Chapter 2
... cell (cytosol, organelles, and inclusions) between the plasma membrane and the nucleus; and (3) the nucleus is the cell’s control center, and it contains all of the genetic material of the cell. 2. The plasma membrane forms the cell border. It is composed of both lipids and proteins. It regulates th ...
... cell (cytosol, organelles, and inclusions) between the plasma membrane and the nucleus; and (3) the nucleus is the cell’s control center, and it contains all of the genetic material of the cell. 2. The plasma membrane forms the cell border. It is composed of both lipids and proteins. It regulates th ...
Chapter 2
... cell (cytosol, organelles, and inclusions) between the plasma membrane and the nucleus; and (3) the nucleus is the cell’s control center, and it contains all of the genetic material of the cell. 2. The plasma membrane forms the cell border. It is composed of both lipids and proteins. It regulates th ...
... cell (cytosol, organelles, and inclusions) between the plasma membrane and the nucleus; and (3) the nucleus is the cell’s control center, and it contains all of the genetic material of the cell. 2. The plasma membrane forms the cell border. It is composed of both lipids and proteins. It regulates th ...
Slideshow
... maintain a voltage difference across the cell membrane called a resting membrane potential. The inside of the cell is more negatively charged in comparison to the outside of the cell – this is shown by a negative sign in front of voltage, (ex., - 70 mV) The big players here are sodium and potassium ...
... maintain a voltage difference across the cell membrane called a resting membrane potential. The inside of the cell is more negatively charged in comparison to the outside of the cell – this is shown by a negative sign in front of voltage, (ex., - 70 mV) The big players here are sodium and potassium ...
“Electrical Properties of Neuron”
... This is a novel technique (developed by Neher and Sakmann et al. for which they were awarded with a Nobel prize) in which physiological currents flowing through the cells can be detected without disrupting the cell or its contents A micropipette (diameter in microns) filled with a buffer solutio ...
... This is a novel technique (developed by Neher and Sakmann et al. for which they were awarded with a Nobel prize) in which physiological currents flowing through the cells can be detected without disrupting the cell or its contents A micropipette (diameter in microns) filled with a buffer solutio ...
Ch 48 Notes - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... Graded potentials are changes in polarization where the magnitude of the change varies with the strength of the stimulus ...
... Graded potentials are changes in polarization where the magnitude of the change varies with the strength of the stimulus ...
The Nervous System
... of K, the outer environment has a high Na concentration. The neuron’s cell membrane has active Na/K gates. When an impulse comes in contact with the membrane, it turns off the gate.[polarized] Na rushes in, K leaves and the electrical impulse passes through the cell body. [wave of depolarization] Af ...
... of K, the outer environment has a high Na concentration. The neuron’s cell membrane has active Na/K gates. When an impulse comes in contact with the membrane, it turns off the gate.[polarized] Na rushes in, K leaves and the electrical impulse passes through the cell body. [wave of depolarization] Af ...
Introduction to the Nervous System Guided Notes are masses of
... (2) _____________ neurons - Efferent neurons that make up efferent component of the PNS; carry instructions from the CNS to the peripheral effectors. (1) ________________ motor neurons – innervate skeletal muscle (conscious control – Somatic Nervous System) (2) _____________ motor neurons – innervat ...
... (2) _____________ neurons - Efferent neurons that make up efferent component of the PNS; carry instructions from the CNS to the peripheral effectors. (1) ________________ motor neurons – innervate skeletal muscle (conscious control – Somatic Nervous System) (2) _____________ motor neurons – innervat ...
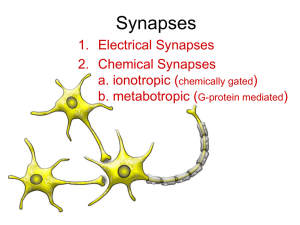
Synapses - Franklin College
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
Membrane Transport
... for specific student populations, or the requirements of a specific course. Please feel free to offer suggestions for improvements, corrections, or additional illustrations. I would be pleased to hear from anyone who finds my work useful, and am always willing to make it better. Also, the images hav ...
... for specific student populations, or the requirements of a specific course. Please feel free to offer suggestions for improvements, corrections, or additional illustrations. I would be pleased to hear from anyone who finds my work useful, and am always willing to make it better. Also, the images hav ...
Homework Questions – Unit 1 – Biochemistry
... This steady state inside a cell is called homeostasis. It is important to cells in order for them to function properly and do their jobs. 6. Diffusion allows for the effective movement of substances over short distances. How is this important for the cell? Cells cannot be too large (surface ar ...
