Ch. 7 part 2 (PM and Osmosis)
... ◦ protein channels allow substances in & out specific channels allow specific material in & out H2O channel, salt channel, sugar channel, etc. ...
... ◦ protein channels allow substances in & out specific channels allow specific material in & out H2O channel, salt channel, sugar channel, etc. ...
Slide ()
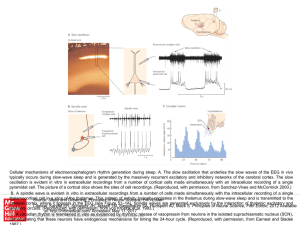
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
... oscillation is evident in vitro in extracellular recordings from a number of cortical cells made simultaneously with an intracellular recording of a single pyramidal cell. The picture of a cortical slice shows the sites of cell recordings. (Reproduced, with permission, from Sanchez-Vives and McCormi ...
PNS and Transmission
... in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through synaptic cleft neurotransmitters bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane. • Depending on t ...
... in the axon terminals. • Impulse reaches terminal opens calcium channels Calcium enters the terminal vesicles move toward membrane for exocytosis neurotransmitters are released and diffuse through synaptic cleft neurotransmitters bind with receptors on postsynaptic membrane. • Depending on t ...
Edvard Moser
... components to be detected in this internal map was the grid cell. Grid cells fire electric impulses when animals are at particular locations that together tile the environment in a periodic hexagonal pattern, like in a Chinese checkerboard. The circuit was soon found to include also other functional ...
... components to be detected in this internal map was the grid cell. Grid cells fire electric impulses when animals are at particular locations that together tile the environment in a periodic hexagonal pattern, like in a Chinese checkerboard. The circuit was soon found to include also other functional ...
THE NEuRoN - Big Picture
... layers of cell membrane that wrap around the axon. The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals ( ‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Myelin reduces leakage of electrical charge from the axon, resulting in a signal that rapidly jumps from one no ...
... layers of cell membrane that wrap around the axon. The sheath is interrupted at regular intervals ( ‘nodes of Ranvier’), where the channels that generate the electrical signal are located. Myelin reduces leakage of electrical charge from the axon, resulting in a signal that rapidly jumps from one no ...
Action potentials travel along the axons of neurons.
... The cell membrane of neurons have an uneven distribution of charges, with the inside more negative than the outside (Resting potential – 10mV) The balance is maintained by the Na/K pump – where Na+ is more concentrated outside the cell, and K+ is more concentrated inside the cell. The cell membrane ...
... The cell membrane of neurons have an uneven distribution of charges, with the inside more negative than the outside (Resting potential – 10mV) The balance is maintained by the Na/K pump – where Na+ is more concentrated outside the cell, and K+ is more concentrated inside the cell. The cell membrane ...
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
... The membrane potential of a nerve cell at rest is called its resting potential. It exists because of differences in the ionic composition of the extracellular and intracellular fluids across the plasma membrane. The concentration of Na+ is higher outside the cell, whereas the concentration of K+ ...
... The membrane potential of a nerve cell at rest is called its resting potential. It exists because of differences in the ionic composition of the extracellular and intracellular fluids across the plasma membrane. The concentration of Na+ is higher outside the cell, whereas the concentration of K+ ...
Neurotransmitter release in the brain
... The human brain consists of around 100 billion neurons each making 100010,000 synaptic connections. The activity of the brain is electrical but the connections between neurons are primarily chemical, across a specialised structure called the synapse. At the synapse, vesicles containing neurotransmit ...
... The human brain consists of around 100 billion neurons each making 100010,000 synaptic connections. The activity of the brain is electrical but the connections between neurons are primarily chemical, across a specialised structure called the synapse. At the synapse, vesicles containing neurotransmit ...
Nerve Chips
... Antennae replaced by electrode Note large electronic backpack required for each case Effect wears off as animal adapts to the stimuli Any social/ethical implications? ...
... Antennae replaced by electrode Note large electronic backpack required for each case Effect wears off as animal adapts to the stimuli Any social/ethical implications? ...
Neurophysiology Complete
... Excitability: the ability to respond to stimuli and convert it to nerve impulses Conductivity: the ability to transmit the impulse to other neurons, muscles or glands In a resting neuron, the outside is more positive than the inside Resting membrane potential: the difference in electrical charges th ...
