________ of ______________. 12. Nerve cells are also known as _________________ ...
nervous system
... ____________ to _____________ charged due to influx of Na+ ions • This change in electrical charge is also known as the ______________ POTENTIAL ...
... ____________ to _____________ charged due to influx of Na+ ions • This change in electrical charge is also known as the ______________ POTENTIAL ...
lesson 6
... potentials that are abrupt, pulse-like changes in the membrane potential that last a few ten thousandths of a second. • Action potentials can be divided into three phases: the resting or polarized state, depolarization, and repolarization • The amplitude of an action potential is nearly constant and ...
... potentials that are abrupt, pulse-like changes in the membrane potential that last a few ten thousandths of a second. • Action potentials can be divided into three phases: the resting or polarized state, depolarization, and repolarization • The amplitude of an action potential is nearly constant and ...
bioii ch10 ppt
... •This is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It is also the major excitatory transmitter in the brain, and major mediator of excitatory signals in the mammalian central nervous system, involved in most aspects of normal brain functions including cognition, ...
... •This is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It is also the major excitatory transmitter in the brain, and major mediator of excitatory signals in the mammalian central nervous system, involved in most aspects of normal brain functions including cognition, ...
48 - Groupfusion.net
... -excitatory or inhibitory at other sites. ex)heart muscles-> inhibitory -certain bacteria produce a toxin that specifically inhibits presynaptic release of acetylcholine; toxin caused of food poisoning called botulism ...
... -excitatory or inhibitory at other sites. ex)heart muscles-> inhibitory -certain bacteria produce a toxin that specifically inhibits presynaptic release of acetylcholine; toxin caused of food poisoning called botulism ...
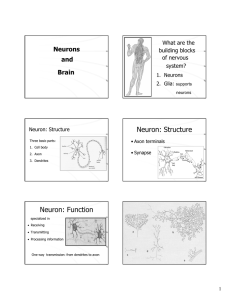
Neuron: Structure Neuron: Function
... Synapse How Neurons Communicate? 2. Chemical Transmission ...
... Synapse How Neurons Communicate? 2. Chemical Transmission ...
Ch 3 Review
... terminal, the synaptic vesicles move to the surface and release neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap Neurotransmitter molecules cross the synaptic gap and attach to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. Neurotransmitters either excite or inhibit the receiving neuron A neuron needs to rece ...
... terminal, the synaptic vesicles move to the surface and release neurotransmitters into the synaptic gap Neurotransmitter molecules cross the synaptic gap and attach to receptor sites on the receiving neuron. Neurotransmitters either excite or inhibit the receiving neuron A neuron needs to rece ...
Neurons and action potential
... 2. Insert a paper clip and penny into a neurotransmitter. 3. Using alligator clips make a connection between two neurons by sending a neurotransmitter from one neuron to another. ...
... 2. Insert a paper clip and penny into a neurotransmitter. 3. Using alligator clips make a connection between two neurons by sending a neurotransmitter from one neuron to another. ...
Lateral inhibition in neuronal interaction as a biological
... 1985, Small et al 1988 and Cottrell et al 1988), in spite of the presence of LI, there is no further provision for other crucial neurobiological features, such as sensitivity to the inhibition to excitation ratio (e.g. Rubenstein and Merzenich 2003, Mel and Schiller 2004), long-term vs. short-term m ...
... 1985, Small et al 1988 and Cottrell et al 1988), in spite of the presence of LI, there is no further provision for other crucial neurobiological features, such as sensitivity to the inhibition to excitation ratio (e.g. Rubenstein and Merzenich 2003, Mel and Schiller 2004), long-term vs. short-term m ...
Chapter 3
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
The Nervous System - Canton Local Schools
... 3. Message is sped up by the Myelin Sheath 4. Message reaches terminal branch and prepares to jump 5. Message jumps synapse 6. Message is received by the next neuron ...
... 3. Message is sped up by the Myelin Sheath 4. Message reaches terminal branch and prepares to jump 5. Message jumps synapse 6. Message is received by the next neuron ...
structure and function of the neurologic system
... – Regeneration more optimistic if injury further away from cell body – With regeneration, see: • Swelling distal to injury • Filaments hypertrophy ...
... – Regeneration more optimistic if injury further away from cell body – With regeneration, see: • Swelling distal to injury • Filaments hypertrophy ...
What is the neuron`s resting potential?
... What causes a neuron to produce an action potential? • A neuron produces an action potential or “fires” when it generates and conducts an electrochemical signal. • A neuron receives electrochemical signals from thousands of adjacent neurons, in the form of “synapses” onto the dendrites or cell body ...
... What causes a neuron to produce an action potential? • A neuron produces an action potential or “fires” when it generates and conducts an electrochemical signal. • A neuron receives electrochemical signals from thousands of adjacent neurons, in the form of “synapses” onto the dendrites or cell body ...
Neural transmission
... system. MS affects young to middle aged adults. Approximately 4 million worldwide have this disease. 400,000 of these people live in the United States. It can affect anyone, and can strike at anytime without warning. Once you develop this disease it will be with you for the remainder of your life, a ...
... system. MS affects young to middle aged adults. Approximately 4 million worldwide have this disease. 400,000 of these people live in the United States. It can affect anyone, and can strike at anytime without warning. Once you develop this disease it will be with you for the remainder of your life, a ...
Chapter 3 Biological Aspects of Psychology
... – Cell membrane keeps out many of the positively charged molecules but some are allowed to enter by passing through special openings called channels (gates) that are normally closed ...
... – Cell membrane keeps out many of the positively charged molecules but some are allowed to enter by passing through special openings called channels (gates) that are normally closed ...
OCR Document - MrsGorukhomework
... The cytoplasm of the neuron is negatively charged with respect to its outside ECF. The cell membrane is said to be polarized - having one side a different charge than the other - called the resting potential. This charge or difference in electrical potential, can actually be measured at -70mV,about ...
... The cytoplasm of the neuron is negatively charged with respect to its outside ECF. The cell membrane is said to be polarized - having one side a different charge than the other - called the resting potential. This charge or difference in electrical potential, can actually be measured at -70mV,about ...