The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
... matter in processing and relaying sensory information and motor commands. • 13-4 Describe the major components of a spinal nerve, and relate the distribution pattern of spinal nerves to the regions they innervate. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... matter in processing and relaying sensory information and motor commands. • 13-4 Describe the major components of a spinal nerve, and relate the distribution pattern of spinal nerves to the regions they innervate. © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Physiology and mathematical modeling of the auditory system
... thalamic nuclei, and auditory cortex). As for other sensory systems, stimulation during this time is essential for normal development. When hearing is impaired in early life, the morphology and function of auditory neurons may be affected. The overall structure of the sub-cortical auditory system an ...
... thalamic nuclei, and auditory cortex). As for other sensory systems, stimulation during this time is essential for normal development. When hearing is impaired in early life, the morphology and function of auditory neurons may be affected. The overall structure of the sub-cortical auditory system an ...
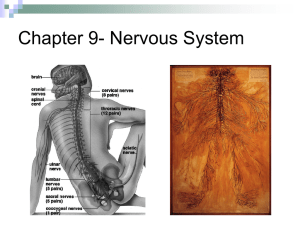
Chapter 9- Nervous System Lecture 9.1
... A. Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. B. When sensory impulses are integrated in the brain as perceptions, this is the integrative function of the nervous system. C. Conscious or subconscious decisions follow, leading to motor fu ...
... A. Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral nerves gather information and convert it into nerve impulses. B. When sensory impulses are integrated in the brain as perceptions, this is the integrative function of the nervous system. C. Conscious or subconscious decisions follow, leading to motor fu ...
Whisker sensory system – From receptor to decision
... contemporary cognitive neuroscience, but building a comprehensive characterization of the neuronal basis of behavior in simpler sensory systems might be possible. Mice and rats were adopted as laboratory animals for reasons having little to do with integrative neuroscience, but we now know that they ...
... contemporary cognitive neuroscience, but building a comprehensive characterization of the neuronal basis of behavior in simpler sensory systems might be possible. Mice and rats were adopted as laboratory animals for reasons having little to do with integrative neuroscience, but we now know that they ...
Chapter 9
... Saltatory conduction is many times faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
... Saltatory conduction is many times faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
Taxane-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity
... nerve biopsy was performed after finishing chemotherapy, showed severe nerve fiber loss, axonal atrophy, and secondary demyelination with a preferentially loss of large myelinated fibers [48]. Evidence of axonal regeneration was present in docetaxel [51] but not in paclitaxel [48–50]. Intriguingly, ...
... nerve biopsy was performed after finishing chemotherapy, showed severe nerve fiber loss, axonal atrophy, and secondary demyelination with a preferentially loss of large myelinated fibers [48]. Evidence of axonal regeneration was present in docetaxel [51] but not in paclitaxel [48–50]. Intriguingly, ...
The Brain and Behavior:
... Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Neuron and the Synapse Identify parts of the neuron and synapse and describe how they communicate information. ...
... Introductory Psychology Concepts: The Neuron and the Synapse Identify parts of the neuron and synapse and describe how they communicate information. ...
Neural correlates of attention in primate visual cortex
... V1 is influenced by the attentional conditions (see Ref. 21 for a review). Second, PET imaging experiments22,23 and a study24 in an individual suffering from a bilateral lesion of the human MT homolog showed specific attentional influences in early areas of the human dorsal visual pathway. These stu ...
... V1 is influenced by the attentional conditions (see Ref. 21 for a review). Second, PET imaging experiments22,23 and a study24 in an individual suffering from a bilateral lesion of the human MT homolog showed specific attentional influences in early areas of the human dorsal visual pathway. These stu ...
a needle into the sub- and the dorsal funiculi. Preganglionic
... level because the length of the spinal cord varies less than the length of the vertebral column. Thus t}.e caudal end of the cord may be as high as the I2th thoracic vertebral body or as low as the 3rd lumbar vertebra, The subarachnoid spzLce caudal to the end of the spinal cord is known as the lumb ...
... level because the length of the spinal cord varies less than the length of the vertebral column. Thus t}.e caudal end of the cord may be as high as the I2th thoracic vertebral body or as low as the 3rd lumbar vertebra, The subarachnoid spzLce caudal to the end of the spinal cord is known as the lumb ...
