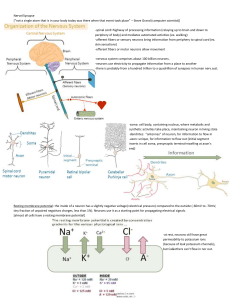
Biology Notes: The Nervous System and Neurons
... ReView (at the end of the PowerPoint you should be able to answer these questions) 1. What is the function of the nervous system? 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they incl ...
... ReView (at the end of the PowerPoint you should be able to answer these questions) 1. What is the function of the nervous system? 2. List the 4 main parts and describe the purpose of the 4 main parts of a neuron. 3. The nervous system is divided into 2 parts. What are they and what do they incl ...
Nervous System
... Drugs and the Nervous System • Different drugs have different affects on the body – Stimulants generally increase activity in the CNS – Cocaine is a highly addictive stimulant. It blocks the normal removal of pleasure neurotransmitters. The excess neurotransmitters cause a temporary “high” that is ...
... Drugs and the Nervous System • Different drugs have different affects on the body – Stimulants generally increase activity in the CNS – Cocaine is a highly addictive stimulant. It blocks the normal removal of pleasure neurotransmitters. The excess neurotransmitters cause a temporary “high” that is ...
CHAPTER 28 Nervous Systems
... An action potential is a nerve signal – It is an electrical change in the plasma membrane voltage from the resting potential to a maximum level and back to the resting potential ...
... An action potential is a nerve signal – It is an electrical change in the plasma membrane voltage from the resting potential to a maximum level and back to the resting potential ...
doc Behavioural_Neuroscience_Jan_11
... How the movement of ions creates electrical charges: A ion is a charged molecule. Cations are positive, and anions are negative. (e.g. NaCl = Na+ cation; Cl! anion). Forces of diffusion move ions from high concentration to low concentrations Electrostatic pressure refers to the attractive or ...
... How the movement of ions creates electrical charges: A ion is a charged molecule. Cations are positive, and anions are negative. (e.g. NaCl = Na+ cation; Cl! anion). Forces of diffusion move ions from high concentration to low concentrations Electrostatic pressure refers to the attractive or ...
Surface Area and Cell Size Lab
... Cell size and shape are important factors in determining the rate of diffusion. Think about cells with specialized functions, such as epithelial cells that line the small intestine or plant root hairs. - What is the shape of these cells? - What size are the cells? - How do intestinal epithelial and ...
... Cell size and shape are important factors in determining the rate of diffusion. Think about cells with specialized functions, such as epithelial cells that line the small intestine or plant root hairs. - What is the shape of these cells? - What size are the cells? - How do intestinal epithelial and ...
ppt
... •open ligand-gated Na+ channels •allows Na+ to flow inside the cell •causing a slight depolarization of the postsynaptic cell •moves the postsynaptic cell closer to firing an action potential ...
... •open ligand-gated Na+ channels •allows Na+ to flow inside the cell •causing a slight depolarization of the postsynaptic cell •moves the postsynaptic cell closer to firing an action potential ...
Nervous System ch 11
... –Na+ cannot enter the cell and K+ cannot exit the cell •Open when a neurotransmitter is attached to the receptor –Na+ enters the cell and K+ exits the cell Operation of a Gated Channel Voltage-Gated Channel ...
... –Na+ cannot enter the cell and K+ cannot exit the cell •Open when a neurotransmitter is attached to the receptor –Na+ enters the cell and K+ exits the cell Operation of a Gated Channel Voltage-Gated Channel ...
Overview Functions of the Nervous System
... • Direct or indirect action – Direct-acting neurotransmitters bind to and open ion channels – Indirect-acting neurotransmitters act through second messengers. ...
... • Direct or indirect action – Direct-acting neurotransmitters bind to and open ion channels – Indirect-acting neurotransmitters act through second messengers. ...
Cell Membrane - VCC Library - Vancouver Community College
... Hydrophilic “heads” – love to interact with water due to their polar nature o In contact with interstitial fluid & cytosol Hydrophobic “tails” – cannot interact with water and other water soluble substances due to their nonpolar nature o Tend to interact with each other and other nonpolar substa ...
... Hydrophilic “heads” – love to interact with water due to their polar nature o In contact with interstitial fluid & cytosol Hydrophobic “tails” – cannot interact with water and other water soluble substances due to their nonpolar nature o Tend to interact with each other and other nonpolar substa ...
Neuron
... cell, usually another nerve or muscle cell. The site of contact of the presynaptic terminal with the adjacent cell is called the synapse. It is formed by the presynaptic terminal of one cell (presynaptic cell), the receptive surface of the ...
... cell, usually another nerve or muscle cell. The site of contact of the presynaptic terminal with the adjacent cell is called the synapse. It is formed by the presynaptic terminal of one cell (presynaptic cell), the receptive surface of the ...
ActionPotentialWebquestCompleteGarrettIan
... 5. How does an action potential conduct along an axon? 6. Describe and draw an action potential. Part 3 – Ions Control Membrane Potential Go to http://www.bristol.ac.uk/synaptic/basics/basics-2.html 1. Neurons maintain different concentrations of certain ions across their cell membranes. What ion is ...
