The Nervous System
... •During stimulation, often by a neurotransmitter, the sodium channel will open, allowing sodium ions to flow into the cell. •This will change the polarity of the neuron locally, an event called depolarization. Locally the inside is now more positive and the outside less positive. This is called a g ...
... •During stimulation, often by a neurotransmitter, the sodium channel will open, allowing sodium ions to flow into the cell. •This will change the polarity of the neuron locally, an event called depolarization. Locally the inside is now more positive and the outside less positive. This is called a g ...
Impulse Conduction Practice Questions
... a. Which area of the graph indicates the diffusion of Na+ ions into the neurons? Explain your answer. (2 marks) ...
... a. Which area of the graph indicates the diffusion of Na+ ions into the neurons? Explain your answer. (2 marks) ...
File
... ________ The nerve cell that carriers impulses from a sense receptor to the brain and spinal cord. ________ The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons. ________ The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or a gland. 3. There are three structural clas ...
... ________ The nerve cell that carriers impulses from a sense receptor to the brain and spinal cord. ________ The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons. ________ The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or a gland. 3. There are three structural clas ...
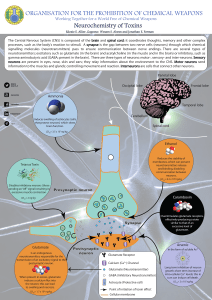
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... ORGANISATION FOR THE PROHIBITION OF CHEMICAL WEAPONS Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons ...
... ORGANISATION FOR THE PROHIBITION OF CHEMICAL WEAPONS Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons ...
Name
... 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous system? 6. What are the structures and functions of the peripheral nervous system? 7. What is a reflex? Give examples 8. What are two ways in which the nervous system can be inj ...
... 4. How do nerve impulses travel from one neuron to another? 5. What are the structure and functions of the central nervous system? 6. What are the structures and functions of the peripheral nervous system? 7. What is a reflex? Give examples 8. What are two ways in which the nervous system can be inj ...
Neurons and Neurotransmitters
... Action Potential: neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon ...
... Action Potential: neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon ...
STRUCTURE OF NEURON AND NEUROGLIA NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Neuron is the basic structural and functional unit of nervous tissue Neuroglia is the supporting or glial tissue that is 10-times more abundant in mammalian brain than neurons NEURON Basic structural unit of the nervous system Specialized cells conduct electrical impulses along the plasma membrane ...
... Neuron is the basic structural and functional unit of nervous tissue Neuroglia is the supporting or glial tissue that is 10-times more abundant in mammalian brain than neurons NEURON Basic structural unit of the nervous system Specialized cells conduct electrical impulses along the plasma membrane ...
Introduction to Anatomy
... basic properties of their cell membranes: 1. There is an electrical voltage, called the resting membrane potential, across the cell membrane. 2. Their cell membranes contain a variety of ion channels (pores) that may be open or ...
... basic properties of their cell membranes: 1. There is an electrical voltage, called the resting membrane potential, across the cell membrane. 2. Their cell membranes contain a variety of ion channels (pores) that may be open or ...
2014 nervous system ppt
... binding of ligand, ion, hormone *Voltage gated = open in response to change in electrical charge across plasma membrane ...
... binding of ligand, ion, hormone *Voltage gated = open in response to change in electrical charge across plasma membrane ...
Pipecleaner Neuron Guide - spectrUM Discovery Area
... • Dendrite–dendrites receive information from other neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons. • Myelin sheath–myelin is a special type of cell that wraps around axons to insulate the information that is being sent and helps deliver it fast ...
... • Dendrite–dendrites receive information from other neurons. The dendrites of one neuron may have between 8,000 and 150,000 contacts with other neurons. • Myelin sheath–myelin is a special type of cell that wraps around axons to insulate the information that is being sent and helps deliver it fast ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
... According to Haykin, S. (1994), Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, NY: Macmillan, p. 2: ...
... According to Haykin, S. (1994), Neural Networks: A Comprehensive Foundation, NY: Macmillan, p. 2: ...