Electrophysiological Identification of Tonic and Phasic Neurons in
... To analyze the potential effects of inflammatory treatments (CFA and melittin) on excitabilities of tonic and phasic types of DRG neurons, we used retrograde tracer 1, 1’-dioctadecyl-3, 3, 3’, 3’-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate (DiI) to identify the cell bodies of DRG neurons innervating the ...
... To analyze the potential effects of inflammatory treatments (CFA and melittin) on excitabilities of tonic and phasic types of DRG neurons, we used retrograde tracer 1, 1’-dioctadecyl-3, 3, 3’, 3’-tetramethylindocarbocyanine perchlorate (DiI) to identify the cell bodies of DRG neurons innervating the ...
Assessment of the Ears
... • Inspection & palpation of external ear • Otoscopic exam including ear canal and tympanic membrane • Testing hearing acuity ...
... • Inspection & palpation of external ear • Otoscopic exam including ear canal and tympanic membrane • Testing hearing acuity ...
The non-classical auditory pathways are involved in hearing in
... pathways was consistent in young individuals but rare in adults. We interpreted our results as signs of involvement of the non-classical pathways that diminished with age, thus probably a sign of normal maturation. The fact that some of the individuals that we studied experienced an increase in loud ...
... pathways was consistent in young individuals but rare in adults. We interpreted our results as signs of involvement of the non-classical pathways that diminished with age, thus probably a sign of normal maturation. The fact that some of the individuals that we studied experienced an increase in loud ...
Duration Sensitivity to Other Response Properties of the Rat
... et al. 2000). Duration-selective neurons have only been found at or above the level of the inferior colliculus (IC) or its homolog in any of the species studied, so this form of neural filtering seems to be an emergent property that results from circuitry operating within the midbrain. The IC is inn ...
... et al. 2000). Duration-selective neurons have only been found at or above the level of the inferior colliculus (IC) or its homolog in any of the species studied, so this form of neural filtering seems to be an emergent property that results from circuitry operating within the midbrain. The IC is inn ...
phys chapter 56 [10-19
... capability, person unable to determine when next sequential movement needs to begin o Helps time events other than movements of body (rates of progression of both auditory and visual phenomena can be predicted by brain, requiring participation of cerebrocerebellum) Visual cues can tell you when yo ...
... capability, person unable to determine when next sequential movement needs to begin o Helps time events other than movements of body (rates of progression of both auditory and visual phenomena can be predicted by brain, requiring participation of cerebrocerebellum) Visual cues can tell you when yo ...
Long Term Potentiation
... has been created. The soluble gas, nitric oxide, most likely accounts for this phenomenon, as evidenced by the fact that, when the synthesis of nitric oxide is inhibited, long term potentiation is inhibited. It is also known that nitric oxide, since it is a soluble gas, could diffuse out of the post ...
... has been created. The soluble gas, nitric oxide, most likely accounts for this phenomenon, as evidenced by the fact that, when the synthesis of nitric oxide is inhibited, long term potentiation is inhibited. It is also known that nitric oxide, since it is a soluble gas, could diffuse out of the post ...
Timescales of Inference in Visual Adaptation
... to different switching periods, we aligned the normalized mean currents for different switching periods at the end of the first, stereotyped component following the luminance increase (Figure 2F). The trajectories diverge from this common starting point. Thus the time constant of luminance adaptatio ...
... to different switching periods, we aligned the normalized mean currents for different switching periods at the end of the first, stereotyped component following the luminance increase (Figure 2F). The trajectories diverge from this common starting point. Thus the time constant of luminance adaptatio ...
video slide
... salt solution. One end of the tube tapers to an extremely fine tip (diameter < 1 µm). While looking through a microscope, the experimenter uses a micropositioner to insert the tip of the microelectrode into a cell. A voltage recorder (usually an oscilloscope or a computer-based system) measures the ...
... salt solution. One end of the tube tapers to an extremely fine tip (diameter < 1 µm). While looking through a microscope, the experimenter uses a micropositioner to insert the tip of the microelectrode into a cell. A voltage recorder (usually an oscilloscope or a computer-based system) measures the ...
Somatosensory Systems: Pain and Temperature - Dr
... anterior spinothalamic tract is located just anterior to the lateral spinothalamic tract within the spinal cord and medulla. Other than this slightly more lateral position, the anterior spinothalamic tract follows the same path as the lateral spinothalamic tract. It begins with receptors in the skin ...
... anterior spinothalamic tract is located just anterior to the lateral spinothalamic tract within the spinal cord and medulla. Other than this slightly more lateral position, the anterior spinothalamic tract follows the same path as the lateral spinothalamic tract. It begins with receptors in the skin ...
