Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... that travels down the axon. It is real electricity, capable of lighting up a light-bulb (if coupled with another handful of neurons). Refractory period = the “recharging phase” when a neuron after firing cannot immediately generate another action potential. Resting potential = state where neuron is ...
... that travels down the axon. It is real electricity, capable of lighting up a light-bulb (if coupled with another handful of neurons). Refractory period = the “recharging phase” when a neuron after firing cannot immediately generate another action potential. Resting potential = state where neuron is ...
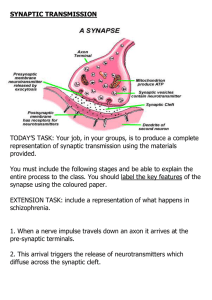
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... Neurotransmitters include: dopamine, acetylcholine and serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, for example, is a mental disorder thought to b ...
... Neurotransmitters include: dopamine, acetylcholine and serotonin. These can all influence the post-synaptic neuron to respond in an inhibitory way (decreases the firing of a cell) or an excitatory way (increases the firing of a cell). Schizophrenia, for example, is a mental disorder thought to b ...
NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS TEST PREVIEW
... 2. What’s the function of the nervous and endocrine systems? 3. What part of a neuron receives impulses and carries it to the cell body? Which part carries impulses away from the cell body? 4. What is the difference between intensity and strength of a nerve impulse? 5. What determines the rate of an ...
... 2. What’s the function of the nervous and endocrine systems? 3. What part of a neuron receives impulses and carries it to the cell body? Which part carries impulses away from the cell body? 4. What is the difference between intensity and strength of a nerve impulse? 5. What determines the rate of an ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... Operating Principle and Required Conditions: The conduction of impulses between neurons operates under an “all-or-none” principle. This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a c ...
... Operating Principle and Required Conditions: The conduction of impulses between neurons operates under an “all-or-none” principle. This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a c ...
Technical Definitions
... Operating Principle and Required Conditions: The conduction of impulses between neurons operates under an “all-or-none” principle. This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a c ...
... Operating Principle and Required Conditions: The conduction of impulses between neurons operates under an “all-or-none” principle. This means that the magnitude of a neuron’s response to a stimulus is independent of the strength of that stimulus. When a single stimulus is strong enough to exceed a c ...
1: Nervous System II: Anatomy Review
... ________________________, and they regulate the amount of ________________________ released by the other neuron. ...
... ________________________, and they regulate the amount of ________________________ released by the other neuron. ...
Neuroanatomy
... and allows positively charged ions into the axon. This overwhelming positive charge causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons via the axon. ...
... and allows positively charged ions into the axon. This overwhelming positive charge causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons via the axon. ...
Slide 1
... and allows positively charged ions into the axon. This overwhelming positive charge causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons via the axon. ...
... and allows positively charged ions into the axon. This overwhelming positive charge causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons via the axon. ...
Biology 3201
... This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside (this is helped by the (-)’ly charged proteins, etc. on the inside) The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This furthe ...
... This causes outside of membrane to have an abundance of + charges compared to inside. The inside of the membrane is negative compared to the outside (this is helped by the (-)’ly charged proteins, etc. on the inside) The “sodium-potassium” pump pulls 2 K+ ions in for 3 Na+ ions sent out. This furthe ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... a neuron is more negative on the inside (Na+ ions more prevalent on outside). When in action potential, polarity switches and cell becomes more positive on inside as ion channels open up and Na+ ions flood in? ...
... a neuron is more negative on the inside (Na+ ions more prevalent on outside). When in action potential, polarity switches and cell becomes more positive on inside as ion channels open up and Na+ ions flood in? ...
Action Potential Webquest
... 4. After sodium ions have flooded into the cell and the sodium gates close, what happens to the potassium ions? 5. How does an action potential conduct along an axon? 6. Describe and draw an action potential. ...
... 4. After sodium ions have flooded into the cell and the sodium gates close, what happens to the potassium ions? 5. How does an action potential conduct along an axon? 6. Describe and draw an action potential. ...
Chapter 10
... • allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information • makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources ...
... • allows nervous system to collect, process, and respond to information • makes it possible for a neuron to sum impulses from different sources ...