1) Which is NOT a characteristic of living organisms
... voltage-gated calcium channel are blocked and can’t open. Which of the following are true? A) A sensory neuron for touch can still fire an action potential. B) Inhibitory neurons would not be able to release GABA from their axon terminals. C) He’s going to die pretty quickly. D) All of the above are ...
... voltage-gated calcium channel are blocked and can’t open. Which of the following are true? A) A sensory neuron for touch can still fire an action potential. B) Inhibitory neurons would not be able to release GABA from their axon terminals. C) He’s going to die pretty quickly. D) All of the above are ...
Slide 1
... 1. Neurons are electrically active; They have a resting voltage, and can undergo electrical changes ...
... 1. Neurons are electrically active; They have a resting voltage, and can undergo electrical changes ...
VII. The Nervous System
... 3. Chemical Synapse- a chemical called a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell and binds to receptors on a postsynaptic cells causing it to fire. a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) ...
... 3. Chemical Synapse- a chemical called a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell and binds to receptors on a postsynaptic cells causing it to fire. a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) ...
Topic 6.5 Neuron and Synapses
... • Entry of positively charged sodium ions into the neuron develops a net positive charge. • Depolarization of the membrane occurs reversing the membrane potential ...
... • Entry of positively charged sodium ions into the neuron develops a net positive charge. • Depolarization of the membrane occurs reversing the membrane potential ...
1 Neurons 2 Electrical activity of neurons at rest.
... species, and some channel types pass more than one type of ion. For example, people often refer to the “leakage channel” which may be a non-specific mix of potassium and chloride channels. This type of channel is important as it is always functional (open) and thus sets the base for the resting pote ...
... species, and some channel types pass more than one type of ion. For example, people often refer to the “leakage channel” which may be a non-specific mix of potassium and chloride channels. This type of channel is important as it is always functional (open) and thus sets the base for the resting pote ...
Resting Membrane Potential
... resting to firing? • The resting membrane potential of a neuron is -70 mV • In order for a neuron to fire a signal, the membrane potential must reach a certain threshold, around -55 mV. • This happens when another neuron stimulates it and allows a few Na+ channels to open and a few Na+ ions enter th ...
... resting to firing? • The resting membrane potential of a neuron is -70 mV • In order for a neuron to fire a signal, the membrane potential must reach a certain threshold, around -55 mV. • This happens when another neuron stimulates it and allows a few Na+ channels to open and a few Na+ ions enter th ...
www.translationalneuromodeling.org
... Post-synaptic potential (PSP) model: convolution of impulse response and pre-synaptic input Impulse response. H is the synaptic gain, t is the time constant Membrane potential to rate for kth subpopulation. c, r and e are population parametrs (e.g. volatge sensitivity) ...
... Post-synaptic potential (PSP) model: convolution of impulse response and pre-synaptic input Impulse response. H is the synaptic gain, t is the time constant Membrane potential to rate for kth subpopulation. c, r and e are population parametrs (e.g. volatge sensitivity) ...
Types of neurons
... Dendrites Information collectors Receive inputs from neighboring neurons Inputs may number in thousands If receives enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
... Dendrites Information collectors Receive inputs from neighboring neurons Inputs may number in thousands If receives enough inputs the cell’s AXON may generate an output ...
CHAPTER 4 STRUCTURE AND CELL BIOLOGY OF THE NEURON
... Figure 4-3. Schematic diagram to illustrate the distribution of ions inside and outside a neuron. The mushroom-like structure on the cell membrane is meant to represent an ion channel, a pore in the membrane that lets a certain kind of ion through under certain circumstances, but closes under other ...
... Figure 4-3. Schematic diagram to illustrate the distribution of ions inside and outside a neuron. The mushroom-like structure on the cell membrane is meant to represent an ion channel, a pore in the membrane that lets a certain kind of ion through under certain circumstances, but closes under other ...
Anatomy and Physiology 241 Lecture Objectives The Nervous
... Differentiate between neurons and neuroglia cells with respect to function. Identify the different types of neuroglia cellsastrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, satellite and Schwann cells. Be able to identify where they are found in the nervous system and give their specific fun ...
... Differentiate between neurons and neuroglia cells with respect to function. Identify the different types of neuroglia cellsastrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, satellite and Schwann cells. Be able to identify where they are found in the nervous system and give their specific fun ...