Chapter 4 Study Guide
... 2. The cell membrane regulates the _____________ of molecules into and out of the cell 3. The cell membrane is largely responsible for maintaining cellular ________________. 4. _______________ bilayer determines the basic structure of the cell membrane. 5. Each phospholipid has a polar head that is ...
... 2. The cell membrane regulates the _____________ of molecules into and out of the cell 3. The cell membrane is largely responsible for maintaining cellular ________________. 4. _______________ bilayer determines the basic structure of the cell membrane. 5. Each phospholipid has a polar head that is ...
irons.conroeisd.net
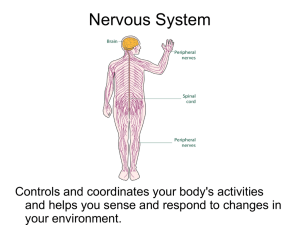
... Controls and coordinates your body's activities and helps you sense and respond to changes in your environment. ...
... Controls and coordinates your body's activities and helps you sense and respond to changes in your environment. ...
Nervous System
... • Interneurons – neurons that integrate sensory input with motor output • Interneuron branches can carry signals to different parts of spinal cord or brain – Convergent circuits bring information from different ...
... • Interneurons – neurons that integrate sensory input with motor output • Interneuron branches can carry signals to different parts of spinal cord or brain – Convergent circuits bring information from different ...
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
... Channels and carriers transport substances across membranes ! Allows cells to adjust pH and salt concentrations ! Allows cells to keep functional chemicals inside ! Allows cells to take up food molecules and exclude toxins ! Allows cells to separate chemical reactions that otherwise would interfere ...
... Channels and carriers transport substances across membranes ! Allows cells to adjust pH and salt concentrations ! Allows cells to keep functional chemicals inside ! Allows cells to take up food molecules and exclude toxins ! Allows cells to separate chemical reactions that otherwise would interfere ...
Supporting Cells - Net Start Class
... membrane near the point of stimulation that generates a nerve impulse. ► Originate from the axon hillock ► Is an “all or none” event Magnitude of the voltage change is the same at each ”firing” regardless of stimuli strength. Stronger stimulus increases the frequency of action potentials but NOT ...
... membrane near the point of stimulation that generates a nerve impulse. ► Originate from the axon hillock ► Is an “all or none” event Magnitude of the voltage change is the same at each ”firing” regardless of stimuli strength. Stronger stimulus increases the frequency of action potentials but NOT ...
Anikeeva
... research is hindered by poor spatial resolution and is often highly invasive. By exploring novel methods of neural stimulation, we hope to realize improvement in targeted and noninvasive stimulation. ...
... research is hindered by poor spatial resolution and is often highly invasive. By exploring novel methods of neural stimulation, we hope to realize improvement in targeted and noninvasive stimulation. ...
The vocabulary of nerve cells
... • Since all external signals must be transduced into voltage in order for the brain to perceive them, and • Since all changes in electrical signals in the nervous system are the result of changes in membrane proteins, then • For any signal (stimulus) to be perceived by a cell there must be one or mo ...
... • Since all external signals must be transduced into voltage in order for the brain to perceive them, and • Since all changes in electrical signals in the nervous system are the result of changes in membrane proteins, then • For any signal (stimulus) to be perceived by a cell there must be one or mo ...
Nervous System - Westminster College
... already less positively charged and since cell pumps them in) As the charge evens out, voltage difference decreases, and more sodium channels open up allowing in even more positive charge – positive feedback loop. Voltage changes from -70 mV to +40 mV. At +40 mV sodium channels close – negative feed ...
... already less positively charged and since cell pumps them in) As the charge evens out, voltage difference decreases, and more sodium channels open up allowing in even more positive charge – positive feedback loop. Voltage changes from -70 mV to +40 mV. At +40 mV sodium channels close – negative feed ...
Bridget Lecture 2 Notes The Neurons o Functional classes (CNS
... ▪ Force of diffusion flows high to low into the cell ▪ Electrostatic pressure based on cell repulsion pushes the ion back out o Intracellular o Anion o High concentration K+ ...
... ▪ Force of diffusion flows high to low into the cell ▪ Electrostatic pressure based on cell repulsion pushes the ion back out o Intracellular o Anion o High concentration K+ ...
Nervous System Vocab1 - Everglades High School
... 28. Neurilemma: Part of the schwann cell, external to the myelin sheath 29. Nodes of Ranvier: gaps or indentations between the schwann cells 30. Ganglia: Small collection of cell bodies outside of the CNS 31. White Matter: Dense collection of myelinated fibers 32. Gray Matter: contains mostly unmyel ...
... 28. Neurilemma: Part of the schwann cell, external to the myelin sheath 29. Nodes of Ranvier: gaps or indentations between the schwann cells 30. Ganglia: Small collection of cell bodies outside of the CNS 31. White Matter: Dense collection of myelinated fibers 32. Gray Matter: contains mostly unmyel ...
Biology II – Chapter 4 Test**
... 2. The cell membrane regulates the ____________________________ of molecules into and out of the cell 3. _____________________________ bilayer determines the basic structure of the cell membrane. 4. _____________________________ are cell-to-cell channels made of protein channels that connect the ins ...
... 2. The cell membrane regulates the ____________________________ of molecules into and out of the cell 3. _____________________________ bilayer determines the basic structure of the cell membrane. 4. _____________________________ are cell-to-cell channels made of protein channels that connect the ins ...