... 5. How does an action potential conduct along an axon? 6. Describe and draw an action potential. Part 3 – Ions Control Membrane Potential Go to http://www.bristol.ac.uk/synaptic/basics/basics-2.html 1. Neurons maintain different concentrations of certain ions across their cell membranes. What ion is ...
Specialised Cells Worksheet
... Many organisms are multi-cellular - they are made up of lots of cells, not just one! Many of these cells are specialised, sharing out the life processes (they work together as a team, supporting the organism). Specialist cells occur in both animals and plants… Animal Cells Draw out the shapes of som ...
... Many organisms are multi-cellular - they are made up of lots of cells, not just one! Many of these cells are specialised, sharing out the life processes (they work together as a team, supporting the organism). Specialist cells occur in both animals and plants… Animal Cells Draw out the shapes of som ...
Overview of the Cells WS
... Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life: Answer the following questions by inserting your responses in the answer blanks. 1. Name the four elements that make up the bulk of living matter. a. _______________________________________________________________ ...
... Overview of the Cellular Basis of Life: Answer the following questions by inserting your responses in the answer blanks. 1. Name the four elements that make up the bulk of living matter. a. _______________________________________________________________ ...
Message Transmission
... So, what happens at the end of the axon? • You run into a synapse. – This is the junction between any two communicating neurons – It really is a gap (the synaptic cleft), the cells don't actually touch each other. • The sender neuron is the presynaptic neuron • The receiving one is the postsynaptic ...
... So, what happens at the end of the axon? • You run into a synapse. – This is the junction between any two communicating neurons – It really is a gap (the synaptic cleft), the cells don't actually touch each other. • The sender neuron is the presynaptic neuron • The receiving one is the postsynaptic ...
9.01 Exam #1 September 27, 2004 30 multiple
... c) The Golgi stain only stains a small percentage of neurons, and even then not completely; the chances of finding a pair of interconnected neurons is too small to determine whether neurons ...
... c) The Golgi stain only stains a small percentage of neurons, and even then not completely; the chances of finding a pair of interconnected neurons is too small to determine whether neurons ...
Nervous System
... • Once a threshold of depolarization is reached (-50 to -55 mV), an action potential will occur • An ‘all or nothing’ response, not graded • Magnitude of the action potential is independent of strength of depolarizing stimuli • Action potentials are the signals by which neurons communicate and sprea ...
... • Once a threshold of depolarization is reached (-50 to -55 mV), an action potential will occur • An ‘all or nothing’ response, not graded • Magnitude of the action potential is independent of strength of depolarizing stimuli • Action potentials are the signals by which neurons communicate and sprea ...
Lect5
... • emfion is the electromotive force acting on an ion • emfion = Vm - Eion Total membrane potential ...
... • emfion is the electromotive force acting on an ion • emfion = Vm - Eion Total membrane potential ...
Nerve cells - Spark (e
... Mirror neurons are a class of neurons that are activated when a person (or animal) observes another person performing an action. ...
... Mirror neurons are a class of neurons that are activated when a person (or animal) observes another person performing an action. ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... Rapid propagation of action potentials is important for survival, especially in situations that require rapid, reflexive responses. In squids, evolution solved the problem of how to send fast-moving signals from one end of the body to the other by making giant axons, 1000 times fatter than our axons ...
... Rapid propagation of action potentials is important for survival, especially in situations that require rapid, reflexive responses. In squids, evolution solved the problem of how to send fast-moving signals from one end of the body to the other by making giant axons, 1000 times fatter than our axons ...
Specialised Cells Worksheet
... Many organisms are multi-cellular - they are made up of lots of cells, not just one! Many of these cells are specialised, sharing out the life processes (they work together as a team, supporting the organism). Specialist cells occur in both animals and plants… Animal Cells Draw out the shapes of som ...
... Many organisms are multi-cellular - they are made up of lots of cells, not just one! Many of these cells are specialised, sharing out the life processes (they work together as a team, supporting the organism). Specialist cells occur in both animals and plants… Animal Cells Draw out the shapes of som ...
Modeling the Cell Membrane
... is selectively permeable meaning that only some things are able to enter and leave the cell easily. Passive transport happens without the cell needing to use any energy to move things through the membrane. Active transport needs some energy to move things through the membrane. The cell membrane is m ...
... is selectively permeable meaning that only some things are able to enter and leave the cell easily. Passive transport happens without the cell needing to use any energy to move things through the membrane. Active transport needs some energy to move things through the membrane. The cell membrane is m ...
Neurons, Synapses, the Nervous System
... membrane potential to a positive value. In order to generate an action potential, a certain level of depolarization must be achieved, known as the threshold. The membrane potential is restored to its normal resting value by the inactivation of the Na+ channels and by opening voltage-gated K+ channel ...
... membrane potential to a positive value. In order to generate an action potential, a certain level of depolarization must be achieved, known as the threshold. The membrane potential is restored to its normal resting value by the inactivation of the Na+ channels and by opening voltage-gated K+ channel ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.