Nervous System - Uplift Education
... Repolarization returns the membrane to resting potential (more negatively charged ...
... Repolarization returns the membrane to resting potential (more negatively charged ...
Slide ()
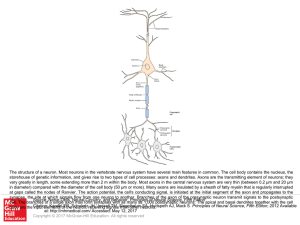
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
Ch. 35.2
... impulses from the environment or other neurons TOWARD the cell body Long fibers AXON carry impulses AWAY from the cell body Neurons may have many dendrites by only one axon Form NERVES when axons and dendrites are clustered together ...
... impulses from the environment or other neurons TOWARD the cell body Long fibers AXON carry impulses AWAY from the cell body Neurons may have many dendrites by only one axon Form NERVES when axons and dendrites are clustered together ...
Action Potentials are - Winona State University
... • Step Two: Voltage gated channels detect a local change in membrane potential that was created (step 1) causing individual VG-Na+ channels to become open for only a few microseconds (Na+), before they close again! • Step Three: Other neighboring voltage gated Na+ channels open (see step 2) further ...
... • Step Two: Voltage gated channels detect a local change in membrane potential that was created (step 1) causing individual VG-Na+ channels to become open for only a few microseconds (Na+), before they close again! • Step Three: Other neighboring voltage gated Na+ channels open (see step 2) further ...
chapter 7 membranes
... Isotonic – solutions with equal solute concentrations Plant cell terms: o Turgid – very firm, when plant has much water o Flaccid – limp, plant cell wilts due to water loss ...
... Isotonic – solutions with equal solute concentrations Plant cell terms: o Turgid – very firm, when plant has much water o Flaccid – limp, plant cell wilts due to water loss ...
Jan 7, 2015. PASSIVE ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF MEMBRANES
... From example trace given in class; Measure time constant Measure change in membrane potential resulting from a given injection of current Calculate input resistance Calculate total capacitance of cell membrane Estimate diameter of the cell ...
... From example trace given in class; Measure time constant Measure change in membrane potential resulting from a given injection of current Calculate input resistance Calculate total capacitance of cell membrane Estimate diameter of the cell ...
cell membranes cw
... potential across a partially permeable membrane. a solution to lose water – water moves from a solution with high water potential to one of lower water potential. Water potential is decreased by the presence of solutes. A liquid that dissolves solids. ...
... potential across a partially permeable membrane. a solution to lose water – water moves from a solution with high water potential to one of lower water potential. Water potential is decreased by the presence of solutes. A liquid that dissolves solids. ...
Nervous system lecture 1
... potentials at the axon hillock can bring about an action potential or inhibit the generation of the action potential. – Spatial: stimulation by many neurons at one time. – Temporal: increased numbers of impulses per minute. ...
... potentials at the axon hillock can bring about an action potential or inhibit the generation of the action potential. – Spatial: stimulation by many neurons at one time. – Temporal: increased numbers of impulses per minute. ...
Active transport - CHS Science Department Mrs. Davis
... Larger molecules can be transported by movements of the cell membrane known as bulk transport. – Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane. • phagocytosis - cell eating • pinocytosis - cell drinking – Exocytosis is a process of releasing large amou ...
... Larger molecules can be transported by movements of the cell membrane known as bulk transport. – Endocytosis is the process of taking material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane. • phagocytosis - cell eating • pinocytosis - cell drinking – Exocytosis is a process of releasing large amou ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel (the receptor), it opens and allows ions to diffuse across the membrane Result- postsynaptic potential (change in membrane potential) Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) membrane potential brought down to threshold Inhibitiory postsynaptic potentials (IPS ...
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel (the receptor), it opens and allows ions to diffuse across the membrane Result- postsynaptic potential (change in membrane potential) Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) membrane potential brought down to threshold Inhibitiory postsynaptic potentials (IPS ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - Fox Valley Lutheran High School
... Much slower than an electric current. (10cm to 1m/sec.) The strength of an impulse is always the same. ...
... Much slower than an electric current. (10cm to 1m/sec.) The strength of an impulse is always the same. ...
Sodium – Potassium Pump
... 3. The pump is now exposed to the outside surface of the cell. 2 K+ ions from outside the cell bind to the pump and the pump changes shape again. 4. K+ ions are transported across the cell membrane and are released inside the cell ...
... 3. The pump is now exposed to the outside surface of the cell. 2 K+ ions from outside the cell bind to the pump and the pump changes shape again. 4. K+ ions are transported across the cell membrane and are released inside the cell ...
3.E.2 Nervous System - kromko
... external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. [See SP 6.2, 7.1] LO 3.44 The student is able to describe how nervous systems detect external and internal signals. [See SP 1.2] LO 3.45 The student is able to describe how nervous systems transmit information. ...
