Review - Wesleyan University
... to an extracellular loop of sixtyproperties in vitro (29). Subsequent in vivo application of the six amino acids (Nogo-66) found in all three Nogo isoforms (23). monoclonal antibody resulted in substantial axonal sprouting and Fortunately, significant progress has been made in the recent some long-d ...
... to an extracellular loop of sixtyproperties in vitro (29). Subsequent in vivo application of the six amino acids (Nogo-66) found in all three Nogo isoforms (23). monoclonal antibody resulted in substantial axonal sprouting and Fortunately, significant progress has been made in the recent some long-d ...
Article
... Skeletal muscle development has been a key model system in the field of developmental genetics, so it is important that the model includes consideration of all relevant factors. Not ...
... Skeletal muscle development has been a key model system in the field of developmental genetics, so it is important that the model includes consideration of all relevant factors. Not ...
MS word - University of Kentucky
... phase-out their response when the source of the stimulus (i.e. the CNS) continues the stimulation in an unchanged manner. Thus, they may fire a burst of signals initially, but quickly decrease their signals over time until no further signals are sent. In contrast, tonic-type neurons adapt slowly (if ...
... phase-out their response when the source of the stimulus (i.e. the CNS) continues the stimulation in an unchanged manner. Thus, they may fire a burst of signals initially, but quickly decrease their signals over time until no further signals are sent. In contrast, tonic-type neurons adapt slowly (if ...
Author`s personal copy - Vanderbilt University
... pressure. Though the precise mechanisms that mediate or transduce this sensitivity are not clear, the axon of the retinal ganglion cell appears to be vulnerable to disease-relevant stressors early in progression. One reason may be because the axon is generally thin for both its unmyelinated and myel ...
... pressure. Though the precise mechanisms that mediate or transduce this sensitivity are not clear, the axon of the retinal ganglion cell appears to be vulnerable to disease-relevant stressors early in progression. One reason may be because the axon is generally thin for both its unmyelinated and myel ...
Visuomotor development
... Visuomotor development Sensorimotor coordination has been an active research topic for both neuroscience and artificial intelligence over the last decade. The integration of sensory information for movement guidance represents perhaps the most basic operation that a nervous (or artificial) system mu ...
... Visuomotor development Sensorimotor coordination has been an active research topic for both neuroscience and artificial intelligence over the last decade. The integration of sensory information for movement guidance represents perhaps the most basic operation that a nervous (or artificial) system mu ...
17. Pathways and Integrative Functions
... 1. Identify and describe the characteristics of sensory and motor pathways in the spinal cord. The CNS communicates with peripheral body structures through pathways. These pathways conduct either sensory or motor information; processing and integration occur continuously along them. These pathways t ...
... 1. Identify and describe the characteristics of sensory and motor pathways in the spinal cord. The CNS communicates with peripheral body structures through pathways. These pathways conduct either sensory or motor information; processing and integration occur continuously along them. These pathways t ...
No Slide Title
... BIFURCATION OF COMMON CAROTID BLOOD SUPPLY-EXTERNAL CAROTID VENOUS DRAIN-INT JUGULAR NERVE SUPPLY- IX NERVE ...
... BIFURCATION OF COMMON CAROTID BLOOD SUPPLY-EXTERNAL CAROTID VENOUS DRAIN-INT JUGULAR NERVE SUPPLY- IX NERVE ...
Correlation between auditory threshold and the auditory brainstem
... impairments. In the ABR, latency of the wave V and of the I–V interval are the two most widely used parameters that reflect neuronal conduction, brainstem´s conduction time, related to myelination and synaptic function; both in the brainstem or in the central auditory pathway [36]. In the study of t ...
... impairments. In the ABR, latency of the wave V and of the I–V interval are the two most widely used parameters that reflect neuronal conduction, brainstem´s conduction time, related to myelination and synaptic function; both in the brainstem or in the central auditory pathway [36]. In the study of t ...
BLoA Neurotransmission
... between the two neurons. The change in potential is going to affect little vesicles, little blobs of membrane inside the presynaptic neuron. These vesicles contain the neurotransmitters, which are synthesized in the presynaptic cell, and stored in the vesicles ...