Passive Properties of Swimmeret Motor Neurons
... The SigmaStat program (Jandel Scientific) was used to calculate statistics of the different parameters we measured and to compare parameters from different types of neurons. Normally distributed data were summarized by mean { SD; other data were described by median, 25th, and 75th percentiles. Devia ...
... The SigmaStat program (Jandel Scientific) was used to calculate statistics of the different parameters we measured and to compare parameters from different types of neurons. Normally distributed data were summarized by mean { SD; other data were described by median, 25th, and 75th percentiles. Devia ...
Experimental spinal cord transplantation as a mechanism of
... innervate muscle.IS Stimulation of the peripheral nerve containing the regenerated axons of the grafted fetal neurons results in contraction of the innervated muscle. This is a significant and major accomplishment. As with the regeneration of peripheral nerves, the reinnerva tion of muscles by graf ...
... innervate muscle.IS Stimulation of the peripheral nerve containing the regenerated axons of the grafted fetal neurons results in contraction of the innervated muscle. This is a significant and major accomplishment. As with the regeneration of peripheral nerves, the reinnerva tion of muscles by graf ...
Document
... Paralysis – loss of motor function Flaccid paralysis – severe damage to the ventral root or anterior horn cells Lower motor neurons are damaged and impulses do not reach muscles ...
... Paralysis – loss of motor function Flaccid paralysis – severe damage to the ventral root or anterior horn cells Lower motor neurons are damaged and impulses do not reach muscles ...
Lecture 1
... Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon ...
... Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon ...
Acute Pain Management Parisa Partownavid, MD Assistant Clinical
... Bind to Opioid Receptors: Mu, Delta and Kappa Morphine, Hydromorphone, Meperidine, Fentanyl, Codeine, Methadone, Oxycodone, Hydrocodone, Tramodol Opioids may be Combined with NSAIDs to Enhance the Opioid Analgesic Effect ...
... Bind to Opioid Receptors: Mu, Delta and Kappa Morphine, Hydromorphone, Meperidine, Fentanyl, Codeine, Methadone, Oxycodone, Hydrocodone, Tramodol Opioids may be Combined with NSAIDs to Enhance the Opioid Analgesic Effect ...
pain - Dog2Doc.com
... • Short duration, sharp, fast, bright, localized sensation (prickling, stinging, burning) ...
... • Short duration, sharp, fast, bright, localized sensation (prickling, stinging, burning) ...
Ascending Sensory Pathways
... vary according to their morphology, the velocity of conduction, and the modality to which they respond, as well as to their location in the body, they generally all function in a similar fashion. The stimulus to which a specific receptor responds causes an alteration in the ionic permeability of the ...
... vary according to their morphology, the velocity of conduction, and the modality to which they respond, as well as to their location in the body, they generally all function in a similar fashion. The stimulus to which a specific receptor responds causes an alteration in the ionic permeability of the ...
Rheobase
Rheobase is a measure of membrane excitability. In neuroscience, rheobase is the minimal current amplitude of infinite duration (in a practical sense, about 300 milliseconds) that results in the depolarization threshold of the cell membranes being reached, such as an action potential or the contraction of a muscle. In Greek, the root ""rhe"" translates to current or flow, and ""basi"" means bottom or foundation: thus the rheobase is the minimum current that will produce an action potential or muscle contraction.Rheobase can be best understood in the context of the strength-duration relationship (Fig. 1). The ease with which a membrane can be stimulated depends on two variables: the strength of the stimulus, and the duration for which the stimulus is applied. These variables are inversely related: as the strength of the applied current increases, the time required to stimulate the membrane decreases (and vice versa) to maintain a constant effect. Mathematically, rheobase is equivalent to half the current that needs to be applied for the duration of chronaxie, which is a strength-duration time constant that corresponds to the duration of time that elicits a response when the nerve is stimulated at twice rheobasic strength.The strength-duration curve was first discovered by G. Weiss in 1901, but it was not until 1909 that Louis Lapicque coined the term ""rheobase"". Many studies are being conducted in relation to rheobase values and the dynamic changes throughout maturation and between different nerve fibers. In the past strength-duration curves and rheobase determinations were used to assess nerve injury; today, they play a role in clinical identification of many neurological pathologies, including as Diabetic neuropathy, CIDP, Machado-Joseph Disease, and ALS.