... external and internal signals, transmit and integrate information, and produce responses. [See SP 6.2, 7.1] LO 3.44 The student is able to describe how nervous systems detect external and internal signals. [See SP 1.2] LO 3.45 The student is able to describe how nervous systems transmit information. ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 4. What other cell parts are housed in this main area? 5. The nerve processes that conduct the impulse/action potential away from the cell body are called _________________. 6. The part of a nerve cell that receives impulses and carries them toward the cell body is called a/an __________________. 7. ...
... 4. What other cell parts are housed in this main area? 5. The nerve processes that conduct the impulse/action potential away from the cell body are called _________________. 6. The part of a nerve cell that receives impulses and carries them toward the cell body is called a/an __________________. 7. ...
1 Neurons 2 Electrical activity of neurons at rest.
... capacitance C) producing the capacitive current C dV dt Ions can move into and out of the cell through ionic channels - special protein complexes, spanning the cellular membrane that allow through only particular kinds of ions. There are several different types of channels for each of the common ion ...
... capacitance C) producing the capacitive current C dV dt Ions can move into and out of the cell through ionic channels - special protein complexes, spanning the cellular membrane that allow through only particular kinds of ions. There are several different types of channels for each of the common ion ...
Transport Across Membranes
... In living cells this movement can cause swelling and shrinking depending on the cell’s surrounding conditions There are three kinds of surrounding conditions (hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic) and each impacts the cell in a ...
... In living cells this movement can cause swelling and shrinking depending on the cell’s surrounding conditions There are three kinds of surrounding conditions (hypotonic, hypertonic and isotonic) and each impacts the cell in a ...
7. Describe what membrane potential is, and how
... 6. What is the purpose of the blood-brain barrier? • This restricts the passage of most substances into the brain • Allows the chemical environment of the CNS to be well controlled ...
... 6. What is the purpose of the blood-brain barrier? • This restricts the passage of most substances into the brain • Allows the chemical environment of the CNS to be well controlled ...
Mind Is Matter
... Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Recep ...
... Nodes of Ranvier 3. Describe the direction of communication within a neuron and between two neurons. 4. Identify the various structures with the synaptic cleft (synapse) from a diagram. Describe the function of each structure. Presynaptic membrane Postsynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter Vesicle Recep ...
Electrical Properties of Neuron
... 2.Two, the membrane must be permeable to one or more of these ion species. The permeability is provided by the existence of channels or pores in the bilayer; these channels are usually permeable to a single species of ions. represents an equilibrium situation at which the driving force for the m ...
... 2.Two, the membrane must be permeable to one or more of these ion species. The permeability is provided by the existence of channels or pores in the bilayer; these channels are usually permeable to a single species of ions. represents an equilibrium situation at which the driving force for the m ...
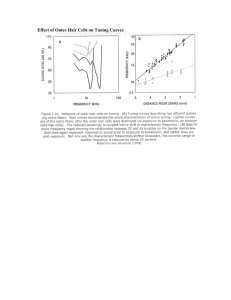
Effect of Outer Hair Cells on Tuning Curves
... potentials in neurons of the spiral ganglion. The patterns of evoked neural activity convey information to the central nervous system (top). In a deafened ear, hair cells have died or no longer function, depriving the spiral ganglion cells of their normal input (bottom). Without regular use, the neu ...
... potentials in neurons of the spiral ganglion. The patterns of evoked neural activity convey information to the central nervous system (top). In a deafened ear, hair cells have died or no longer function, depriving the spiral ganglion cells of their normal input (bottom). Without regular use, the neu ...
Frontiers in , Ph.D. Pharmacology Proudly Presents
... The electrical properties of neurons depend not only on the types of ion channels and receptors expressed, but also on the location of these channels in the cell membrane. Two extreme examples that illustrate the subcellular polarized nature of neurons and the tight regulation of ion channel localiz ...
... The electrical properties of neurons depend not only on the types of ion channels and receptors expressed, but also on the location of these channels in the cell membrane. Two extreme examples that illustrate the subcellular polarized nature of neurons and the tight regulation of ion channel localiz ...
Action Potentials
... The Refractory Period • Resists stimulation • ________________________ – as long as Na+ gates are open – _________________________ ...
... The Refractory Period • Resists stimulation • ________________________ – as long as Na+ gates are open – _________________________ ...
QUEST Study guide Organic molecules Proteins, carbohydrates
... Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, & nucleic acids (just know that these are DNA & RNA) Notes & power point on website Know the biological functions of ALL these molecules Know how to test for glucose, starch, protein, lipids ...
... Proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, & nucleic acids (just know that these are DNA & RNA) Notes & power point on website Know the biological functions of ALL these molecules Know how to test for glucose, starch, protein, lipids ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.