... between the two neurons. The change in potential is going to affect little vesicles, little blobs of membrane inside the presynaptic neuron. These vesicles contain the neurotransmitters, which are synthesized in the presynaptic cell, and stored in the vesicles ...
Human Reflexes Introductory Reading and
... smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. Somatic reflexes involve stimulation of skeletal muscles by the somatic or voluntary division of the nervous system. Most reflexes are polysynaptical (involving more than two neurons) and involve the activity of interneurons (or association neurons) in the ...
... smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands. Somatic reflexes involve stimulation of skeletal muscles by the somatic or voluntary division of the nervous system. Most reflexes are polysynaptical (involving more than two neurons) and involve the activity of interneurons (or association neurons) in the ...
The Scientific Foundations of Applied Kinesiology
... level of the spine treated. This finding supports the increased tone in muscles found through AKMMT after SMT to the level of spinal nerve supply to the tested muscle. 29 Other studies have shown both facilitation and inhibition from the same SMT event suggesting a somato-somatic and neuro-modulatin ...
... level of the spine treated. This finding supports the increased tone in muscles found through AKMMT after SMT to the level of spinal nerve supply to the tested muscle. 29 Other studies have shown both facilitation and inhibition from the same SMT event suggesting a somato-somatic and neuro-modulatin ...
Cerebral Cortex Lect
... 0.4 mm diameter) extending the entire thickness of the cortex (including all six layers). Each vertical column is a functional unit because all cells within an individual column are activated by the same particular feature of a stimulus. The vertical organization is the result of neuronal connection ...
... 0.4 mm diameter) extending the entire thickness of the cortex (including all six layers). Each vertical column is a functional unit because all cells within an individual column are activated by the same particular feature of a stimulus. The vertical organization is the result of neuronal connection ...
Diseases of the Basal Ganglia
... movements are hard mo initiate (akinesia) and they are slower and smaller than normal (bradykinesia). The akinesia also leads to a conspicuous lack of facial movements (mask like face). In addition, there is an increased ...
... movements are hard mo initiate (akinesia) and they are slower and smaller than normal (bradykinesia). The akinesia also leads to a conspicuous lack of facial movements (mask like face). In addition, there is an increased ...
Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels
... • Cav1 = initiate contraction, secretion, and regulation of gene expression, integration of synaptic input in neurons, and synaptic transmission at ribbon synapses of specialized sensory cells • Cav2 = synaptic transmission of fast synapses • Cav3 = important for repetitive or rhythmic firing of Aps ...
... • Cav1 = initiate contraction, secretion, and regulation of gene expression, integration of synaptic input in neurons, and synaptic transmission at ribbon synapses of specialized sensory cells • Cav2 = synaptic transmission of fast synapses • Cav3 = important for repetitive or rhythmic firing of Aps ...
4-22-05
... occurs at synapses • Electrical Synapses. – Action potentials travels directly from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells via gap junctions. – Invertebrate giant axons – Present in vertebrate brain in stereotype behavior like a fish flapping its tail to escape a predator. – Are fast connections. ...
... occurs at synapses • Electrical Synapses. – Action potentials travels directly from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells via gap junctions. – Invertebrate giant axons – Present in vertebrate brain in stereotype behavior like a fish flapping its tail to escape a predator. – Are fast connections. ...
Nervous System I - Union County College
... of the axon more positively charged. As the cell becomes more positive, the THRESHOLD stimulus level is reached. Na+ DEPOLARIZES the membrane. • As the action potential reaches its peak, sodium channels (or gates) close and the potassium channels (or gates) open so K+ diffuses to the outside of the ...
... of the axon more positively charged. As the cell becomes more positive, the THRESHOLD stimulus level is reached. Na+ DEPOLARIZES the membrane. • As the action potential reaches its peak, sodium channels (or gates) close and the potassium channels (or gates) open so K+ diffuses to the outside of the ...