... Excitability: the ability to respond to stimuli and convert it to nerve impulses Conductivity: the ability to transmit the impulse to other neurons, muscles or glands In a resting neuron, the outside is more positive than the inside Resting membrane potential: the difference in electrical charges th ...
document
... forced out of the cell. As the action potential peaks, Na+ channels close, and no more Na+ enters the cell. K+ is forced out of the cell, which decreases the charge inside the cell and K+ channels close. K+ ions trapped outside of the cell result in a temporary hyperpolarized membrane potential. Ion ...
... forced out of the cell. As the action potential peaks, Na+ channels close, and no more Na+ enters the cell. K+ is forced out of the cell, which decreases the charge inside the cell and K+ channels close. K+ ions trapped outside of the cell result in a temporary hyperpolarized membrane potential. Ion ...
Practice Exam 4
... C. Voltage gated ion channel D. Ligand gated ion channel E. All of the above are cellular membrane receptors ...
... C. Voltage gated ion channel D. Ligand gated ion channel E. All of the above are cellular membrane receptors ...
Lecture 2 - Nerve Impulse
... The Nervous Impulse The balance of the electrical charges on either side of the neuron’s PM influences the membrane potential MP. Resting MP is -70 mV. ...
... The Nervous Impulse The balance of the electrical charges on either side of the neuron’s PM influences the membrane potential MP. Resting MP is -70 mV. ...
Types of neurons - Brigham Young University
... Some Drugs work on receptors Some drugs are shaped like neurotransmitters Antagonists : fit the receptor but poorly and block the NT e.g. beta blockers ...
... Some Drugs work on receptors Some drugs are shaped like neurotransmitters Antagonists : fit the receptor but poorly and block the NT e.g. beta blockers ...
HONORS BIOLOGY Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
... Sending (presynaptic) cell secretes a chemical signal, a neurotransmitter ...
... Sending (presynaptic) cell secretes a chemical signal, a neurotransmitter ...
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling
... synapse in rapid succession- in this case the EPSP’s add together. Spatial Summation- two EPSP’s produced simultaneously at different synapses on the same postsynaptic neuronEPSP’s added together. ...
... synapse in rapid succession- in this case the EPSP’s add together. Spatial Summation- two EPSP’s produced simultaneously at different synapses on the same postsynaptic neuronEPSP’s added together. ...
Action potential
... The voltage clamp uses a negative feedback mechanism. The membrane potential amplifier measures membrane voltage and sends output to the feedback amplifier. The feedback amplifier subtracts the membrane voltage from the command voltage, which it receives from the signal generator. This signal is am ...
... The voltage clamp uses a negative feedback mechanism. The membrane potential amplifier measures membrane voltage and sends output to the feedback amplifier. The feedback amplifier subtracts the membrane voltage from the command voltage, which it receives from the signal generator. This signal is am ...
Slide 1
... phosphate heads orient themselves toward the water; nonpolar, hydrophobic fatty acid tails make up the interior of the membrane and orient themselves AWAY from water •phospholipids form a bilayer; • cholesterol also found among fatty acid tails ...
... phosphate heads orient themselves toward the water; nonpolar, hydrophobic fatty acid tails make up the interior of the membrane and orient themselves AWAY from water •phospholipids form a bilayer; • cholesterol also found among fatty acid tails ...
Practice Quiz: Honors Biology Chapter 03 What type of microscope
... Where in the cell is a great deal of rRNA formed? The brain of the cell Supports, protects and is permeable to water and gases Part of the cytoskeleton, hollow structure Connected to the nucleus, has ribosomes on it Dense area in the center of the nucleus What do you call the fluid portion of the ce ...
... Where in the cell is a great deal of rRNA formed? The brain of the cell Supports, protects and is permeable to water and gases Part of the cytoskeleton, hollow structure Connected to the nucleus, has ribosomes on it Dense area in the center of the nucleus What do you call the fluid portion of the ce ...
Action Potential revisited When a stimulus reaches threshold level
... cell is said to be in a refractory period (toilet flushing) The Sodium-Potassium pump moves ions back across the membrane against the concentration gradient, and resting potential is restored. The refractory period helps to ensure that stimulus only flows in one direction. ...
... cell is said to be in a refractory period (toilet flushing) The Sodium-Potassium pump moves ions back across the membrane against the concentration gradient, and resting potential is restored. The refractory period helps to ensure that stimulus only flows in one direction. ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.