... This steady state inside a cell is called homeostasis. It is important to cells in order for them to function properly and do their jobs. 6. Diffusion allows for the effective movement of substances over short distances. How is this important for the cell? Cells cannot be too large (surface ar ...
Cell Differentiation PPT
... together what you think happens in cell differentiation. Begin filling out your KWL chart – fill in what you already know and what you want to know. There will be time at the end of class to fill in what you learned. ...
... together what you think happens in cell differentiation. Begin filling out your KWL chart – fill in what you already know and what you want to know. There will be time at the end of class to fill in what you learned. ...
آلفا با دامنهي زياد
... only if the activity of the underlying neurons adds up. To add up the activity must be generated by parallel neurons. The neocortex is composed of pyramidal cells aligned in parallel. ...
... only if the activity of the underlying neurons adds up. To add up the activity must be generated by parallel neurons. The neocortex is composed of pyramidal cells aligned in parallel. ...
Muscles and Nerve Tissue
... • Attach to bones • Multinucleated • nuclei located near cell membrane • Cells contract when stimulated via nerve ...
... • Attach to bones • Multinucleated • nuclei located near cell membrane • Cells contract when stimulated via nerve ...
Your Nervous System
... sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after depolarization; the neuron cannot be stimulated ...
... sheath (Schwann Cells), an insulator Myelin sheath causes the ion exchange to occur only at the nodes which speeds up the process For a short time after depolarization; the neuron cannot be stimulated ...
Neuron Function
... Channels differ in the stimulus that causes them to open and how long they stay open Voltage gated channels - respond to specific voltage changes across the PM; imp in AP Ligand gated channels - open when particular molecules bind to the channel; imp in chemical communication between neurons acro ...
... Channels differ in the stimulus that causes them to open and how long they stay open Voltage gated channels - respond to specific voltage changes across the PM; imp in AP Ligand gated channels - open when particular molecules bind to the channel; imp in chemical communication between neurons acro ...
Nervous System - De Anza College
... neuron (presynaptic cell) to the receiving neuron (postsynaptic cell) Synaptic terminals ...
... neuron (presynaptic cell) to the receiving neuron (postsynaptic cell) Synaptic terminals ...
The Cell Membrane
... from one environment to the other. Transports raw materials into the cell and waste out of the cell. Prevents the entry of unwanted matter and the escape of needed materials. Maintain a steady environment: Homeostasis ...
... from one environment to the other. Transports raw materials into the cell and waste out of the cell. Prevents the entry of unwanted matter and the escape of needed materials. Maintain a steady environment: Homeostasis ...
Abstract
... even consciousness are thought to be realized through complex interactions of streams of millisecond-order electrical spikes (known as action potentials) generated by billions of neurons. How can one investigate such a complicated organ? As action potentials are electric signals mediated by flows of ...
... even consciousness are thought to be realized through complex interactions of streams of millisecond-order electrical spikes (known as action potentials) generated by billions of neurons. How can one investigate such a complicated organ? As action potentials are electric signals mediated by flows of ...
P416 COMPARATIVE ANIMAL PHYSIOLOGY
... Electrical Activity of Neurons: Electrical Signals • Electrical signals – due to changes in membrane permeability and altering flow of charged particles – changes in permeability are due to changing the number of open membrane channels -70 mV ...
... Electrical Activity of Neurons: Electrical Signals • Electrical signals – due to changes in membrane permeability and altering flow of charged particles – changes in permeability are due to changing the number of open membrane channels -70 mV ...
CS 256: Neural Computation Lecture Notes
... From Peter Dayan and L. F. Abbott, Theoretical Neuroscience, 2001, p. 6. ...
... From Peter Dayan and L. F. Abbott, Theoretical Neuroscience, 2001, p. 6. ...
Press Release - Max-Planck
... Max Planck researchers clarify the structure of the cell membrane As the interface between the cell and its environment, the cell membrane, which consists of fats and proteins, fulfils a variety of vital functions. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Martinsried near Munich hav ...
... Max Planck researchers clarify the structure of the cell membrane As the interface between the cell and its environment, the cell membrane, which consists of fats and proteins, fulfils a variety of vital functions. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry in Martinsried near Munich hav ...
VII. The Nervous System
... 3. Chemical Synapse- a chemical called a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell and binds to receptors on a postsynaptic cells causing it to fire. a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) ...
... 3. Chemical Synapse- a chemical called a neurotransmitter is released from the presynaptic cell and binds to receptors on a postsynaptic cells causing it to fire. a) An action potential arriving at the synaptic terminal at the end of an axon causes Ca+2 to rush through voltage sensitive channels b) ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.