Neurons and Neurotransmission - Milton
... “One-third of humanity has perished from the plague. 2.3 billion people have died, and countless more are quickly moving towards the final stages of the disease. There is reason to believe that in a short time, nearly everyone on Earth will be infected. The virus continues to spread exponentially, a ...
... “One-third of humanity has perished from the plague. 2.3 billion people have died, and countless more are quickly moving towards the final stages of the disease. There is reason to believe that in a short time, nearly everyone on Earth will be infected. The virus continues to spread exponentially, a ...
Biology Cells unit: LT8 Review
... Put the images in the correct order to represent the sodiumpotassium pump. The first one is already labeled #1. ...
... Put the images in the correct order to represent the sodiumpotassium pump. The first one is already labeled #1. ...
Neuroanatomy PP - Rincon History Department
... The electrical impulse • Positive ions will flow into the neuron if not stopped or pumped out by the membrane. This is called the electrical potential, which is measured in millivolts. • The resting potential is the neuron’s usual charge, which is – 70 millivolts. • When the resting potential has c ...
... The electrical impulse • Positive ions will flow into the neuron if not stopped or pumped out by the membrane. This is called the electrical potential, which is measured in millivolts. • The resting potential is the neuron’s usual charge, which is – 70 millivolts. • When the resting potential has c ...
Power Point
... During an action potential, depolarization can change the membrane potential from –70 mV to about +30 mV. During repolarization the membrane potential returns to –70 mV. The nerve fiber cannot be stimulated again until repolarization is complete. This period is called the refractory period. If the s ...
... During an action potential, depolarization can change the membrane potential from –70 mV to about +30 mV. During repolarization the membrane potential returns to –70 mV. The nerve fiber cannot be stimulated again until repolarization is complete. This period is called the refractory period. If the s ...
Artificial Intelligence Methods
... Desire to understand the brain and to imitate some of its strength Traditional computers implement a sequence of logical and arithmetic operations but don’t have the ability to adapt their structure or learn Learn from examples, Generalisation ...
... Desire to understand the brain and to imitate some of its strength Traditional computers implement a sequence of logical and arithmetic operations but don’t have the ability to adapt their structure or learn Learn from examples, Generalisation ...
Failure in recycling cellular membrane may be a
... Failure in recycling cellular membrane may be a trigger of Parkinson's 23 February 2017 Cao, a member of the De Camilli lab, recreated the patients' mutation in mice, which developed movement problems and epilepsy similar to the neurological problems found in Parkinson's. Synaptojanin 1 plays a key ...
... Failure in recycling cellular membrane may be a trigger of Parkinson's 23 February 2017 Cao, a member of the De Camilli lab, recreated the patients' mutation in mice, which developed movement problems and epilepsy similar to the neurological problems found in Parkinson's. Synaptojanin 1 plays a key ...
McCulloch-Pitts Neuron
... to perform the OR function. Train a McCulloch-Pitts neural network to perform the AND function. Train a McCulloch-Pitts neural network to perform the AND NOT function. Train a McCulloch-Pitts neural network to perform the XOR function. The McCulloch-Pitts Neuron ...
... to perform the OR function. Train a McCulloch-Pitts neural network to perform the AND function. Train a McCulloch-Pitts neural network to perform the AND NOT function. Train a McCulloch-Pitts neural network to perform the XOR function. The McCulloch-Pitts Neuron ...
PNS and Transmission
... in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through synaptic cleft neurotransmitters bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane. • Depending on t ...
... in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through synaptic cleft neurotransmitters bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane. • Depending on t ...
Resting Potential
... 2. Passive properties: Signaling in the nervous system depends upon changes from the resting membrane potential that are produced by currents that flow when channels in the membrane open or close at synaptic connections or during action potentials. We need to understand something about what influenc ...
... 2. Passive properties: Signaling in the nervous system depends upon changes from the resting membrane potential that are produced by currents that flow when channels in the membrane open or close at synaptic connections or during action potentials. We need to understand something about what influenc ...
DOC - ADAM Interactive Anatomy
... The autonomic nervous system (ANS) consists two divisions, each innervating the effector organs. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) generally speeds up everything except digestion. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) generally slows down everything but digestion. Signals from the SNS cause th ...
... The autonomic nervous system (ANS) consists two divisions, each innervating the effector organs. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) generally speeds up everything except digestion. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) generally slows down everything but digestion. Signals from the SNS cause th ...