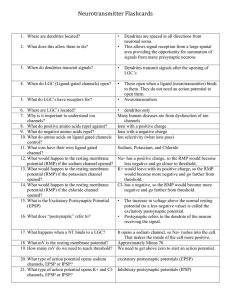
Neurotransmitter Flashcards
... postsynaptic cell if it experiences an EPSP? 88. What happens to the voltage on the postsynaptic cell if it experiences an IPSP? 89. Neurotransmitters are released in response to what? 90. When NTs are released in response to presynaptic depolarization, what is molecule is ...
... postsynaptic cell if it experiences an EPSP? 88. What happens to the voltage on the postsynaptic cell if it experiences an IPSP? 89. Neurotransmitters are released in response to what? 90. When NTs are released in response to presynaptic depolarization, what is molecule is ...
Relative timing: from behaviour to neurons
... Timing is central for myriad aspects of behaviour. All forms of life generate behaviours that play out according to precise sequences in time, spanning multiple temporal scales. Complex behaviours such as locomotion or grasping and manipulation require coordinated temporal cascades of muscular activ ...
... Timing is central for myriad aspects of behaviour. All forms of life generate behaviours that play out according to precise sequences in time, spanning multiple temporal scales. Complex behaviours such as locomotion or grasping and manipulation require coordinated temporal cascades of muscular activ ...
Synaptic Transmisson
... neurotransmitter to trigger a new action potential in the postsynaptic neurone. They, can be made to do so by a process called summation where neurotransmitter builds up in the synapse by one of two methods: a) ...
... neurotransmitter to trigger a new action potential in the postsynaptic neurone. They, can be made to do so by a process called summation where neurotransmitter builds up in the synapse by one of two methods: a) ...
Muscle Coordination 1 Changes in Muscle Coordination with
... level of input to the spinal motor neurons that is associated with a particular degree of muscle activation or joint torque is lower than that present prior to training (see also (27)). In so much as there has been a modification of the relationship between the level of activity in the cortical moto ...
... level of input to the spinal motor neurons that is associated with a particular degree of muscle activation or joint torque is lower than that present prior to training (see also (27)). In so much as there has been a modification of the relationship between the level of activity in the cortical moto ...
read - StarkeyPro
... be informed that their baby’s auditory capacity or speech, language, and communication development cannot be predicted on the basis of the initial evaluation. Ongoing monitoring of their infant’s auditory, speech, language, communication, and general development is essential. Families should be made ...
... be informed that their baby’s auditory capacity or speech, language, and communication development cannot be predicted on the basis of the initial evaluation. Ongoing monitoring of their infant’s auditory, speech, language, communication, and general development is essential. Families should be made ...
evolution of the first nervous systems ii
... reduced immune complement in ctenophores. Although two distinct nervous systems are well-recognized in ctenophores, many bilaterian neuron-specific genes and genes of “classical” neurotransmitter pathways either are absent or, if present, are not expressed in neurons. Second, we discover several doz ...
... reduced immune complement in ctenophores. Although two distinct nervous systems are well-recognized in ctenophores, many bilaterian neuron-specific genes and genes of “classical” neurotransmitter pathways either are absent or, if present, are not expressed in neurons. Second, we discover several doz ...
The Red Nucleus: Past, Present, and Future
... Expansion of the pyramidal tract in primates has paralleled the regression of RNm [3]. One study has shown that axons from both the rubrospinal and pyramidal tracts end on the same segmental interneurons and propriospinal neurons [10]. An experiment involving lesions of the pyramidal tract in monkey ...
... Expansion of the pyramidal tract in primates has paralleled the regression of RNm [3]. One study has shown that axons from both the rubrospinal and pyramidal tracts end on the same segmental interneurons and propriospinal neurons [10]. An experiment involving lesions of the pyramidal tract in monkey ...
Nerves
... the limbic system and other parts of the brain including the sensory areas • The limbic system is a ring of structures around the brainstem that includes the amygdala, hippocampus, and parts of the thalamus • The amygdala is located in the temporal lobe and helps store an emotional experience as an ...
... the limbic system and other parts of the brain including the sensory areas • The limbic system is a ring of structures around the brainstem that includes the amygdala, hippocampus, and parts of the thalamus • The amygdala is located in the temporal lobe and helps store an emotional experience as an ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.