Neurones & the Action Potential
... Contribution of Active Transport There are different numbers of potassium ions (K+) and sodium ions (Na+) on either side of the membrane. Even when a nerve cell is not conducting an impulse, for each ATP molecule that’s hydrolysed, it is actively transporting 3 molecules Na+ out of the cell and 2 m ...
... Contribution of Active Transport There are different numbers of potassium ions (K+) and sodium ions (Na+) on either side of the membrane. Even when a nerve cell is not conducting an impulse, for each ATP molecule that’s hydrolysed, it is actively transporting 3 molecules Na+ out of the cell and 2 m ...
BLM 3 7 FluidMosaicModelAnswers File
... fluid consistency. Various types of proteins are scattered throughout this phospholipid bilayer. Both the phospholipids and proteins move among each other. The lipid bilayer represents the “fluid” part of the fluid-mosaic model, while the various proteins found embedded in the cell membrane account ...
... fluid consistency. Various types of proteins are scattered throughout this phospholipid bilayer. Both the phospholipids and proteins move among each other. The lipid bilayer represents the “fluid” part of the fluid-mosaic model, while the various proteins found embedded in the cell membrane account ...
Active Transport vs. Passive Transport both processes move things
... moves down concentration gradient moves from high-->low concent moves with the natural flow passage is due to inherent E present w/in substances (e-) can occur in living, nonliving, & artificial systems ex: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion ...
... moves down concentration gradient moves from high-->low concent moves with the natural flow passage is due to inherent E present w/in substances (e-) can occur in living, nonliving, & artificial systems ex: diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion ...
biology - TeacherWeb
... problem-solving, movement (___________ cortex), and some aspects of speech (____________ area); also considered the area where the seat of ______________ lies b. temporal lobe = part of the cerebrum in charge of _____________, speech reception, and some parts of the ________________ (hippocampus) c. ...
... problem-solving, movement (___________ cortex), and some aspects of speech (____________ area); also considered the area where the seat of ______________ lies b. temporal lobe = part of the cerebrum in charge of _____________, speech reception, and some parts of the ________________ (hippocampus) c. ...
Nerve Cell Impulses
... membrane pores/gates: in Æ out pores • Na+ (sodium) ions have restricted access • Action potential increases permeability of Na+ • There is selectivity in opening/closing Na+ and K+ gates • Remember: Plasma membrane is semi-permeable to K+ – Physico-chemical ion selectivity channels – (i.e., K+ weak ...
... membrane pores/gates: in Æ out pores • Na+ (sodium) ions have restricted access • Action potential increases permeability of Na+ • There is selectivity in opening/closing Na+ and K+ gates • Remember: Plasma membrane is semi-permeable to K+ – Physico-chemical ion selectivity channels – (i.e., K+ weak ...
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... What is an action potential? Graph and describe different parts of process • --Conduction of electric current • 1. If above threshold, voltage gated channels open = rapid depolarization • 2. Action potential ends; K+ channels open leading to hyperpolarization ...
... What is an action potential? Graph and describe different parts of process • --Conduction of electric current • 1. If above threshold, voltage gated channels open = rapid depolarization • 2. Action potential ends; K+ channels open leading to hyperpolarization ...
Chapter Eleven
... • Action potentials, or nerve impulses, are: – __________________________________ carried along the length of axons ...
... • Action potentials, or nerve impulses, are: – __________________________________ carried along the length of axons ...
Tyrosine Kinases
... triggering physiological changes; one of the first components of intracellular signal transduction cascades c) They are called secondary messengers because it is stimulated or stopped by the receptor after the first messengers bind to the receptor d) Cell signaling allows communication between group ...
... triggering physiological changes; one of the first components of intracellular signal transduction cascades c) They are called secondary messengers because it is stimulated or stopped by the receptor after the first messengers bind to the receptor d) Cell signaling allows communication between group ...
OCR Document - MrsGorukhomework
... When a stimulus reaches threshold level, this will cause the neural membrane to become permeable to sodium ions. The voltage-gated sodium channels open up and Na+ can move into the cell. Na+ enters by facilitated diffusion and causes depolarization. Some Na+ ions drift over to the next part of the n ...
... When a stimulus reaches threshold level, this will cause the neural membrane to become permeable to sodium ions. The voltage-gated sodium channels open up and Na+ can move into the cell. Na+ enters by facilitated diffusion and causes depolarization. Some Na+ ions drift over to the next part of the n ...
Nervous System
... - increases permeability to Na+ - rushes into cell o Domino affect = one Na+ opening triggers the next and so on… causes membrane potential increases to +35 mV (outside = - ; inside = +) • all or none principle: all the way to +35 mV or not o So long as they can reach the threshold of the cell, st ...
... - increases permeability to Na+ - rushes into cell o Domino affect = one Na+ opening triggers the next and so on… causes membrane potential increases to +35 mV (outside = - ; inside = +) • all or none principle: all the way to +35 mV or not o So long as they can reach the threshold of the cell, st ...
Neurons - Jordan High School
... Chemically gated channels need specific chemicals Voltage-gated channels respond to changes in transmembrane potential ...
... Chemically gated channels need specific chemicals Voltage-gated channels respond to changes in transmembrane potential ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.